![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is matter? |
Particles taking up space |
|
|
|
4 classes of matter |
Elements, compounds, mixtures, solutions |
|
|
|
Elements |
Pure atoms |
|
|
|
Compounds |
Pure molecules |
|
|
|
Mixtures |
Heterogeneous (can see the difference, not completely mixed) |
|
|
|
Solution |
Homogeneous (Cannot see difference, completely mixed) |
|
|
|
Mass |
Grams |
|
|
|
Length |
Meters |
|
|
|
Temperature |
Kelvin (or Celsius) |
|
|
|
# of particules |
Moles |
|
|
|
Time |
Seconds |
|
|
|
Volume |
mL or cm^3 |
|
|
|
Density |
(g/mL) Mass over Volume |
|
|
|
Zero Sig Figs Rules |
Front never, middle always, end only if theres a decimal |
|
|
|
How many sig figs - 2000 |
1 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs - 2000. |
4 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs - 0.0009 |
1 |
Zeros appearing in front of all nonzero figures are not significant |
|
|
How many sig figs - 9.000,000,000 |
10 |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Center, protons & neutrons |
|
|
|
What dicate an atom's identity? |
Protons |
|
|
|
What holds nuclear particles together? |
Nuclear forces |
Short range. Proton-neutron, proton-proton, neutron-neutron |
|
|
Relative mass of electrons in amu |
0.000,5486 |
|
|
|
Relative mass of protons in amu |
1.007,276 |
|
|
|
Relative mass of neutrons in amu |
1.008,665 |
|
|
|
Mole |
Special unit used to express amounts of particles like atoms and molecules |
|
|
|
Nuclide |
General term for a specific isotope of an element |
|
|
|
Mole |
The SI unit for amount of substance |
|
|
|
Avogadro's Number |
6.022 141 79 × 10^23 -the number of particles in exactly one mole of a pure substance |
|
|
|
Molar Mass |
The mass of one mole of a pure suvstance is called the molar mass of that substance |
|
|
|
Order of electron configurations |
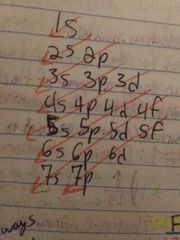
That ^ |
|
|
|
Metallic Characteristics |
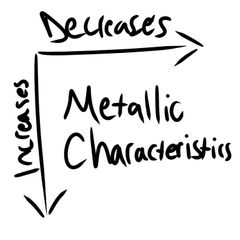
|
|
|
|
Valence e- |
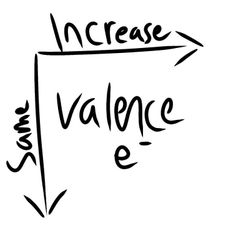
|
|
|
|
Atomic Radius |
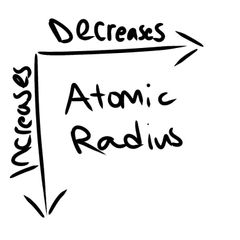
|
|
|
|
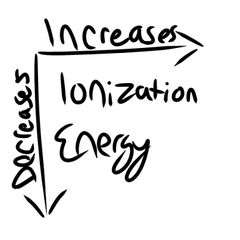
Ionization Energy |
|
|
|
|
Electron Affinity |

|
|
|
|
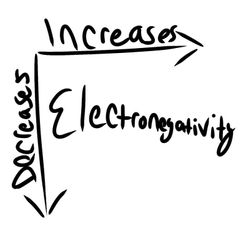
Electronegativity |
|
|
|
|
Nonpolar Covalent |
Equal sharing of electrons to create full outershell |
|
|
|
Covalent |
Sharing valence electrons |
|
|
|
Polar Covalent |
Partial sharing of electrons, creating some attraction |
|
|
|
Ionic |
Complete transfer of electron creating ions |
|
|
|
Percent comp. Formula |
Mass of element over mass of compount x 100 |
|
|
|
Percent comp example |

|
|

