![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Passive Movement occurs in... |
...Simple Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion & Osmosis (does not need ATP) |
|
|
Diffusion is... |
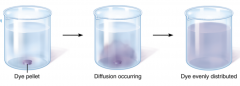
...the movement of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration. |
|
|
In Simple Diffusion... |
...lipid soluble particles freely enter and leave through the cell membrane (lipid bi-layer). Examples: oxygen, carbon dioxide |
|
|
In Facilitated Diffusion... |
...a channel or carrier protein must be present so the transported substance can bind to protein carrier or move through water filled protein channels. |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion... |
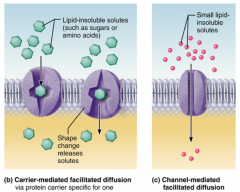
Carrier-mediated: glucose or amino acids (moves through membrane channel) Channel-mediated: ions or water (attaches to membrane channel (protein) and moved across membrane |
|
|
Osmosis is... |
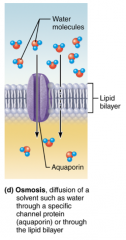
...the diffusion of water. (Water likes to go where the parti (particles) is at! |
|
|
In Isotonic solutions... |
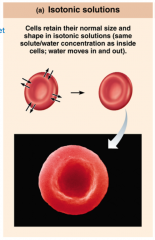
...cells maintain normal shape and size. |
|
|
In Hypertonic solutions... |
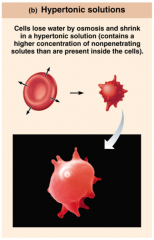
...cells shrink. |
|
|
In Hypotonic solutions... |
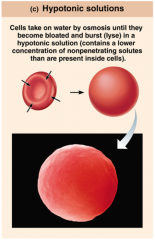
...cells swell & may burst. |
|
|
Passive Membrane Transport Processes: Diffusion |
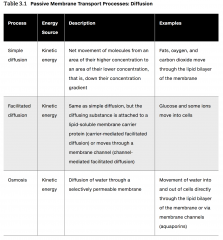
|
|
|
Active Transport occurs in... |
...Endocytosis & Exocytosis & Na+ -K+ pump (needs ATP to work, may or may not follow diffusion) |
|
|
In Primary Active Transport... |
...the energy to do work comes directly from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
|
|
Primary Active Transport system includes... |
...calcium and hydrogen pumps, but most importantly the Na+ -K+ pump (sodium-potassium). |
|
|
Na+ -K+ pump... |
...moves (3) Na+ out of the cell and (2) K+ into the cell. (40% of our ATP is used to power this) ***Potassium lives inside the cell.*** |
|
|
Events of Endocytosis... |
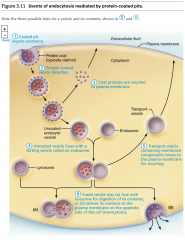
|
|
|
The 3 types of Endocytosis are... |
...Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis & Receptor-mediated Endocytosis. |
|
|
Phagocytosis... |
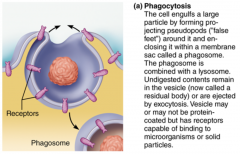
..."cell eating" cell engulfs large or solid material such as a clump of bacteria, cell debris or inanimate particles. Example: WBC's |
|
|
Pinocytosis... |
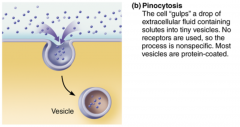
..."cell drinking" a bit of membrane surrounds small volume of extracellular fluid containing dissolved molecules Example: Intestinal Cells |
|
|
Receptor-mediated Endocytosis... |
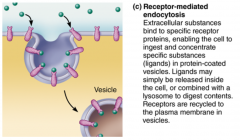
...before molecule is taken in, it has to bind to certain receptors. Example: the way cells take in LDL (bad cholesterol) |
|
|
Exocytosis... |
...process that ejects substances from the cell into the extracellular fluid. (Calcium (Ca2+) is required) Example: neurons --> release neurotransmitter |
|
|
Vesicular Transport... |
