![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidermis |
Tissue is stratified squamous epithelial with 90% of cells being keratinocytes. |
|
|
Dermis |
Tissue is dense irregular CT. Primary cell is a fibrocyte with many associated cells and structures. |
|
|
Hypodermis |
Adipose and Areolar CT; also called the superficial fascia. |
|
|
Superior (Cranial) |
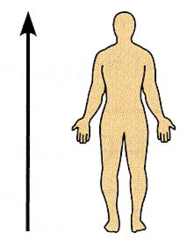
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above.
|
|
|
Inferior (Caudal) |
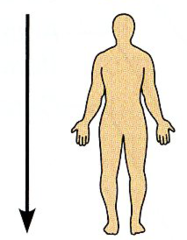
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below. |
|
|
Ventral (Anterior) |
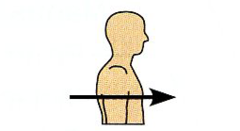
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of. |
|
|
Dorsal (Posterior) |
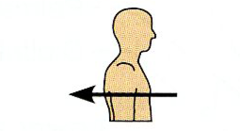
Toward or at the back of the body. |
|
|
Medial |
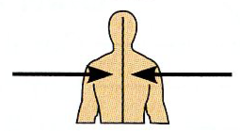
Toward or at the midline of the body; On the inner side of. |
|
|
Lateral |
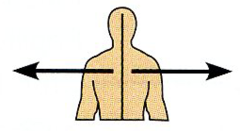
Away from the midline of the body; On the outer side of. |
|
|
Intermediate |
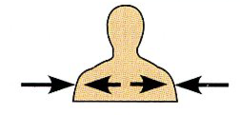
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure. |
|
|
Proximial |
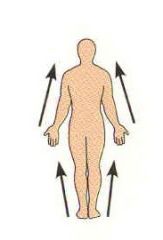
Close to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment to a limb to the body trunk. |
|
|
Distal |
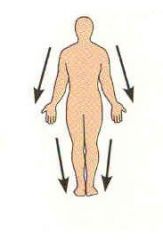
Farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment to the limb to the body trunk. |
|
|
Deep (Internal) |
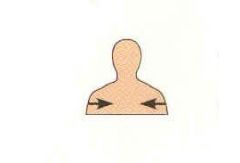
Away from the body surface; more internal |
|
|
Superficial (External) |
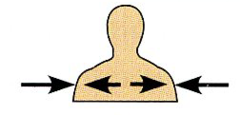
Toward or at the body surface. |
|
|
Which organs make up the RIGHT hypochondriac region? |
The liver and gallbladder. |
|
|
What organ makes up the RIGHT lumbar region? |
The Ascending colon of the large intestine. |
|
|
Which organs make up the RIGHT iliac region? |
The Cecum and Appendix. |
|
|
Which organ makes up the Epigastric region? |
The stomach. |
|
|
Which organs make up the LEFT hypochondriac region? |
The Diaphragm and Spleen. |
|
|
Which organ makes up the LEFT lumbar region. |
The descending colon of the large intestine. |
|
|
Which organ makes up the Umbilical region? |
The Small intestine. |
|
|
Which organ makes up the Hypogastric region of the body? |
The Urinary bladder. |
|
|
Which organ makes up the LEFT iliac region? |
The initial part of the sigmoid colon. |
|
|
Axial |
Relating to the head, neck, and trunk; one of the two major divisions of the body. |
|
|
Appendicular |
Consists of the appendages, or limbs, which are attached to the body's axis. s |
|
|
Sagittal Plane |
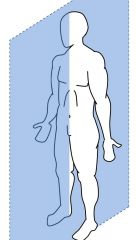
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts. |
|
|
Median Plane (Sagittal plane) |
A sagittal plane that lies exactly in the midline of the body. (Midsagittal Plane) |
|
|
Frontal or Coronal Plane |
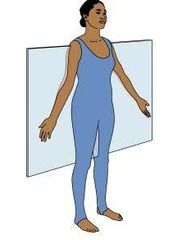
A plane that lies horizontally and divides the body into anterior & posterior parts. |
|
|
Transverse or horizontal plane |
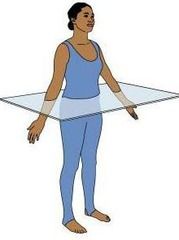
Divides the body into Superior (Cranial) and Inferior (Caudal) parts. |
|
|
right upper quadrant |
RUQ- contains right lobe of liver (bulk of liver), right kidney, upper portion of right ureter, pancreas (small section), gallbladder, and portions of colon and intestine |
|
|
right lower quadrant |
RLQ- contains lower portion of right ureter, portions of clon and intestine, appendix, right ovary and fallopian tube (in females), and right vas deferens and seminal vesicle (in males) |
|
|
left upper quadrant |
LUQ- contains stomach, spleen, left lobe of liver (smaller), pancreas (most of organ), left kidney, upper portion of left ureter, portions of colon and intestines |
|
|
left lower quadrant |
