![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
131 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Secondary structure of a protein |
Segments of polypeptide chains repeatedly coiled or folded in patterns that contribute to the proteins overall shape [Regions stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone (not the amino side chains)] |
|
|
When does a fourth level, quaternary structure, arise in a protein? |
When a protein consists of two or more polypeptide chains. |
|
|
Enzymatic protein: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Selective acceleration of chemical reactions (b) Digestive enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules |
|
|
True or False. Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that does not include true polymers. |
True |
|
|
DNA Structure |
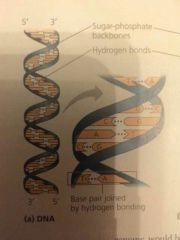
|
|
|
Nearly all double bonds in naturally occurring fatty acids are |
Cis double bonds |
|
|
Structural Proteins: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Support (b) Keratin is the protein of hair, horns, feathers, and other skin appendages. Insects and spiders use silk fibers to make their cocoons and webs. Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. |
|
|
Genes consist of what? |
DNA |
|
|
Defensive Proteins: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Protection against disease (b) Antibodies inactivate and help destroy viruses and bacteria |
|
|
Glucose, as well as most other five- and six-carbon sugars, form what shape when in aqueous solutions. |
Rings |
|
|
(a) DNA sugar (b) RNA sugar Difference between a and b |
(a) Deoxyribose (b) Ribose Deoxyribose lacks an oxygen on the second carbon in the ring |
|
|
Polypeptide Backbone |
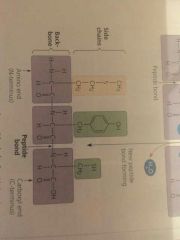
The repeating sequence of amino acid carboxyl and amino groups |
|
|
Chitin |
The carbohydrate used by arthropods to build their exoskeletons. A strong flexible surgical thread that decomposes. |
|
|
Storage Proteins: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Storage of amino acids (b) Casein, the protein of milk, is the major source of amino acids for baby mammals. Plants have storage proteins in their seeds. Ovalbumin is the protein of egg white, used as an amino acid source for the developing embryo. |
|
|
Simplest carbohydrates |
monosaccharides |
|
|
What is the most structurally sophisticated molecule known? |
Proteins |
|
|
Nearly every dynamic function of a living being depends on what? |
Proteins |
|
|
Cells as we know them could not exist without this type of lipid. |
Phospholipids |
|
|
Nucleic acids exist as ____1_____. ____1_____ consist of _____2______ ______2____ consist of ______3______ |
1. Polymers called polynucleotides 2. Nucleotides 3. (a) Five-carbon sugar (pentose) (b) Nitrogen-containing base (nitrogenous) (c) One or more Phosphate groups |
|
|
The most common monosaccharide, of central importance in the chemistry of life |
Glucose |
|
|
Tertiary structure of a protein |
The overall shape of a polypeptide resulting from interactions between the side chains (R groups) of the various amino acids. |
|
|
Contractile and motor proteins: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Movement (b) Motor proteins are responsible for the undulations of cilia and flagella. Actin and myosin proteins are responsible for the contraction of muscles. |
|
|
Disulfide bridges |
Form where 2 cysteine monomers, which have sulfhydryl groups (-SH) on their side chains, are brought together by the folding of the protein. The sulfur of 1 cysteine bonds to the sulfur of the second and the disulfide bridge (-S-S-) rivets part of the protein together (tertiary). |
|
|
-ose |
Sugar |
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acid |
Has one or more double bonds, with one fewer hydrogen atom on each double-bonded carbon. |
|
|
Important uses/functions of cellulose. |
Paper Cotton (only component) Insoluble fiber (scrapes digestive tract) |
|
|
Where is glycogen in vertebrates primarily stored? |
Liver and muscle cells |
|
|
Dehydration Reaction |
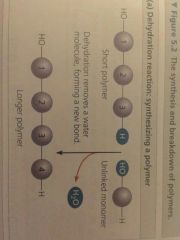
Synthesizing a polymer |
|
|
Proteomics |
Analysis of large sets of proteins, including their sequences. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a phospholipid bilayer? |
It forms a boundary between the cell and its external environment |
|
|
Phospholipid |
Similar to a fat molecule but has only two fatty acids attached to glycerol rather than three. the 3rd hydroxyl group is joined to a phosphate group. Major constituents of cell membranes. |
|
|
What does the term "hydrogenated" or "trans fat" refer to? |
Synthetically converting unsaturated fats into saturated fats by adding hydrogen. |
|
|
Ketoses (Ketone Sugars) |
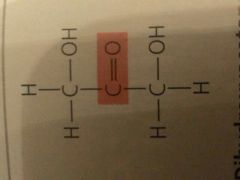
Carbonyl group within the carbon skeleton |
|
|
All proteins share how many super-imposed levels of structure? What are they? |
3 Primary, Secondary, Tertiary |
|
|
Enzyme |
Act as catalysts, chemical agents that selectively speed up chemical reactions without being consumed by the reaction. |
|
|
Denaturation |
Weak chemical bonds and interactions within a protein are destroyed causing a protein to unravel and lose its shape. |
|
|
Most important large molecules (Life's organic compounds) |
