![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and occupies space. Ex: Earth, chair, humans |
|
|
What is property? |
Characteristic useful for identifying a substance or object |
|
|
Physical Property |
Inherent characteristics of substances determined without altering composition. Ex: color,taste,odor,state of matter, boiling/meltingpoint |
|
|
Chemical Property |
Ability of substance to form new substances. Changing the chemical make up. Ex: flammability, inert news (not reacting at all) combustible |
|
|
What two types of change can matter undergo? |
1. Physical Change: change in substance where you NO chemical reaction takes place and no new substances are formed. EX: change in size, shape, state 2. Chemical Change: change in chemical makeup of a substance. New substances are formed with different properties & composition. EX: rusting of iron, burning of gas, digestion of food, cooking. |
|
|
Hydrogen+Oxygen = Water. This is an example of what? |
Chemical Change |
|
|
What are 3 states of matter? |
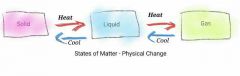
1. Solid - usually room temperature or freezing point 2. Liquid - Melting Point 3. Gas - Boiling Point
*All interchangeable and can go back to previous stages depending on temp applied |
|
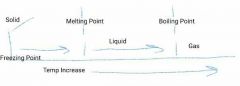
What is this diagram an example of? |
States of Matter - Physical Change |
|
|
Pure Substance |
A substance that has a uniform chemical composition throughout. Can't be broken down chemically into any simpler substance.
Ex: sugar water, urine, air |
|
|
Define Element |
A substance that can't be broken down chemically into any simpler substance. |
|
|
What is a compound? |
Two or more different elements chemically combined. Properties of compound always differ from those of the constituent elements. Two or more atoms of different elements are chemically bonded. Ex: H2O, CO2 |
|
|
Define mixture and name 2 types |
Blend of 2 or more substances, each retains its chemical identity. 1. Homeogenous 2. Heterogenous |
|
|
Homogenous Mixture |

Uniform mixture that has the same composition throughout. Individual parts of the mixture are not easily identifiable. Homogeneous mixtures are also referred to as solutions. Ex: sugar water, salt water, blood |
|
|
What is a Heterogenous Mixture? |

Non-Uniform mixture that has regions of different composition. Substances do not blend smoothly throughout. Individual substances that compose the mixture can be detected. Can typically be separated back into their individual components through chemical or physical means. Ex: Water & Oil, Soup, Concrete. |
|
|
Total # of elements |
118 elements with 91 of them occurring naturally. |
|
|
What is the Periodic Table divided into? |
1. Metals 2. Non- Metals 3. Metalloids/Semi Metals that have properties of metals & non-metals |
|
|
Properties of Metal |
1. Shiny 2. Solid (except mercury) 3. Good conductors of heat & electricity 4. Malleable & NOT Brittle so can be pounder into different shapes without breaking. 5. Found on left side of periodic table Ex: Gold, Zinc & Copper |
|
|
Properties of Non-Metal |
1. Some are solid, liquid, or gas. 2. Poor conductors of heat & electricity. 3. Brittle. 4. Located on right side of periodic table. Ex: Bromine (only one that's a liquid @ room temp), Oxygen, Nitrogen & Sulfur. |
|
|
Properties of Metalloids |
1. Properties are intermediate between metals and non-metals. 2. Not as good conductors of heat and electricity. 3. Occur on zig-zag portion of periodic table. Ex: boron, silicon, & arsenic. |
|
|
What is the symbol for the following elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen & Nitrogen |
Carbon - C Hydrogen - H Oxygen - O Nitrogen - N |
|
|
What is the symbol for the following elements: Arsenic, Boron, Calcium, Chlorine, Chromium |
Arsenic - As Boron - B Calcium - Ca Chlorine - Cl Chromium - Cr |
|
|
What is the symbol for the following elements: Cobalt, Copper, Flourine, Iodine, Iron |
Cobalt - Co Copper - Cu Flourine - F Iodine - I Iron - Fe |
|
|
What is the symbol for the following elements: Magnesium, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Phosphorous |
Magnesium - Mg Manganese - Mn Molybdenum - Mo Nickel - Ni Phosphorus - P |
|
|
What is the symbol for the following elements: Potassium, Selenium, Silicon, Sodium, Sulfur, Zinc |
Potassium - K Selenium - Se Silicon - Si Sodium - Na Sulfur - S Zinc - Zn |
|
|
Chemical Reactions? |
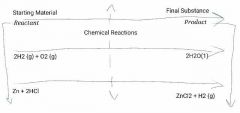
1.Process of chemical change 2. New substance is formed 3. Described by chemical equation |
|
|
How many ways can you write a chemical reaction? |
Two ways: 1. Word Equation & 2. Formula Equation |
|
|
Physical Quantity |
Physical Property that can be measured. Ex: Mass, Volume, Temp, Density |
|
|
Unit the Two Unit Systems? |
Defined quantity used as a standard of measurement. 1. International System of Units (SI) 2. Metric System based on #10
Quantity SI Metric Mass Kilogram (kg) Gram (g) Length Meter (m) Meter (m) Volume Cubic meters (m3) Liter (L) Temperature Kelvin (K) Celsius (C°) Time Seconds (s) Seconds (s) |
|
|
Prefixes for Multiples of Metric & SI Units |

