![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Traits shared between Plants and Charophytes (Chara and Coleochaete)
|
*Rosette/Rings of cellulose-synthesizing proteins( make cellulose microfibrils of cell wall)
* Peroxisome enzymes (minimize organic product loss from photorespiration) * Structure of flagellated sperm *Formation of phragmoplast (microtubule beginning of cell plate in mitosis) *Sporopollenin (prevents desiccation) |
|
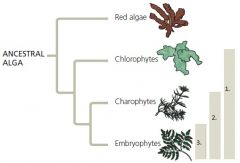
1. Includes Chorophytes, Charophytes and Embyophytes
2. Charaphytes and Embryophytes 3. Embryophytes only |
1.Viridiplantae
2.Streptophyta 3.Plantae |
|
|
Derived Traits of Land Plants
|
*Alteration of Generations
*Walled spores made in Sporangia *Multicellular Gametangia *Apical Meristems *Multicellular dependent embyos |
|
|
Alternation of generations
|
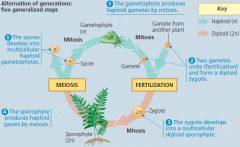
Multicellular Sporophyte (2n) -> Meiosis -> spores(n)->
Multicellular Gametophyte (n)->fertilization ->zygote(2n) |
|
|
Sporangium
|
multicellular organ that produces spores
|
|
|
Gametangia (m and f gametangia)
|
multicellular organ that makes gametes. Either Archegonia egg (f) or Antheridia sperm (m). Need water to transfer.
|
|
|
Apical Meristem
|
region of cell division at tips of roots and shoots.
|
|
|
Cuticle
|
another adaptation. waxy substance upon the epidermis to resist desiccation.
|
|
|
Placental Transfer
|
elaborate ingrowths fo the wall surface to enhance transfer of parental (n) tissues provide developing embryo with nutrients
|
|
|
Embyophytes
|
Name for land plants derived from their multicellular dependent embryo.
|
|
|
Vascular Tissue
|
cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients though out the plant.
*Xylem (water) *Phloem (nutrients) *Allows for taller growing |
|
|
Vascular plants
|
plants with a complex vascular system.
|
|
|
Bryophytes
|
*Non-vascular plants
*"bryon"-moss ""phyton"-plant *Liverworts *Mosses *Hornworts *Lack roots and true leaves *low ground plants b/c no vascular support |
|
|
Bryophyte Life cycle
|
*Dominant gametophyte in life cycle
* reduced sporophyte *spores make protenema (one cell thick filaments that enhances absorption) which generate gametophore |
|
|
Gametophore
|
gamete producing structure
|
|
|
rhizoids
|
*anchor gametophytes, made of long, tubular single cells or fillaments of cells
*Not made of of tissues *no water and nutrient in take |
|
|
Lycophytes
|
*Seedless Vascular plant
*ex. Club mosses, pike mosses, quillworts *grade not clade *leaves: microphylls |
|
|
Pterophytes
|
*Seedless Vascularascular plant
*ex. ferns, horse tails, whisk ferns *grade not clade *Vascular tissue *roots *leaves: megaphylls |
|
|
Sorus/sori
|
cluster of sporangium
|
|
|
Xylem
|
*Made of Tracheids (tube shaped cells)
*transports water * cell walls strengthened by lignin |
|
|
Phloem
|
Distribute sugars, amino acids, organic products
|
|
|
roots
|
absorb water and nutrients from soil
|
|
|
Leaves
|
Increase surface area of plant and serve as area of primary photosynthetic processes
|
|
|
Microphylls
|
*characteristic to lycophytes
*small spine shaped leaves *single vascular tissue |
|
|
megaphylls
|
highly branched vascular system
|
|
|
Sporophylls
|
*modified leaves that bear sporangia
*produce sori |
|
|
Homosporous
|
*one type of sporangium that produces one type of spore
*usually bixesual gamete |
|
|
heterosporous
|
two types of sporangia:
*Megaspores ->f gamete->egg *microspores-> m gamete-> sperm |

