![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Memory |
An active system that receives organizes alters stores and retrieves information |
|
|
|
Three processes of memory |
Encoding,Storage And retrieval |
|
|
|
Encoding process of memory |
Does set of mental operations that people perform on sensory information to convert that information into a form that is usable in the brain storage systems |
Programming information |
|
|
Storage process of memory |
Holding onto information for some period of time |
|
|
|
Retrieval process of memory |
Getting information that is in storage into a form that can be used |
|
|
|
Model of memory that assumes the processing of information for memory storage is similar to the way a computer process his memory and a series of three stages |
Model of memory that assumes the processing of information for memory storage is similar to the way a computer process his memory and a series of three stages: sensory memory ,short term memory and long-term memory |
|
|
|
Iconic memory (Sensory Memory) |
Visual sensory memory lasting only a fraction of a second |
Visual encoding |
|
|
Capacity(Sensory Memory Iconic |
Everything that can be seen at one time |
|
|
|
Duration(Sensory Memory Iconic |
Inflammation that has just entered iconic memory will be pushed out very quickly by new information a process called masking |
|
|
|
Echoic memory (Sensory Memory) |
The brief memory of something a person has just heard
Capacity: limited to what can be heard at any one moment and is smaller than the capacity of iconic memory Duration lasts longer than iconic about 2 to 4 seconds |
Acoustic encoding |
|
|
Short term memory (working memory) STM |
The memory system in which information is held for brief proves of time while being use. |
|
|
|
Selective attention (STM) |
The ability to focus on only one stimulus from among all systems input |
|
|
|
Digit span test (STM) |
Memory test in which a series of numbers is read to subjects in the experiments who I then asked to recall the numbers in order (George Miller) |
|
|
|
Digit Span test (STM) C conclusions |
Conclusions are that girl capacity of STM is about seven items or pieces of information plus or minus 2 items or from 5 to 9 bits of information( 7+ or -2 ) :magical number 7+2 chunking |
|
|
|
(maintenance rehearsal). Short term memory and rehearsal |
The conscious repetition of information to be remembered to maintain it in short-term memory (S TM’s tend to be encode in auditory form) |
|
|
|
Duration of STM |
Lasts from about 15 to 30 seconds without rehearsal (20 seconds on average) |
|
|
|
STM |
Is susceptible to interference e.g. is counting is interrupted have to start over |
|
|
|
Long term memory |
The continuance storage of information |
|
|
|
Memory consolidation |
The transfer of information from STM N to LTM by making the information meaningful in someway (elaborative rehearsal) |
|
|
|
Types of LTM procedural/implicit non-declarative of memory |
Type of long-term memory including memory for skills,procedures habits and condition responses these memories are not conscious but Are implied to exist because they affect conscience behavior |
|
|
|
Declarative LTM( Declarative memory |
Type of long-term memory containing information that is conscious and known (memory for facts )all the things that people know |
|
|
|
Semantic memory |
Type of declarative memory containing general knowledge such as knowledge of language and information learned in formal education |
|
|
|
Episodic memory |
Type of declarative memory contain personal information not really available to others such as daily activities and events |
|
|
|
Explicit memory |
Memory that is consciously known. Semantic and episodic memories are forms of explicit memory |
|
|
|
Retrieving information( Recall) |
Type of memory retrieval in which the information due to be retrieved must be pulled from memory with very few external clues |
Examples essays fill in the blanks and short answer exams are based on recall |
|
|
Retrieving information (recognition) |
The ability to Match a piece of information or a stimulus to a stored image or fact |
Examples the multiple-choice true or false and matching exams our assessment based on recognition |
|
|
(Re-learning) retrieving information |
Involves learning information that you previously learned |
Example after not speaking Spanish for 13 years Whitney was able to learn it rather quickly |
|
|
(Serial position effect )remembering information |
Better recall of information at the start and end of a list of data |
|
|
|
(Primary effect) Serial position effect Remembering information |
Tendency to remember information at the beginning of a body of information better than the information that follows |
|
|
|
(Recency effect) Serial position effect Remember information |
Tendency to remember information at the end of a body of information better than the information ahead of it |
|
|
|
Arousal theory |
The Balis the strong emotions trigger the formation of strong memories and we could emotions from weaker memories |
|
|
|
Flashbulb memory |
Type of automatic and coding that occurs because an unexpected event has strong emotional associations for the person remembering it generally result in an exceptional clear recollection |
|
|
|
Forgetting types and causes |
Forgetting is the loss of information from a long time memory |
|
|
|
Forgetting types and causes (Encoding failure) |
Encoding failure is failure to process information into memory |
|
|
|
Forgetting:Memory trace theory Decay (Transcience) |
DECAY transcience :is loss of memory due to the passage of time during which the memory trace is not used |
|
|
|
DIsuse |
Another name for DEcay assuming that memories that are not usually eventually decay and disappear |
|
|
|
Forgetting memory errors Psychologist Daniel scatter |
Office seven ways L memories tend to feel us something he refers to as the seventh sins of memory |
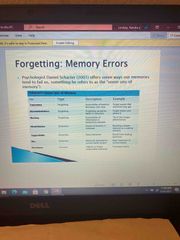
|
|
|
Proactive interference Forgetting interference theory |
Memory retrieval problem that occurs when all the information prevents or interferes with the retrieval of newer information |
|
|
|
Retroactive interference Forgetting interference theory |
Memory retrieval problem that occurs when newer information prevents or interferes with the retrieval of older information |
|

