![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a pathogen? |
A microorganism that causes disease, e.g a bacterium, virus, protist or fungus |
|
|
What is a communicable disease? |
A disease that can be spread between individuals |
|
|
What is Bacteria? |
Bacteria are very small cells (about 1/100th the size of body cells), which can reproduce rapidly inside your body. They can make you feel ill by producing toxins that damage your cells and tissues. |
|
|
What is a toxin? |
A poison. Toxins are often produced by bacteria |
|
|
What is a virus? |
A disease-causing agent about 1/100th of the size of a bacterial cell. They can only replicate within host body cells |
|
|
How do viruses replicate? |
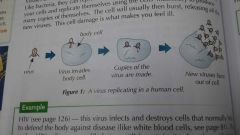
They live inside your cells and replicate themselves using the cells' machinery to produce many copies of themselves. The cell will usually then burst, releasing all the new viruses. The cell damage is what makes you feel ill. |
|
|
What is a protist? |
A pathogen that is often transferred to other organisms like a vector, which doesn't get the disease itself.
There a lots of different types of protists. But they are all eukaryotes and most of them are single-celled. Some protistsare parasites. Parasites live on or inside other organisms and can cause them damage. They are often transferred to the organisms and can cause them damage. They are often transferred to the organism by a vector, which doesn't get the disease ifself-e.g. an insect that carries the protist. |
|
|
Define fungus |
A microorganism that can cause disease, and that produces spores that can be spread to other organisms. |
|
|
Facts about fungi |
>Some fungi are single-celled. Others have a body which is made up of hyphae (thread-like structures) These hyphae can grow and penetrate human skin and the surface of plants, causing diseases >The hyphae can produce spores, which can be spread to other plants and animals. |
|
|
The spread of Pathogens by water |
>Water-some pathogens can be picked up by drinking or bathing in dirty water E.g. Cholera is a bacterial infection that's spread by drinking water contaminated with the diarrhoea of other sufferers |
|
|
The spread of pathogens by air |
Pathogens can be carried in the air and can then be breathed in E.g. The influenza virus that causes flu is spread in the air in droplets produced when you cough or sneeze |
|
|
The spread of pathogens by direct contact |
Some pathogens can be picked up by touching contaminated surfaces, including the skin E.g. Ahthletes foot is a fungus which makes the skin itch and flake off. It's most commonly spread by touching the same things as an infected person, e.g. shower floors and towels |

