![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
kills gram-positive bacteria such as staph and strep |
Penicillin |
|
|
Ways that Antimicrobial drugs can interfere |
1. Destroy cell wall (poke hole/damage) 2. Interrupt Protein synthesis (Translation) 3. Interrupt Nucleic acid synthesis (DNA Rep/RNA Transcription) 4. Interrupt cell wall synthesis 5. Folic acid interruption by competitie inhibition |
|
|
Narrow spectrum drug that inteferes with cell wall synthesis of mycobacterium as in the case of TB.
|
isoniazad |
|
|
This drug destroys anthrax. It blocks DNA Synthesis in gram neg and gram positive. |
Quinolones |
|
|
Beta lactamase |
inactivates the beta lactam antibiotics; resistant |
|
|
Betalactam |
inhibits cell wall synthesis; a part of pencillin |
|
|
Cephalosporin (big head) |
1. resemble penicillin 2. inhibit cell wall synth 3. alternative to pencillin for pen resistance 4. Broad spectrum (against gram neg) 5. resistant to betalactamase |
|
|
Monobactam |
Narrow spectrum. Not recognized by betalactamases; can kill gram neg aerobe rod.
|
|
|
Vancomycin |
Cell wall inhibitor IV administered against gram pos like staph "drug of last resort" - damages ears and kidneys microbes can't resist |
|
|
1. Topical (skin) - cyclic polypeptid 2. interferes with transport of cell wall precursors through bacterial cell membrane; can't build walls. 3. kills gram positive
|
Bacitracin |
|
|
Polymyxins |
1. cyclic polypeptide 2. increase bacteria permeability, leading to cell death 3. efffective against infections in wounds, burns and abrasions. |
|
|
How do antibiotics effect protein synthesis in bacteria, but not the host? |
Antibiotics target the bacteria's ribosomes, which are smaller than human. |
|
|
Attach to bacterial ribosomes, blocking translation
|
Aminoglycosides
(Amino-Glyco) |
|
|
Examples of Aminoglycosides |
Streptomycin - tb Gentamicin - uti Neomycin - cuts |
|
|
Streptomycin |
Sometimes used in TB can damage the auditory nerves - deafness |
|
|
Gentamicin |
used for UTI (gram neg infection) |
|
|
ointment - combo with bacitrain and polyxmyxi as neosporin |
Neomycin |
|
|
Which antibiotic causes the teeth to stain? |
Tetracycline; targets tRNA 30S |
|
|
Which antibiotic can cross the blood brain barrier? |
Chloramphenicol |
|
|
What diseases is chloramphenicol used to treat? |
Seriously life threatening disease Brain affected diseases:Meningitis and Typhoid Fever; as well as cholera and rocky mtn fever |
|
|
How does chloramphenicol work? |
bacteriostatic; interferes with protein synthesis (peptide bond formation in bacterial ribosome) |
|
|
What causes gray syndrome? |
Chloramphenicol; accumulates in the blood of baby, causing toxic reaction and sudden breakdown of cardiovascular system. Can also cause aplastic anemia |
|
|
How does Rifampin work? |
Interferes with RNA synthesis (transcription)
|
|
|
What is a drug used in penicillin allergic patients? |
Erythromycin (although CP can't use this either) |
|
|
Antibiotics that affect protein synthesis |
Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Macrolides Licosamides Streptogramins oxazolidiones |
|
|
What are assays used for? |
To tell if an antibiotic is working |
|
|
What are two assays used? |
Tube dilution method Disk diffusion
|
|
|
Tube Dilution method |
An assay determines lowest concentration of antibiotic that will prevent growth of pathogen (MIC) |
|
|
Lowest conc of antibiotic to prevent growth of pathogen. |
MIC Minimum Inhibitory Concentration - lowest conc of antibiotic to prevent growth of pathogen |
|
|
What is the Disk Diffusion Method? How does it work? |
It is an assay
Antibiotic disk diffused in agar dish. zone of inhibition (Clearing) means the drug is working to inhibit bacteria.
