![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A compound that has a cabonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl group, (RCOOH).
|
Carboxylic acid
|
|
|
A compound that has a carbonyl group bonded to an -OR' group, (RCOOR').
|
Ester
|
|
|
A compound that has a carbonyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom group, RCONR'₂, where the R' groups may be alkyl groups or hydrogen atoms.
|
Amide
|
|
|
A reaction in which a new group replaces (substitutes for) a group attached to a carbonyl-group carbon.
|
Carbonyl-group substitution reaction
|
|
|
An RC=O group.
|
Acyl group
|
|
|
The -COOH functional group.
|
Carboxyl group
|
|
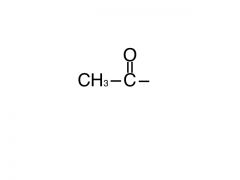
This group is?
|
Acetyl group
|
|
|
The anion that results from ionization of a carboxylic acid, RCOO⁻.
|
Carboxylate anion.
|
|
|
An ionic compound containing a cation and a carboxylate acid anion.
|
Carboxylic acid salt
|
|
|
The reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid to yield an ester plus water.
|
Esterification
|
|
|
The reaction of an ester with aqueous hydroxide ion to yield an alcohol and the metal salt of a carboxylic acid.
|
Saponification
|
|
|
A compound formed by reaction of an alcohol with phosphoric acid; may be a monester, ROPO₃H₂; a diester, (RO)₂PO₃H; or a triester, (RO)₃PO; also may be a di-or triphosphate.
|
Phosphate ester
|
|
|
The -PO₃²⁻ group in organic phosphates.
|
Phosphoryl group
|
|
|
Transfer of a phosphoryl group, -PO₃²⁻, between organic molecules.
|
Phosphorylation.
|
|
|
In Carboxylic acid derivatives, what is replaced by other groups?
|
the -OH group of the Carboxylic acid.
|
|
|
Which have higher B.P.s, carboxylic acids and their derivatives, or comparable alkanes?
|
carboxylic acids and their derivatives, because they are polar. Also, carboxylic acids and amides that have an H atom can H bond.
|
|
|
The portion of the carboxylic acid that does not change during a carbonyl-group substitution reaction is known as:
|
an acyl group
|
|
|
The most significant property of carboxylic acids is:
|
their behavior as weak acids.
|
|
|
When acting as weak acids, carboxylic acids surrender:
|
the H atom of the carboxyl group.
|
|
|
Do carboxylic acids H bond with each other?
|
yes
|
|
|
Describe the states of carboxylic acids:
|
Those with:
-Up to 4 carbons are water soluble. -Straight-chain R groups of up to 9 carbons are volatile liquids with strong, unpleasant odors. -Acids with R-groups larger than 9 carbons are waxy, odorless solids. |
|
|
How are carboxylic acids named?
|
By replacing the -e ending of the alkane name with -oic acid.
If alkyl substituents or other functional groups are present, number the chain starting with the carboxyl end. |
|
|
More so than other families of organic molecules, many carboxylic acids are named:
|
using common names because they were some of the first organic compounds to be isolated.
|
|
|
When using common names, the carbon
atoms attached to the carboxyl group (-COOH) are identified by: |
the Greek letters α, β, γ, δ, ϵ, and so on rather than numbers.
|
|
|
The acyl group that remains after a carboxylic acid loses its -OH is named by:
One very important exception is: |
replacing the -ic ending of the acid name with -oyl. eg.. benzoic acid with the -OH removed is called a benzoyl group.
One very important exception is the acyl group from acetic acid, which is traditionally called an acetyl group. |
|
|
How are dicarboxylic acids named?
|
By keeping the -e on the alkene name and adding the ending -dioic acid.
|
|
|
Most dicarboxylic acids are named by:
|
their common names.
|
|
|
How are unsaturated carboxylic acids named:
|
By adding -enoic acid to the root name of the alkene. e.g... H₂C=CHCOOH is named propenoic acid.
|
|
|
Describe the carbonyl group substitution reaction:
|
The carboxylic acid reacts with H-Z where is loses its -OH group and gains the Z. The -OH reacts with the H to form water.
|
|
|
Which have higher boiling points. Carboxylic acids or esters?
|
Esters have lower B.P.s than carboxylic acids because they cannot H bond with each other. They can still H bond with water though.
|
|
|
Describe the properties of esters:
|
-colorless
-volatile liquids with pleasant odors -many contribute to the fragrances of flowers and fruits. |
|
|
How are esters made?
|
Through the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
|
|
|
How are esters named?
|
1) They are named using two words.
2) The first word is the alkyl group name of the alcohol used to make the ester. 3) The second word is the parent name of the carboxylic acid used to make the ester, with the -ic acid ending changed to -ate. eg.. The reaction of acetic acid and ethyl alcohol yields the ester: ethyl acetate. |
|
|
What is the name of an ester formed from ethanol and benzoic acid?
|
ethyl benzoate
|
|
|
Which have higher boiling points, carboxylic acids or unsubstituted amides?
|
unsubstituted amides have higher B.P.s because they have two H atoms which can form multiple H bonds.
|
|
|
Are amides basic like amines?
|
NO! The positive charge of the carbonyl group attracts the lone pair of the N atom strongly enough to prevent it from acting as a base by accepting an H atom.
|
|
|
How are unsubstituted amides named?
|
By replacing the -ic acid or -oic acid ending with -amide.
|
|
|
How are substituted amides named?
|
By identifying the subs with N locants and naming the parent as an unsubstituted amide.
|
|
|
All unsubstituted amides (except formamide) are in what state?
|
They are all solids.
|
|
|
Do carboxylic acids, esters, and amides all undergo carbonyl-substitution reactions?
|
yes
|
|
|
Can disubstituted amides and esters H bond with one another?
|
No, they don't have H atoms. They can H bond with water however.
|
|
|
Describe the pH of each:
-carboxylic acids -esters -amides |
-carboxylic acids are acidic
-esters and amides are pH neutral |
|
|
Describe the odor of each:
-carboxylic acids -esters -amides |
-carboxylic acids: pungent
-esters: pleasant -amides: generally odorless |