LLQ- contains lower portion of left ureter, portions of colon and intestine, sigmoid colon, left ovary and fallopian tube (in females), and left vas deferens and seminal vesicle (in males) |
|
|
Triglycerides |
Made by dehydration synthesis from: 3 Fatty acids bound to glycerol. |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Have 2 Fatty acids + a phosphate group (with an R group) bound to glycerol |
|
|
Steroids |
4 interlocking hydrocarbon rings. All sterols in the body are modified from cholesterol. Examples include: bile salts and hormones (sex hormones and adrenocortical hormones) |
|
|
Cells are usually NEVER symmetrical. T/F |
True. When a cell is perfectly round, it is usually a cancer cell, because cells round up when they are scared. |
|
|
T/F Abundance of organelles dictate the function of the cell. |
TRUE. |
|
|
Nucleus |
Responsible for housing DNA, & for making protein. |
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) |
Makes secretory proteins. Ex. Liver; has a lot of RER. Breast cells also. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
The powerhouse of cell. Makes ATP. You will find a lot of mitochondria in muscle, it is red because there is COPPER in mitochondria.
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
Smooth ER. The shipping center of the cell. Takes proteins & ships them to specific destinations. |
|
|
Vesicles |
Vesicles are the transport busses of the cell. <-- They are critical of the cell. They carry material to specific places.
|
|
|
Centrioles |
Important in cell division. |
|
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) |
Important in making lipids (Lipid synthesis) Also important in detoxification. |
|
|
Homeostasis |
maintenance of a uniform state. |
|
|
What are the general functions for bones (Osseus Tissue)? |

Supports + Protects (By enclosing); Provides leverage for muscle. |
|
|
What are the general functions for Hyaline cartilage? |
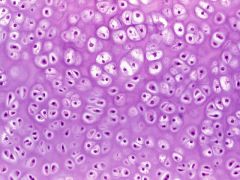
Supports & Reinforces; Resists compressive stress. |
|
|
What is the general function for Stratified squamous epithelia? |
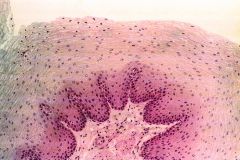
Protection under tissues in areas subjected to abrasion. Made up of keratinized cells. |
|
|
What is the general function for Cardiac muscle? |
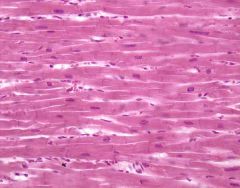
As it contracts it propels blood into the circulation; Involuntary control. |
|
|
What are the general functions for skeletal muscle? |

Voluntary movement, locomotion, & Facial expression. Skeletal muscle is always Striated. |
|
|
What are the general functions for Simple Columnar Epithelia? |
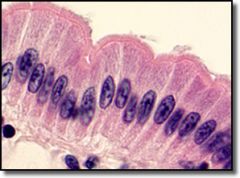
Absorbtion & Secretion of mucus. |
|
|
What are the general functions for Elastic Connective tissue? |
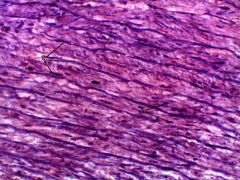
Function: Allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration. |
|
|
What are the functions of Simple squamous epithelium? |
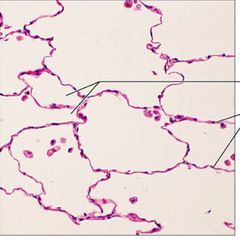
Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; secretes lubricating substances in serosae. |
|
|
What are the general functions of dense irregular CT? |
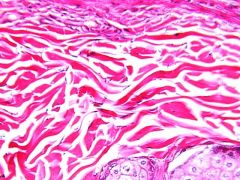
Able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength |
|
|
What are the general functions of Dense Regular CT? |

Attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction |
|
|
What are the general functions of Loose Areolar CT? |
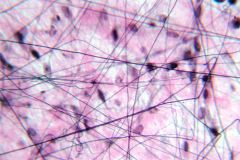
Wraps and cushions organs |
|
|
What are the general functions of Loose Adipose CT? |
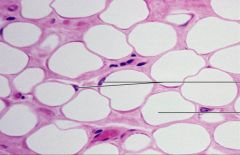
Provides reserve fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs |
|
|
What are the general functions of Reticular Connective fibers? |
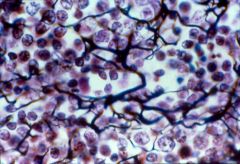
