![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
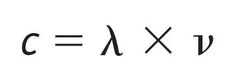
|
The product of the wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν) of electromagnetic radiation is equal to the speed of light (c). |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
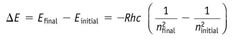
|

|
|
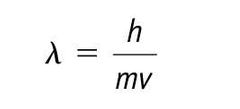
|
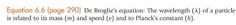
|
|
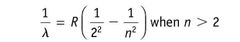
|
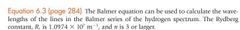
|
|
|
Electron configuration exceptions |

Cr, Mo, W Cu, Ag, Au
They prefer half filled valence shells.
|
|
|
How to form transition metal ions |

Transition metal ions form only cations
Take electrons away from s orbital first
Ex.:
|
|
|
I ****** Claire's hymen and breasts |
I=1 bond Iodine (I) Flouirine (F) Chlorine (Cl) Hydrogen (H) Bromine (Br) |
|
|
Electronegativity |
The measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. |
|
|
Polar covalent bond |

A bond in which the two atoms have partial electrostatic charges |
|
|
Principle of electroneutrality |
Electrons will be distributed in such a way that the charges on all atoms are as close to zero as possible. Second, if a negative charge is present, it should reside on the most electronegative atoms. Similarly, positive charges are expected on the least electronegative atoms. |
|
|
Molecular polarity |
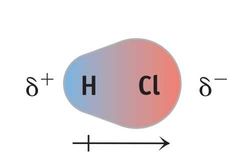
In a polar molecule, electron density accumulates toward one side of the molecule, giving that side a partial negative charge (δ−), and leaving the other side with an equal but positive partial charge (δ+). |
|
|
Stronger nucleus electron attraction means... |
Electron is at lower energy |
|
|
The higher the effective nuclear charge... |
The lower the electron's energy |