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids |
|
|
Hydrophobic Interaction |
As a polypeptide folds into its functional shape, amino acids with hydrophobic (nonpolar) side chains usually end up in clusters at the core of the protein. (exclusion of nonpolar substances by water molecules) |
|
|
Bilayers |
Phospholipids have a hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail and a hydrophilic phosphate group (head). When added to water, they self-assemble into double-layered structures. |
|
|
A fat is constructed from ____1____ and ___2_____ through ______3_____ |
1. Glycerol 2. Fatty Acids 3. Dehydration Reactions |
|
|
Proteins have how many kinds of amino acids? |
20 |
|
|
The bond between amino acids is called what? |
A peptide bond |
|
|
Flow of genetic information |
DNA --------> RNA -------> Protein Transcription Translation |
|
|
Two types of nucleic acids. |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) |
|
|
Sugar-phosphate backbone |
In the polynucleotide, adjacent nucleotides are joined by a phosphodiester linkage, which consists of a phosphate group that links the sugars of two nucleotides. This bonding results in a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphate units. |
|
|
Proteins are all constructed from |
20 amino acids, linked in unbranched polymers. |
|
|
Alpha Carbon |
An asymmetric carbon atom at the center of an amino acid. |
|
|
1-2 glycosidic linkage of glucose and fructose |
Sucrose |
|
|
Plants store polysaccharides in the form of |
Starch (a polymer of glucose monomers) |
|
|
The molecular building blocks of fat are |
One molecule of glycerol Three molecules of fatty acids (triacylglycerol/triglyceride) |
|
|
Site of protein synthesis |
Ribosomes |
|
|
A polymer of amino acids is called? |
A polypeptide |
|
|
Where is cholesterol synthesized/obtained by vertebrates? |
Liver Diet |
|
|
Animals stored polysaccharides as |
Glycogen |
|
|
What is the major function of fats? |
Energy Storage |
|
|
Steroid |
Lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings. |
|
|
Proteins account for how much of the dry mass of most cells? |
More than 50% |
|
|
Enzymes can be thought of as |
Workhorses that keep cells running by carrying out the processes of life. |
|
|
Genomics |
Analyzing large sets of genes or comparing whole genomes of different species |
|
|
Polymers are linked by |
Covalent Bonds |
|
|
1-4 glycosidic linkage of two glucose molecules |
Maltose |
|
|
All polypeptides terminate in |
A single amino end (N-terminus) and a single carboxyl end (C-terminus) |
|
|
Enzymes |
Specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions |
|
|
How are steroids distinguishable from one another? |
By the particular chemical groups attached to the ensemble (four fused) of rings. |
|
|
The most abundant organic compound on Earth |
Cellulose |
|
|
Monomers |
The repeating units that serve as the building blocks of a polymer |
|
|
What is the difference between the Alpha and Beta forms of glucose? |
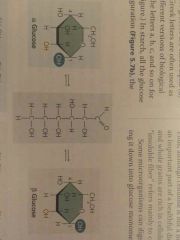
Placement of hydroxyl group |
|
|
Chaperonins (Chaperone proteins) |
Protein molecules that assist in the proper folding of other proteins |
|
|
Protein |
A biologically functional molecule made up of one or more polypeptides each folded and coiled into a specific three-dimensional structure. |
|
|
Peptide Bond |
Covalent bond formed by a dehydration reaction when two amino acids are positioned with a carboxyl group adjacent to an amino group. |
|
|
Simplest form of starch |
Amylose (unbranched) |
|
|
Genome |
The entire sequence of the full complement of DNA |
|
|
Aldoses (Aldehyde sugars) |
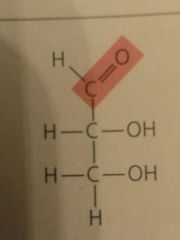
Carbonyl group at end of carbon skeleton |
|
|
What is responsible for the kink in the hydrocarbon chain of an unsaturated fat? |
Cis double bond |
|
|
Glycosidic Linkage |
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction |
|
|
Why are lipid compounds grouped together? |
Beacuse they mix poorly if at all with water |
|
|
In a polypeptide of any significant size the chemical nature is determined by? |
The kind and sequence of the side chains (R group) |
|
|
Dehydration Reaction |
Monomers are connected by a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other, with the loss of a water molecule |
|
|
Lipids consist mostly of |
Hydrocarbon Regions |
|
|
Transport Proteins: (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Transport of substances (b) Hemoglobin, the iron-containing protein of vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across membranes. |
|
|
Polymer |
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds |
|
|
The methods that makes working out 3D structures of proteins possible |
X-ray crystallography Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy Bioinformatics |
|
|
Starch is stored in |
Plastids |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
Cells extract energy from glucose molecules by breaking them down in a series of reactions |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
The disassembly of polymers into monomers |
|
|
Receptor Proteins (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Response of cell to chemical stimuli (b) Receptors built into the membrane of a nerve cell detect signaling molecules released by other nerve cells. |
|
|