Fibers form a soft internal skeleton that supports other cell types, including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages |
|
|
What are the general functions of simple cuboidal epithelia? |
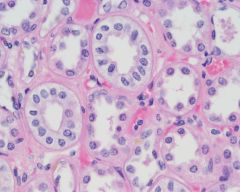
Secretion and absorption |
|
|
What is the function for Stratified cuboidal Epithelia? |
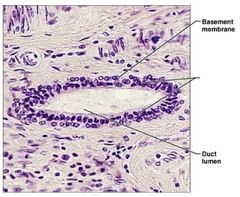
Protection |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium |
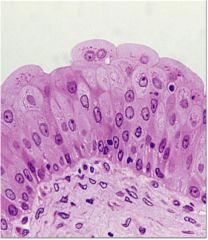
Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine |
|
|
What makes up the afferent pathway in Homeostasis? |
1.) Stimulus: Produces change in Variable 2.) Receptor: Detects Change 3.) Input: Information sent along afferent pathway to control center. |
|
|
What makes up the Efferent pathway in Homeostasis? |
4.) Output: Information sent along efferent pathway to effector. 5.) Response: of effector feeds back to reduce the effect of stimulus and returns variable to homeostatic level. |
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Cyt- Cells; Cytoskeleton made up of microtubules, they are thick & Microfilaments made up of actin. 3 important things, 1. Cell transport, 2. Provide shape & support for the cell, and 3. Cell division. |
|
|
Lysosomes |
Have a lot of acid in them. Bodies in the cell that are responsible for breakdown. They have enzymes in there responsible for breakdown. |
|
|
Peroxisome |
Breaking fat down. Beta- Oxidation = Fat breakdown |
|
|
Extra- |
Outside |
|
|
Intra- |
Inside |
|
|
Plasma- |
Life |
|
|
Inter- |
Between |
|
|
Interstitial Fluid (66% of body) |
-Aka cytosol or cytoplasm
-A colloid
-Rich in K+ (Potassium)
-Very low in Na+ (sodium) & Ca++ (Calcium)
-Rich in proteins (including enzymes) Compartmentalized in organelles |
|
|
Extracellular Fluid (33% of body) |
-Includes interstitial, blood, lymph, CSF, synovial, & others
-High in Na+ and Cl
-Low in K+ and proteins (with exception of blood)
-Most types freely exchange with each other |
|
|
Integral Membrane Proteins (IMPs) |
Proteins that go all the way across the membrane. Very tightly embedded in membrane. Very TIGHTLY held. Can serve as channels or pumps. |
|
|
Peripheral Membrane Proteins (PMPs) |
Membrane proteins that don't go all the way across. They only go halfway, or stuck on one side. Very loose & mobile. |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Amphipathic molecules that determine which molecules cross the membrane by simple diffusion. |
|
|
Simple diffusion |
In a solution or gas that has an area of high numbers of particles and an area of lower numbers of particles, the particles will diffuse/move from the area of higher to lower concentration. Non-polar uncharged and small molecules e.g. Oxygen |
|
|
Uniport |
A transport mechanism that drives a single compound or ion across a membrane, not coupled with transport of any other compound or ion |
|
|
Antiport |
A transport mechanism that simultaneously drives two different compounds or ions in opposite directions across a membrane. |
|
|
Symport |
A transport mechanism that simultaneously drives two different compounds or ions in the same direction across a membrane. |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
A transport mechanism that moves compounds or ions down a concentration gradient, and requires no energy; also known asaccelerated diffusion or mediated transport. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Very SLOW. |
|
|
If you see the word CHANNEL, then it's automatically... |
Facilitated diffusion. |
|
|
If you see the word PUMP, then it is automatically... |
primary active transport. |
|
|
Equilibrium potential |
The membrane potential when concentration gradient = electrical and no net ion movement occurs. |
|
|
Tight junctions |
Water tight seals & prevent protein migrations from one side of the cell to the other.