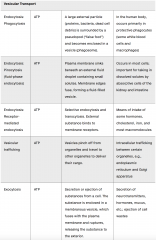
|
|
|
Organelles are... |
...functional compartments in the cell. |
|
|
Mitochondria... |
...is the "powerplant" of the cell. It supplies the cell with energy in the form of ATP. Example: uses O2 & Nutrients to make ATP, CO2 is a bi-product of process |
|
|
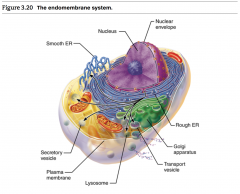
Rough ER (Endoplasmic reticulum)... |
..."membrane factory" is Ribosomal (makes protein) & makes Phospholipids. |
|
|
Smooth ER... |
...makes Phospholipids, steroid hormones & stores Ca2+ |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus... |
...packages and ships substances made in RER & SER to their appropriate destinations. |
|
|
The Endomembrane System... |
|
|
|
Peroxisomes... |
...spherical membranous sacs that take in and destroy oxidants "free radicals" (detoxifier of the cell). Example: liver cells have lots of peroxisomes |
|
|
Lysosomes... |
..."demolition crew" spherical membranous organelles that are used to destroy foreign particles or digest old cell parts. ***Large and abundant in phagocytes*** |
|
|
Cytoskeleton components... |
..."cell skeleton" made up of 3 types of rods. Microfilaments, Microtubules & Intermediate Filaments |
|
|
Microfilaments... |
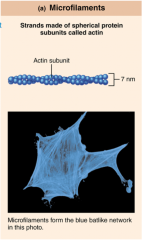
...smallest & thinnest semi-flexible strands of proteins that change the shape of the cell membrane and allow the cell to move. |
|
|
Microtubules... |
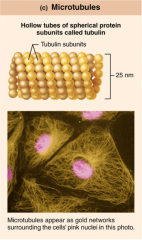
...largest, intracellular roads along which organelles move and are positioned (important in cell division). |
|
|
Intermediate Filaments... |
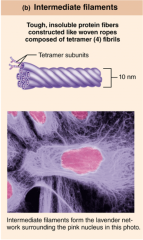
...strongest, intracellular cables or beams that give the cell its strength. Ex. Keratin |
|
|
Centrosome... |
..."cell center" is the place where all microtubules converge. |
|
|
Cilia... |
...are whiplike and propel substances along the surface of a cell Ex. mucus in the airway, oocytes along the oviduct |
|
|
Flagellar... |
...only flagellated cell in the human body is a sperm. (propels the cell itself) |
|
|
Microvilli... |
...very short, immovable cellular extensions. Purpose: absorption Ex. kidney tubule cells & intestinal cells |
|
|
Nucleus... |
... has a double membrane and has pores for entry of proteins and exit of RNA (nucleolus contains rRNA) |
|
|
Chromatin & chromosome structure... |
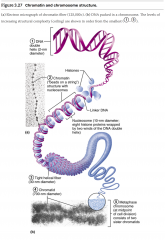
1. DNA 2. DNA wrapped around histomes (protein) 3. Chromosome: very large unit of chromatin |
|
|
Replication of DNA: |
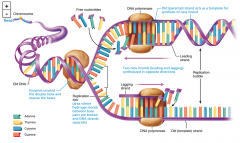
1. Pull apart 2. Add new bases (letters) |
|
|
Transcription... |
...information from DNA is used to make RNA (RNA contains A,U,G,C) |
|
|
The 2 parts of protein synthesis are... |
...transcription (DNA--> mRNA) and translation (mRNA--> Protein) **translator- ribosomes in cytoplasm** **Protein- building blocks for amino acids** |
|
|
The 3 types of RNA in protein synthesis... |
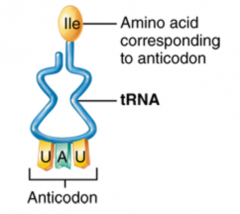
1. mRNA--> has codons (message from Gene) 2. rRNA--> on ribosome 3. tRNA--> transfers amino acids (has anti-codon) |