Amino Acid |
An organic molecule with both an amino group and a carboxyl group |
|
|
The two monosaccharides of a disaccharide are joined by |
a glycosidic linkage |
|
|
The families of nitrogenous bases |
Pyrimidines Purines |
|
|
Accounts for 40% of the protein in a human body? |
Collagen |
|
|
What fats are most biologically important? |
Fats Phospholipids Steroids |
|
|
Carbohydrates include |
Sugars and Polymers of sugars |
|
|
Common causes of denaturation of proteins? |
Nonpolar Solvents ether chloroform Excessive Heat Disruptive Chemicals hydrogen bonds ionic bonds disulfide bridges |
|
|
Disaccharides |
Double sugars, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by covalent bond. |
|
|
Primary structure of a protein |
Its sequence of amino acids (linear chain of amino acids) |
|
|
A fatty acid has a long carbon skeleton, usually ____ to _____ carbon atoms in length |
16 18 |
|
|
Why is cholesterol a crucial molecule in animals? |
It is a component of animal cell membranes and is also the precursor from which other steroids, such as vertebrate sex hormones, are synthesized. |
|
|
The phosphate group of a nucleotide is attached to? |
The 5' carbon of the sugar |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Generally have molecular formulas that are some multiple of the unit CH2O (glucose) |
|
|
Nucleic acids consist of |
Nucleotides |
|
|
Saturated and trans fats exert their negative impact on health by affecting what? |
Cholesterol levels |
|
|
Pyrimidine Purine |
One six-membered ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms Cytosine Thymine Uracil Larger, with a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring Adenine Guanine |
|
|
Asymmetric Carbon |
A carbon attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms |
|
|
Quaternary structure of a protein |
Overall protein structure that results from the aggregation of these polypeptide subunits. (association of two or more polypeptides- some proteins only) Ex. Collagen, hemoglobin |
|
|
Polysaccharides fill which two roles? These roles are determined by? |
Storage material Building material for structures that protect the cell or the whole organism. Sugar monomers The position of its glycosidic linkages |
|
|
Protein functions |
Enzymatic Storage Hormonal Contractile & Motor Defensive Transport Receptor Structural |
|
|
Portion of a nucleotide without a phosphate groups? |
Nucleoside |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
Carbohydrate macromolecules Composed of many sugar building blocks Polymers with a few hundred to a few thousand monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages |
|
|
Hormonal Proteins (a) Function (b) Example |
(a) Coordination of an organism's activities (b) Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, causes other tissues to take up glucose, thus regulating blood sugar concentration |
|
|
3 groups of amino acids |
Nonpolar side chains; hydrophobic Polar side chains; hydrophilic Electrically charged side chains; hydrophilic |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
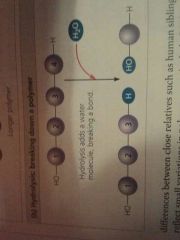
Breaking down a polymer |
|
|
Saturated fatty acid |
No double bonds between carbon atoms allowing as many hydrogen atoms as possible to bond to the carbon skeleton (saturated with hydrogen). |
|
|
Gene expression |
DNA provides directions for its own replication (unique among molecules) DNA directs RNA synthesis DNA, through RNA, controls protein synthesis |
|
|
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by |
Gene |
|
|
Common structure of an amino acid |
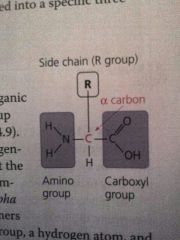
R group differs with each amino acid |
|
|
Monosaccharides are sorted by what attributes |
Location of carbonyl group aldose ketose Size of the carbon skeleton triose pentose hexose The spatial arrangement of their parts around asymmetric carbons |
|
|
Major nutrients for cells |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
What is 1-4 linkage? |
The number 1 carbon is linked to the number 4 carbon |
|
|
Two types of secondary structure of a protein |
Alpha Helix A delicate coil held together by hydrogen bonding between every fourth amino acid Beta Pleated two or more segments of the polypeptide chain lying side by side (Beta strands) are connected by hydrogen bonds between parts of the 2 parallel segments of the polypeptide backbone |
|
|
Is a fatty acid formed by a dehydration reaction? |
No |
|
|
Is glucose a polymer? |
No |
|
|
Chemical reaction cells use to make polymers from monomers? |
Dehydration reaction |
|
|
3 molecules of glucose (C6H12O6) has what chemical makeup? |
C18H32O16 {[(C6 x 3 H12 X3 O6 x3) - (H2 X 3) - (O x 3)] glucose x3 minus 3 water} |
|
|
A molecule with a chemical formula of C6H12 is |
A carbohydrate and a monosaccharide |
|
|
Insoluble fiber is |
Cellulose |
|
|
Lactose (two milk sugars) is classified as |
A disaccharide |
|
|
Lard and butter are examples of |
saturated fatty acids |
|
|
What separates one amino acid from another? |
Different R group (side group) attached to an alpha carbon |
|
|
What stabilizes alpha and beta structures of proteins? |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Which of the following is not a polymer Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids Fatty Acids |
Fatty Acids |

