![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Heuristics |
Heursitics - enabling a person to discover and learn something for themselves Aristotle thought of humans as rational beings Tversky and Kahneman 70's showed that when people are uncertain about judgements, heuristic principles (rules of thumb, cognitive shortcuts) applied to make decisions |
|
|
Tversky and Kahneman |
Participants read description of Linda, seen as bright and outspoken Linda occupation probability ranked from a list of possible occupations 85%said Linda more likely to be feminist bank teller than just bank teller (1983) |
|
|
Conjunction fallacy in the case of Linda |
More likely Linda would fit into a big group (bank teller or feminist) than a small overlap(feminist bank teller) Error of logic, probability of both being true cannot be larger than the probability of either single event (bank teller/feminist) being true |
|
|
Representativeness heuristic-conjunction fallacy In the case of Linda |
Tversky and Kahneman 1983 A feminist bank teller seems more representative of Linda even if it is less probable mathematically Events that are typical or representative of a class are assigned a high probability of occurrence, fits in with schema |
|
|
Solving the Linda problem Fiedler 1988 |
Participants told 100 people fit the Linda description Asked how many are banktellers Asked how many are banktellers and feminists Using orginal Tversky and Kahneman method, 91% commit conjunction fallacy but using frequency method only 22% commit the error Making it more obvious changes outcome |
|
|
Gamblers fallacy |
If the last 4 spins land on red, do you bet on black? (Same probability due to randomness) Representativeness heuristic could account for this, predicted sequence more representative so expected to occur, Causes larger betting |
|
|
Neglect of base rate T and K 1973 |
Another example of representativeness heuristic. Jack described as maried man that spends time sailing and solving maths puzzles Participants told 70% people lawyers 30% engineers and Jack has randomly been picked out of group of people 90& said Jack was engineer showing base rate info ignored Shows rationalization of information as awell as stereotyping |
|
|
The availability heuristic |
People judge probability of event by seeing how many examples of that event they can think of More target events thought more likely it is to happen Events that make more of an impact (train crashes) result in frequency being overestimated compared to more common events (Car crashes) Personal experience - friends cars keep breaking down, cars are unreliable |
|
|
Availibility Heuristic Tversky and Kahneman 1973 |
Ppt asked letter r most common 1st or 3rd word Easier to recall words that start with r In fact r is more common as a 3rd letter Less effort to think of words that begin with r Availibility heuristic use = error |
|
|
Familiarity effect Herbert 2010 |
If something comes to mind quickly, trust it, it must be there for a reason Useful for selecting a brand of yoghurt or cereal from supermarket makes sense on how much money spent on brand familiarity |
|
|
Support theory |
Tversky and Koehler 1994 How likely event seen as occuring An explicit description, attention to aspects that are less obvious = more availibility Subjective probability of event increases Mentioned explicitly becomes salient conspicous |
|
|
Explicitness of information experiment Support theory |
Taversky and Kohloer 1994 How explicitness of information influenced probability judgements Ppt asked how likely are you to die on holiday vs how likely are you to die on holiday as a result of a disease, car accident or another cause Explicit information about ways of death increased ratings for probability of occurance |
|
|
Mandel's support theory experimet |
Mandel 2005 Estimated probability of a terrorist attack Attack by Al Qaeda vs Attack by unnamed terrorist group, Al Qaeda attack increases probability |
|
|
Anchoring |
Heuristics also influences numeric estimates Quantatative estimates affected by heuristics such as anchoring on a number and adjusting for what we know Something as random as last two digits of number influences how much people will pay Simonson and Drolet 2004 analysed willingness to pay based on last two digits of social security number If SSN <$50 would pay $35 for phone If SSN > $50 willing to pay $64, Anchoring on meaningless value and using it as a WTP guide |
|
|
Anchoring experiment 1 Englich and Mussweiler 2001 |
Judges asked by prosecuters for High sentence/low sentence of time in prison On average 8 months longer for high sentence request even in identical crime |
|
|
Anchoring experiment 2 Chapman and Bornstein 1996 |
Personal injury awards -influenced by the amount requested where a woman's ovarian cancer was caused by prescription drung Compensation sought varied between $100 to $1billion with intermediate steps of $20,000 and $5million Ppts awarded larger amounts as compensation request increased, argued that the requested amount was anchor and adjustments made based on facts |
|
|
Anchoring and credit cards |
2003, minimum credit card payment legislation introduced with idea that would protect people cfrom credit debt, theorized getting people to pay something would lead to less outstanding balance |
|
|
Anchoring and credit cards experiment Stewart 2008 |
Mock credit card bill $435.76 Half shown recommended minimum payment £5.42 Minimum payments = smaller repayment amounts Strong correlation between minimum payment and amount actually repaid Minimum payment anchoring = higher repayment costs |
|
|
Hindsight Bias |
Outcome of event is judged more likely than it would've been before case occurred People believe falsely they would have predicted outcome once knowing outcome Quiz questions - contestants miss-recalled answers as being more accurate Fischoff 1977 Hindsight bias - likely when there's well defined outcome or with particular emotional/moral importance |
|
|
Lab testing of hindsight bias |
Football Match One group told outcome One group not told Asked probability of them predicting outcome Individuals with hindsight estimated higher probability of correct prediction Denial of influence |
|
|
Hindsight bias influence |
Casper, Benedict and Kelly 1988 Investigated search and seizure cases Civil case allowed if no due cause Mock jurors - two outcome conditions Evidence of illegal activity found vs no evidence found Jurors in found evidence condition more likely to conclude illegal search was legal Outomes and legality unable to be seperated |
|
|
The recognition heuristic |
Goldstein and Gigerenzer 199 USA cities San diego vs San Antonio Which has biggest population 62% American students correct 100% German students correct American students recognised both whilst german students recognised one Bigger city = bigger news coverage |
|
|
How does recognition heuristic work |
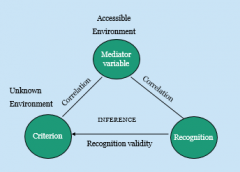
Mediator variable - represents exposure in the environment, correlates with amount you recognise it, inference made and criterion assumed (city is bigger) |
|
|
Less is more effect |
Frosch, Beaman and McCloy, 2007 Names from Sunday times rich list presented Identify richest to poorest Recognition = more wealth If all names are recognised, no useful cues Higher performance in those knowing less rich people Less is more |
|
|
Are Heurstics always bad? |
Fast and frugal heuristics are decision making cuts Rules of thumb exist for a reason Often good enough to be efficient Need to be wary |

