![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
wavelength (λ) |
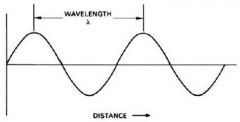
The distance between two adjacent peek in a wave |
|
|
Frequency (ν) |
The number of wavelengths that pass a point in one second |
|
|
c= λν |
c= speed of light (3.00 x 10⁸ ms⁻¹) λ= wavelength ν= frequency |
|
|
electromagnetic radiation |
carries energy through space microwaves, x-rays, infrared, visible light etc |
|
|
quantum |
smallest amount of energy that can be absorbed or emitted as electromagnetic radiation |
|
|
E= hν |
E= energy (J) h = plack's constant (6.626 x 10⁻⁴⁸ J-s) ν = frequency |
|
|
Light |
Behaves as both a particle and a wave |
|
|
ground state |
Lowest energy state for a electron
|
|
|
excited state |
when electron has high energy |
|
|
Bohr model |
1. Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy. 2. The energy of the orbit is related to its size. The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit. 3. Radiation is absorbed or emitted when an electron moves from one orbit to another. |
|
|
Heisenberg uncertainty principle |
its impossible to know exactly where an electron is and what its speed simultaneously |
|
|
radical probability function |
|