Know the highlighted ones! |
|
|
Derived Unit Formulas |
Speed: Length over Time --> m/s meters per second Area: length x length --> square meter m2 Volume: length x 3 --> cubic meter m3 Density: mass over volume --> |
|
|
Mass |
Measure of amount of matter in object |
|
|
Weight |
Measure of gravitational force the earth or other large body exerts on an object |
|
|
Volume |
Amount of space occupied by an object. SI unit for volume is the cubic meter or m3 |
|
|
Significant Figures |
Is the # of meaningful digits used to express a value. Every experimental measurement has a degree of uncertainty. Value recorded should use all the digits known with certainty plus one estimated digit. |
|
|
Significant Figure Rule #1 |
0's in the middle of the # are like any other digit; they are ALWAYS significant. Ex: 15.06 = four significant figures |
|
|
Significant Figures Rule #2 |
0's at the beginning of a # are NOT significant; they act only to locate the decimal point. Ex: 0.06 = one significant # |
|
|
Significant Figures Rule #3 |
0's at the end of a # and after the decimal point are significant. It is assumed that these 0's won't be shown unless they were significant. Ex: 4.500=4 significant figures |
|
|
Significant Figure Rule #4 |
0's at the end of a # and before an implied decimal point are not significant. Ex: 4500 = 2 significant figures |
|
|
Ion |
An electrically charged atom or group of atoms |
|
|
Anion |
A negatively charged ion |
|
|
Cation |
A positively charged ion |
|
|
Ionization Energy |
The energy required to remove one electron from a single atom in the gaseous state. |
|
|
Electron Affinity |
The energy released on adding an electron to a single atom in the gaseous state |
|
|
Ionic bond |
The electrical attractions between ions of opposite charge in a crystal. |
|
|
Ionic solid |
A crystalline solid held together by ionic bonds |
|
|
Ionic compound |
A compound that contains ionic bonds |
|
|
Octet rule |
Main group elements tend to undergo reactions that leave them with 8 valence electrons |
|
|
Polyatomic ion |
An ion that is composed of more than one atom |
|
|
Formula unit |
The formula that identifies the smallest neutral unit of an iconic compound |
|
|
Acid |
A substance that provides H+ ions in water |
|
|
Base |
A substance that provides OH- ions in water |
|
|
When the #s & kinds of iins are known in a compound, use these rules when writing them. |
1. List the cation first and the anion second. Ex: NaCl rather than ClNa 2. Do not write the charges of the ions. Ex: KF rather than K+F- 3. Use parentheses around a polyatomic ion formula if it has a subscript. Ex: Al2 (SO4) rather than Al2SO43● |

