![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Weber
|
Tuning fork on vertex of head
|
|
|
Rhinne
|
Tuning fork on mastoid then in front of ear
|
|
|
Weber and Rhinne sensorineural hearing loss.
|
Sensorineural defect
Weber test: lateralizes to normal ear (contralateral ear is affected). Rinne test: air conduction > bone conduction in both normal and affected ear |
|
|
Weber and Rhine conduction hearing loss
|
Conduction defect
Weber test: lateralizes to affected ear Rinne test: bone conduction > air conduction in affected ear |
|
|
pathogenesis of Meniere’s disease
|
Increased endolymph in inner ear and loss of cochlear hairs
|
|
|
clinical findings of Meniere’s disease
|
Clinical: dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
how Meniere’s disease differs for an acoustic neuroma
|
Vertigo, patient feel likes room is spinning, in Meneire's disease.
|
|
|
pathogenesis of presbycusis
|
Due to degeneration of cochlear hairs in organ of Corti
|
|
|
type of hearing loss in presbycusis
|
Sensorineural hearing loss
|
|
|
clinical finding in the elderly in presbycusis
|
Most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss in elderly
|
|
|
pathogenesis of otosclerosis
|
-Due to fusion of middle ear ossicles
-Other causes of conduction defects: -impacted cerumen in outer ear canal; -otitis media |
|
|
type of hearing loss of otosclerosis
|
Most common cause of conduction deafness in elderly
|
|
|
clinical findings of otosclerosis
|
Conduction defect
Weber test: lateralizes to affected ear Rinne test: bone conduction > air conduction |
|
|
type of hearing loss in otitis media
|
Most common cause of conduction deafness in children
|
|
|
common pathogens associated with otitis media
|
Most commonly due to Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Other causes: H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis |
|
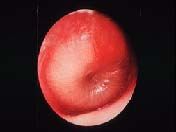
clinical findings (be able to recognize)in otitis media
slide 74 |
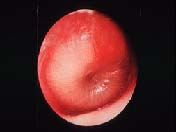
Conduction defect
Weber test: lateralizes to affected ear Rinne test: bone conduction > air conduction |
|
|
definition of external otitis
|
Inflammation of outer ear canal
|
|
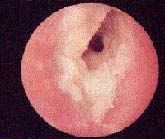
pathogens in swimmer’s ear (be able to recognize) in external otitis
Slide 75 |
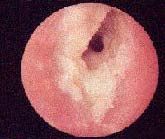
"Swimmer's ear: due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. aureus, Aspergillus species
|
|
|
cause of malignant external otitis in diabetics.
|
Malignant external otitis: severe infection of outer ear canal in patients with diabetes mellitus. Pseudomonas aeruginosa most common cause.
|

