![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What did land plants evolve from?
|
Charophytes (Green algae)
|
|
|
|
Similarities between land plants and their closest relative
|
multicellular, eukaryotic, and photosynthetic. have similar dna and chlorophyll. They also have similar mechanisms of mitosis and cytokinesis.
|
|
|
|
derived traits of plants 5 key traits
|
Alterationof generations
multicellular dependent embryos walled spore produced in sporangia multicellular gametangia apical meristems |
|
|
|
What was needed by plants to evolve from algae to get onto land? and how did plants solve this
|
a way tokeepwater- roots to absorb water and nutrients
structure- cellulose availability of light- leave photosynthesis ability to reproduce, protected from air |
|
|
|
What are the phylums and common names of the nonvascular seeldless plants?
|
Bryophyta mosses
hepatophyta liverwort anthocerophyta hornwart |
|
|
|
What is the life cycle dependent on for mosses?
|
Water, the sperm has to swim to the egg
|
|
|
|
What are the phylums and common names of seedless vascular plants
|
Lycophyta club mosses spike mosses quill worts
pterophyta horsetail ferns whisk ferns |
|
|
|
Facts about bryophytes
|
seedless nonvascular plants
moist habitats depends on water for reproduction no conducting tissue no true roots |

|
|
|
facts about hepatophytes
|
small plants
moist shaded soil |

|
|
|
anthocerophyta
|
horn wart
|

|
|
|
life cycle of mosses
|
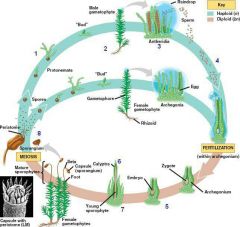
|
|

