![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
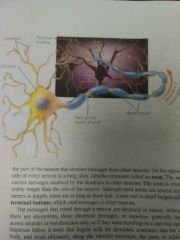
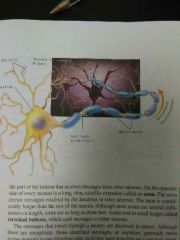
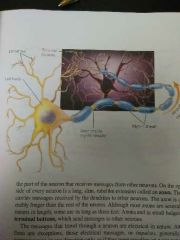
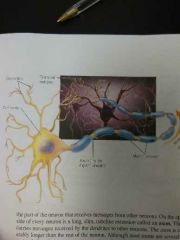
Neuron |
Nerve cells, the basic elements of the nervous system |
|
|
|
Dendrite |
A cluster of fibers at one end of the neuron that receive messages from other neurons |
|
|
|
Axon |
The part of the neuron that carries messages destined for other neurons |
|
|
|
Terminal Buttons |
Small bulges at the end of axons that send messages to other neurons |
|
|
|
Myelin Sheath |
A protective coat of fat and protein that wraps around the neuron |
|
|
|
All or none law |
The rule that neurons are either on or off |
|
|
|
Resting State |
The state in which there is a negative charge of about-70 millivolts within a neuron |
|
|
|
Action potential |
An electric nerve impulse that travels through a neuron when it is set off by a trigger changing the neuron charge from negative to positive |
|
|
|
Mirror Neuron |
Specialized neurons that fire not only when a person enacts a particular behavior but also when a person simply observes another individual carrying out the same behavior |
|
|
|
Synapse |
The space between two neurons where the axon of a sending neuron communicates with the dendrites of a receiving neuron by using chemical messages |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
Chemicals that carry messages across the synapse to the dendrite (sometimes the cell body) of a receiver neuron. |
|
|
|
Excitatory Messages |
Chemical messages that make it more likely that a receiving neuron will fire |
|
|
|
Reuptake |
The absorption of neurotransmitters by a terminal button |
|
|
|
Central Nervous System (CNS) |
The part of your nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
|
Spinal Cord |
A bundle of neurons that leaves the brain and runs down the length of the back and is the main means for transmitting messages between the brain and the body |
|
|
|
Reflex |
An automatic involuntary response to an incoming stimulus |
|
|
|
Sensory (efferent) Neurons |
Neurons that transmit information from the perimeter of the body to the central nervous system |
|
|
|
Motor(efferent) neurons |
Neurons that communicate information from the nervous system to muscles and glands |
|
|
|
Interneurons |
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons, carrying messages between the two |
|
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System |
The part of the nervous system that includes the autonomic and somatic subdivisions made up of neurons with long axons and dendrites, it branches out from the spinal cord and brain and reaches the extremities of the body |
|
|
|
Somatic division |
The part of the peripheral nervous system that specializes in the control of voluntary movements and the communication of information to and from the sense organs |
|
|
|
Autonomic division |
The part of the autonomic division of the nervous system that acts to prepare the body for action in stressful situations, engaging all the organism's resources to respond to a threat |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic division |
The part of the autonomic division of the nervous system that acts to prepare the body for action in stressful situations, engaging all the organism's resources to respond to a threat |
|
|
|
Behavioral Genetics |
The study of the effects of hereditary on behavior |
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
A chemical communication network that sends messages throughout the body via the bloodstream |
|
|
|
Hormones |
Chemicals that circulate though the blood and regulate the functioning or growth of the body |
|
|
|
Pituitary gland |
The major component of the endocrine system or master gland which secretes hormones that control growth and other parts of the endocrine system |
|
|
|
Central Core |
The old brain which controls basic functions such as eating and sleeping and is common to all vertebrates |
|
|
|
Cerebellum |
The part of the brain that controls bodily balance |
|
|
|
Reticular formation |
The part of the brain extending from the medulla through the pons and made up of groups of nerve cells that can immediately activate other parts of the brain to produce general bodily arousal |
|
|
|
Thalamus |
The part of the brain located in the middle of the central core that acts primarily to relay information about the senses |
|
|
|
Hypothalamus |
A tiny part of the brain, located below the thalamus, that maintains homeostasis and produced and regulates vital behavior such as eating drinking and sexual behavior |
|
|
|
Limbic System |
The part of the brain that includes the amygdala and hippocampus and controls eating aggression and reproduction |
|
|
|
The cerebral cortex |
Responsible for the most sophisticated information processing in the brain; contains four lobes |
|
|
|
Lobes |
The four major sections of the cerebral cortex frontal parietal temporal and occipital |
|
|
|
Motor area |
the part of the cortex that is largely responsible for the body's voluntary movements |
|
|
|
Sensory area |
The site in the brain of the tissue that corresponds to each of the senses with the degree of sensitivity related to the amount of the tissue allocated to that sense |
|
|
|
Association areas |
One of the major regions of the cerebral cortex; the site of the higher mental processes, such as thought, language, memory, and steech |
|
|
|
Neuroplasticity |
Changes in the brain that occur throughout the life span relating to the addition of new neurons new interconnections between neurons and the reorganization of information processing areas |
|
|
|
Hemisphere |
Symmetrical left and right halves of the brain that control the side of the body opposite to their location |
|
|
|
Lateralization |
The dominance of one hemisphere of the brain in specific functions such as language |
|
|
|
Biofeedback |
A procedure in which a person learns to control through conscious thought internal physiological processes such as blood pressure, heart and restoration rate, skin temperature, sweating, and the construction of particular muscles |
|