-Can form water tight seals between neighboring cells. |
|
|
Gap junctions |
Transmit current and substances between the cells. Enable nutrients/waste to be exchanged.
-Form electrical synapses that enable adjacent cells to act electrically as one cell by allowing current to flow between cells |
|
|
Anchoring junctions (Desmosomes) |
Junctions that mechanically attach cells and their cytoskeletons to their neighbors and to the extracellular matrix. |
|
|
Desmosomes |
Binds adjacent cell membranes together for structural strength, but permeable to interstitial fluid flow. When combined with intermediate filaments gives sheet of tissue “tensile strength”. |
|
|
Collagen fibers |
Forms very strong fibers and may be found in bundles to impart tensile strength. |
|
|
Reticular fibers |
Forms a “soft skeleton” for supporting a network of cells; holds cells in a matrix |
|
|
Elastic fibers |
Enables tissues to be stretchy but strong. |
|
|
G Protein |
As long as the Ligand is bound to the receptor, the receptor Keeps kicking the G protein, then the G protein goes and activates an enzyme. Kick robot dog, dog does task, dog comes back, kicks again |
|
|
How does the Ligand trigger Various cell responses? |
1.) First the Ligand binds to the Receptor
2.) Then the Receptor binds to G Protein & activates (Kicks it)
3.) The G Protein then binds & activates an effector protein (Enzyme)
4.) The shape changes & reactions produce 2nd messengers in the cell
5.) 2nd messengers activate kinase enzymes!
6.) These kinase enzymes then trigger various cell responses.
|
|
|
Osmoregulation |
Prevent excessive water loss (epidermis) |
|
|
Thermoregulation |
acts as an effector n cooling and warming core temperature (dermis & hypodermis) |
|
|
Thin Skin |
Has 4 Layers; Stratum corneum, Stratum granulosum, Stratum spinosum, and Stratum basale. |
|
|
Stratum Corneum |
Most superficial layer; 20-30 layers of dead cells represented only by flat membranous sacs filled with keratin. |
|
|
Stratum granulosum |
3-5 layers of flattened cells, organelles deteriorating. Granules observed. |
|
|
Stratum spinosum |
Several layers of keratinocytes unified by desmosomes. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin. |
|
|
Stratum Basale |
Deepest epidermal layer; One row of actively mitotic stem cells. |
|
|
Thick skin |
Has all 4 layers of Thin skin, plus the Clear stratum Lucidae layer found beneath the Stratum corneum. A lot of dead cells make up this layer. |
|
|
Stratum Lucidem |
Clear layer. In this layer it looks empty because the cells are dying. |
|
|
Melanocytes |
Found in strata basale and lower layers of Strata spinosum where there are no desmosomes. Produce melanin taken up by keratinocytes.