|
|
|
What is the name of the clearing around the disk in disk diffusion? |
Zone of inhibition |
|
|
Drugs made in the lab |
Chemotherapeutics.Synthetic |
|
|
Medicine made from microbes to kill microbes |
Antibiotics |
|
|
Concentration causing harm to host |
toxic dose |
|
|
concentration eliminating pathogen |
therpeutic dose |
|
|
Kills a wide variety of microbes |
broad spectrum |
|
|
Kills a small number of microbes |
narrow spectrum |
|
|
Example of a broad spectrum that kills almost all bacteria except mycobacterium. |
Tetracycline |
|
|
This drug uses competitve inhibition to interrupt folic acid synthesis |
Sulfanilamide (sulfonamide) |
|

|
How antibiotics work: Protein synthesis, cell wall synthesis, Nucleic Acid synthesis, cell membrane, fam |
|
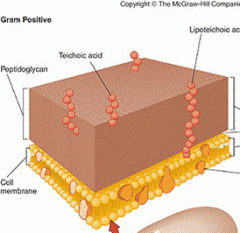
Explain how penicillin interferes with cell wall synthesis in rapidly growing cells,.
|
The cell can no longer make peptidoglycan; causes the cell wall to become weak and the cell to burst |
|
|
True/False?: Rifampin interferes with transcription of RNA |
True |
|
|
Drugs that treat meningitis |
Rifampin Chloramphenicol |
|
|
Name the ways that antibiotic resistance takes place in a cell |
Mutations Gene transfer Antibiotic modification (ie. betalactamase) Altering metabolic pathways (folic acid) Membrane Modification (permeability) Target Modification (ribsome mod)
|
|
|
Three methods of horizontal gene transfer |
conjugation transformation transduction |
|
|
Human contributions to antibiotic resistance |
Available over the counter in some countries Used in livestock feeds Excessive use of antibiotics
|
|
|
Sulfonamides interfere with ______ ________ synthesis. |
Folic Acid synthesis |
|
|
If folic acid synthesis is blocked, ______ ________ and _________ __________ synthesis cannot take place. |
DNA Replication / Nucleic Acid Synthesis |
|
|
Two drugs together work better is called __________ _______________. |
Drug Synergism |
|
|
This antibiotic interferes with folic acid metabolism. |
Sulfonamide |
|
|
This drug is used to treat a mycobacterium such as TB. It interferes with cell wall synthesis |
Isoniazid |
|
|
True or False: Isoniazid is a narrow spectrum drug that is bacteriostatic. |
True |
|
|
This drug blocks DNA Synthesis in Gram Neg and Gram positive |
quionolones |
|
|
Antiobiotics can interfere with the synthesis of the cell wall. What is the component of the cell wall it interferes with? What happens to the cell? |
Peptidoglycan. The wall becomes weak, the osmotic pressure changes and the cell burst. |
|
|
Is penicillin bacteriostatic or bactericidal when the cells are multiplying rapidly? |
Bactericidal |
|
|
In synthetic penicillin, what differs from drug to drug creating resistance to beta lactamase? |
The side group |
|
|
BetaLactam Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis: |
Betalactam belongs to pencillin and similar drugs. |
|
|
Vancomycin is bacteri___________ and inhibits _______ _________ __________. It treats gram __________ staph where penicillin allergies or resistance occurs. |
bactericidal / cell wall synthesis / positive |
|
|
T or F: Vancomycin has become the drug of coice for MRSA. |
True |
|
|
Polypeptide antibiotics such as polymixins and bacitracin are too toxic to ingest. They are used topically. How does this affect the organism causing the infection? |
It affects the cell membrane |
|
|
Bacitracin works by |
by interfering with transport of cell wall precursors through the cell membrane. (GRAM POS ...positively polypeptide!) |
|
|
polymixins work by |
increasing the cells permeability |
|
|
Gentamicin is used to treat what type of infection? How does it affect organism? |
Urinary Tract Infection (gent...genitalia...);
Inhibits Protein synthesis |
|
|
Streptomycin, Gentamicin are both in the group.... |
aminglycosides |
|
|
True or False: tetracycline group is broad spectrum includes doxycycline and is used to treat rickettsial and chlamydial diseases as well as gram negativepneumonia syphilis, gonorrhea. |
True |
|
|
Chloramphenicol is a broad spectrum bacteriostatic drug How does it effect the organism? (ie cws, ps etc) |
Inhibits protein synthesis |

