![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the normal breathing rates for: Adult Child Infant |
Adult 10-20 Child 24-40 Infant 30-40 |
|
|
DEFINE RISE N FALL |
Rate Injuries Symmetry Effort of breathing N- Trachea Wounds Emphysema Larynx Veins Every time Feel for crepitus Access resonance Listen Look |
|
|
Define respiratory arrest |
Cessation of breathing |
|
|
5 signs and symptoms of open pneumothorax |
Cough Rapid breathing Rapid heart rate Obvs wound Reduced chest movement |
|
|
Causes of tension pneumothorax |
Pneumothorax Blunt trauma Chest injury
|
|
|
6 signs and symptoms of tension pneumothorax |
Tracheal deviation Rapid breathing Cyanosis Hypertension Hypoxia Breathing sound absent on affected side |
|
|
Where do you perform needle decompression |
Midclabicular line in 2nd intercostal space, just above 3rd rib |
|
|
Two types of haemothorax |
Massive Simple |
|
|
Define flail segment |
Multiple adjacent ribs are broken in multiple places |
|
|
Name the movement of a flail segment |
Paradoxical breathing |
|
|
Three types of asthma |
Mild Life threatening Severe |
|
|
Define anaphylactic shock |
An acute allergic reaction that affects the whole body and is life threatening |
|
|
Two categories of bleeding |
External Internal |
|
|
What is the pulse rate higher than if a patient is tachycardic |
100bpm |
|
|
Define CRAMP |
Chest Recto perineal sweep Abdo Missing long bones Pelvis |
|
|
Cause of hypovolaemic shock |
Loss of blood/ fluid Significant bleeding from blunt trauma, pregnancy, vaginal or wounds |
|
|
Cause of hypovolaemic shock |
Loss of blood/ fluid Significant bleeding from blunt trauma, pregnancy, vaginal or wounds |
|
|
What type of shock involves head or spinal injury |
Neurogenic shock |
|
|
What type of shock is meningococcal meningitis |
Septic shock |
|
|
What type of shock is myocardial infarction |
Cardiogenic shock |
|
|
What is the blood loss in % in the following stages of hypovolaemic shock |
1. 750ml <15% 2. 750-1500ml 15-30% 3. 1500-200ml. 30-40% 4. 2000ml > 40% |
|
|
3 possible injury’s during Ops |
GSW Blast injury IED Burns RTC |
|
|
Define SAFE |
Send, shout, signal for help Access for danger Find and free casualties Evaluate CABCD |
|
|
CSCATTT (Scene management) |
Command and control Safe environment Communication Access + egress Triage Treatment Transport |
|
|
5 treatments for burns |
Check ABC Cool for 10 mins Burn bags Pain relief Remove hot clothing |
|

Front (Term) |
Normal sinus rhythm5 |
|
|
What is used to assess the surface area of a burn |
Palm of the casualty Rule of 9 |
|
|
4 s+s of severe asthma attack |
Cyanosis ALOC Bradycardia Peak flow under 50 |
|
|
3 indications for bladder catheterisation |
Unable to pass urine Abdo injury Pre/post surgery |
|
|
Major contra indications of bladder catheterisation |
Urethra bleeding Major pelvic injuries |
|
|
What fluids are used for IV fluid administration |
Colloids Crystaloids |
|
|
3 classification of head injury |
Scalp wound Skull fracture Brain injury |
|
|
Define needle thoracentesis |
Insertion of a large bore cannula through the 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line on the effected side to alleviate a life threatening tension pneumothorax |
|
|
Potential complications of needle thoracentesis |
Plura infection Haematoma Incorrect placement Infection |
|
|
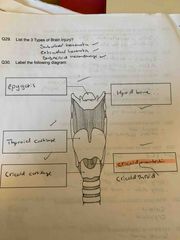
List 3 types of brain injury |
Subdural haematoma Extradural haematoma Subarachnoid haemorrhage |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Normal sinus rhythm5 |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Learn |
|
|
State three ways you asses a casualty’s airway |
Check Clear Maintain |
|
|
What is the first stage of labout |
Painful contractions up to full dilation |
|
|
2nd stage of labour |
From full dilation to complete delivery of the baby |
|
|
define shock |
An acute medical condition associated with fall in BP, caused by blood loss, severe burns, allergic reaction etc |
|
|
Hazard spectrum |
Burns/trauma Environment Medical/toxilogocal |
|
|
3 major incident levels of command |
Bronze Silver gold |
|
|
What are the colours of the following triage tag T1 T2 T3 |
T1 Red T2 yellow/ amber T3 Green |
|
Front (Term) |
Learn |

