![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Chemotherapy
|
The use of drugs to treat a disease
|
|
|
Chemotheraputic agent
|
Interfere with the growth of microbes within a host
(many are antibiotics) |
|
|
Antibiotic
|
Microbial metabolic product with antimicrobial activity
|
|
|
Selective toxicity
|
A drug that kills microbes without damaging the host
|
|
|
Common Microbes that Produce Antibiotics
|
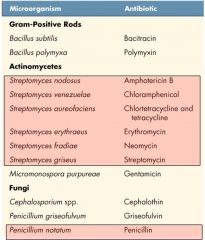
|
|
|
Broad verses Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics
|
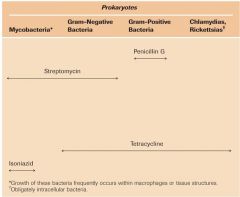
Narrow spectrum antibiotics can’t penetrate G- outer membrane
|
|
|
The Action of Antimicrobial Drugs
|
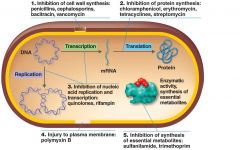
|
|
|
Natural penicillins
|
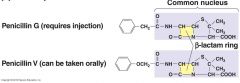
Natural penicillins (penicillin G, and V)
narrow spectrum (mostly G+) Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Clostridium Few gram negative Neisseria (gonorrhoeae, meningitis), Treponema (syphilis) |
|
|
Penr Bacteria may produce Penicillinase
|
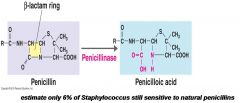
|
|
|
Semi-Synthetic Penicillins
|
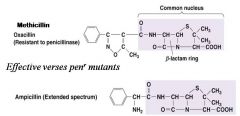
broad spectrum BUT sensitive to penicillinase
AugmentinTM : ampicillin plus penicillinase inhibitor |
|
|
Cephalosporins
|
marine microbe
1st generation broad spectrum 2nd, 3rd, and 4th generations more effective against gram-negatives and less effective against G+ Alternative where penicilin resistance is encountered Now encounter extended spectrum lactamase producing microbes -ex: 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins (cefotaxime, cetepmie) used to be effective against penicillin resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae |
|
|
Bacitracin
|
Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis
Polypeptide antibiotic Bacillus subtilis topical application : NeosporinTM against gram-positives |
|
|
Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis
|
Vancomycin
Bacitracin Penicillins cephalosporins |
|
|
Vancomycin
|
Glycopeptide
Important "last line" against MRSA Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
|
Chloramphenicol
Tetracyclines Erythromycin |
|
|
Chloramphenicol
|
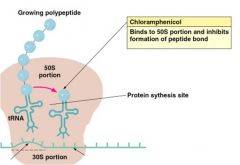
Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
1st Broad spectrum discovered Binds 50S subunit, inhibits peptide bond formation Meningitis,Typhoid fever and RMSF Reserved serious infection only Crosses blood brain barrier Bone marrow depression |
|
|
Tetracyclines
|
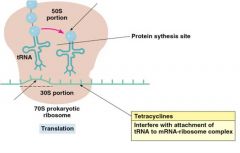
Tetracyclines
Broad spectrum Interferes with tRNA attachment Indiscriminate use despite side effects Stain teeth and destroy intestinal bacteria Making comeback chlamydia, rickettsia, variety G-, syphilis, gonorrhea, pneumoniae |
|
|
Polymyxin B
|
Topical application only
Destroys cell membranes in bacteria and eucaryotes Combined with bacitracin and neomycin in over-the-counter preparation NeosporinTM |
|
|
NeosporinTM
|
bacitracin
neomycin Polymyxin B |
|
|
Rifamycin
|
Inhibit Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Inhibits RNA synthesis Anti tuberculosis In combo with INH and ethambutol (three drug cocktail) Meningococcal and Haemophilus meningitis |
|
|
Quinolones and fluoroquinolones
|
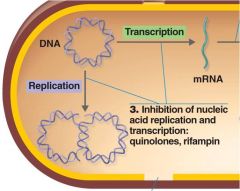
nalidixic acid ex: CiprofloxacinTM
Inhibits DNA gyrase Urinary tract infections |
|
|
Disk-Diffusion and E Test
|
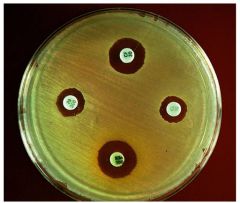
|
|
|
MBC
|
Minimal bactericidal concentration
|
|
|
Broth Dilution Test
|
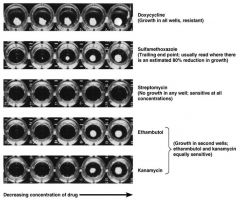
|
|
|
Antibiotic Resistance
|
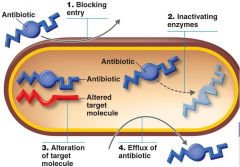
A variety of mutations can lead to antibiotic resistance
1. Prevention of penetration of drug (cell wall/outer membrane protein) 2. Enzymatic destruction of drug (penicillinase) 3. mutate drug's target site (penicillin binding protein30S ribosomal subunit) 4. Rapid ejection of the drug (revolving door mechanism) Resistance genes are often on plasmids that can be transferred between bacteria |
|
|
Resistant population takes over sensitive population
|
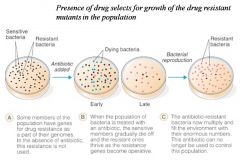
|
|
|
Effects of Combinations of Drugs
|
1. Synergism : the effect of two drugs used together is greater than the expected additive effect of both used alone.
therefore, can lower the dosage and get greater kill and less drug toxicity 2. Inhibit emergence of drug resistant mutants EX Rifamycin + INH + ethambutol Anti tuberculosis XDR extensively drug resistant tuberculosis (INH, rifampin, fluroquinolone) Sulfonalimide + trimethoprine STMP Urinary tract infections Traveler's diarrhea |
|
|
Super Bug
|

|