-Protects against UV radiation by filling itself with melanin & surrounding deeper mitotic keratinocytes |
|
|
Dendritic macrophage |
A fixed phagocyte of immune system. |
|
|
Tactile (Merkel) cell |
A Sensory receptor for light touch. It is a modified epithelial cell contacted by a sensory nerve axon. |
|
|
Dermal papillae |
Joins the basement membrane of epidermis to dermis and adds texture to epidermal surface. |
|
|
Papillary layer |
is made of areolar CT and push into lower epidermal layers to form “papillae” (looks like dust bunnies) |
|
|
Reticular Layer |
is made of dense regular CT. Bundling of collagen fibers adds tensile strength. (These look like nookos) |
|
|
Arrector pili |
A microscopic band of muscle tissue which connects a hair follicle to the dermis. When stimulated, the arrector pili will contract and cause the hair to raise to the skin surface (stand on end). (Goosebumps) |
|
|
Sebaceous Glands |
Usually associated with hair follicles. Secrete same components as in sweat plus lipids (sebrum).
-Hormone receptors increase secretions at puberty |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
The area of the brain where The Receptor and Control Center is in. |
|
|
Acclimitization |
Long term decreases or increases in environmental temperature (such as summer to winter) alter basal metabolic rates to enable us to adapt to colder or warmer environments.
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of bone tissue? |
1. Compact
2. Spongy |
|
|
What are the 3 types of cartilage in bone? |
1. Elastic
2. Hyaline
3. Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Chondro- |
Cartilage |
|
|
What is the main cartilage that is found in the skeletal system? |
Chondrocytes; They secrete a large amount of ECM. The Inside cartilage slowly gets converted into bone. Depend on external sources of calcium.
|
|
|
Osteons |
A central canal and the concentric osseous lamellae encircling it, occurring in compact bone. Also called haversian system.
|
|
|
Trabeculae |
Any of the supporting strands of connective tissue projecting into an organ and constituting part of the framework of that organ. (How spongy bone is arranged) |
|
|
Osteocytes
|
An osteocyte is a bone-forming cell that has become entrapped within the bone matrix (the hard part of bone). It lies within a lacuna (a small pit) and communicates with its surroundings through tiny channels called canaliculi. |
|
|
Lamellae |
ECM of Calcified GAGs (Glycoproteins) and circularly arranged bundles of parallel collagen fibers bound to each other. |
|
|
Articular cartilage |
Hyaline cartilage cushions areas within joints. |
|
|
Circumferential lamellae |
Found at the outer and inner surfaces of the bone, where they are covered by the periosteum and endosteum. |
|
|
Periosteum
|
A membrane with a fibrous outer layer and a cellular inner layer. 3 functions: |
|
|
Endosteum
|
Is an incomplete cellular layer and lines the medullary cavity. This layer, which is active during bone growth, repair, and remodeling, covers the trabeculae of spongy bone and lines the inner surfaces of the central canal. |
|
|
Red Bone Marrow
|
Responsible for blood cell formation
|
|
|
Yellow Bone Marrow
|
Adipose tissue important as an energy reserve. |
|
|
Diaphysis |
The shaft of a long bone. |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
A cell that nibbles at and breaks down bone and is responsible for bone resorption. |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
A cell that makes bone. It does so by producing a matrix that then becomes mineralized. Bone mass is maintained by a balance between the activity of osteoblasts that form bone and other cells called osteoclasts that break it down. |
|
|
Osteoprogenitor/Osteogenic cells |
Bone stem cells |
|
|
Osteoid |
The organic matrix of bone; young bone that has not undergone calcification. Skeletal ECM |
|
|
What's the difference between the organized & disorganized Skeletal collagen fibers? |
-If you have disorganized collagen fibers = immature bone -If you have ORGANIZED collagen fibers = mature bone. |
|
|
fibrocartilage
|
Strongest, most durable type of cartilage. contains many collagen fibers. Found in intervertebral disk of the back and in the knee joint. also found in the symphysis pubis. |
|
|
Glycocalyx |
The outer layer of a bacteria cell. It helps the cell "stick" to other cells and other objects, as well as retain water. -Its a gelatinous sticky substance that surrounds the outside of the cell for Prokaryotes. |

