![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nervous system functions |
•Communication •sends signal from outside to brain •command body to react •gather info and interpret what is important and what is not |
|
|
Functional organization |
1. Sensory input/Afferent 2.Integration 3.Motor output/efferent |
|
|
Structural Organization |
•Central Nervous System(CNS), •Peripheral Nervous system (PNS) |
|
|
What is the CNS made up of? PNS? |
CNS made of: Brain & Spinal cord
•PNS made of: Nerves outside the brain and the spinal cord; •Communication roadways that link the body to the brain and vice versa. Cranial Nerves, Spinal Nerves, Ganglia |
|
|
Afferent/Sensory |
•Transmits signal towards CNS from PNS, Sensory receptors perceive stimuli (internal & external) throughout the body, send info to the brain. (Temperature, Pain, Stretch) |
|
|
Efferent/Motor |
•Transmits signals away from CNS towards PNS, Signals from the brain that travel to effector organs to elicit an effect. |
|
|
5 divisions of the PNS: 1)Somatic sensory division |
•Afferent signals originating from the skin, articulations, and SKM •Stimulated to perceive: touch, Pain, pressure, vibration, and temperature |
|
|
5 divisions of the PNS: 2)Special Sensory Division |
•Afferent signal originating from eyes, nose, ears, and mouth, and balance •Special senses: Vision, Smell, hearing, equilibrium and taste |
|
|
5 divisions of the PNS: 3) Visceral sensory division |
•Afferent signals originating from the viscera/internal organs •Stimulated to perceive: stretch, Pain, temperature, hunger, nausea, etc |
|
|
5 divisions of the PNS: 4)Somatic motor division/ Voluntary Nervous system |
•Signals that controls SKM •Voluntary |
|
|
5 divisions of the PNS: 5)Visceral Motor division/ Autonomic Nervous System |
•Signals that controls smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands •Involuntary
|
|
|
What is a neuron? |
•Neurons are highly specialized, excitable cells that transmit electrical signals. |
|
|
What are neuron functions? |
•Conducts electric signals along their plasma membrane = Nerve impulse/ action potential •Highly metabolic rate - ton calories, 2nd most •Extreme longevity •Cannot undergo mitosis but axons can regenerate if damaged • Can stimulate other neurons, muscle tissue, and glands |
|
|
Supporting cells: Sensory/afferent |
Transmits signal towards CNS from PNS |
|
|
Supporting cells: Motor/ efferent |
Transmits signals away from CNS towards PNS |
|
|
Supporting cells: Interneurons/ association neurons |
•Between Afferent and efferent •Confined within the CNS |
|
|
Supporting cells: Neuroglia/ Glial cells |
4 types in CNS; 2 types in PNS |
|
|
Supporting cells of the CNS: 1)Astrocytes |
•Combine with brain capillaries to form the blood brain barrier: protects the brain from pathogens •Controls the chemical composition surrounding neurons; ensures that neurons can respond to stimulus •Provide 3D framework for CNS; structural support and mechanical strength |
|
|
Supporting cells of the CNS: 2. Microglia |
•Immune cells of the CNS •Phagocytosis of pathogens and dead neurons |
|
|
Supporting cells of the CNS: 3. Ependymal |
•Ciliated cells that circulate cerebro spinal fluid |
|
|
Supporting cells of the CNS: 4. Oligodendrocytes |
•Produces Myelin Sheath |
|
|
Supporting Cells of PNS: 1. Satellite cells |
•Organize somas inside the ganglion •Regulate nutrient and waste exchange between the neurons in the ganglion and the interstitial fluid |
|
|
Supporting Cells of PNS: 2. Neurolemmocytes/Schwann cells |
•Produce Myelin Sheath •Repair damaged axons |
|
|
What is the myelin sheath? |
•Segmented structures that surround some axons. •Provides insulations/Prevents signal from leaking •Increase conduction speed by facilitating the jumping of electric signal from node to node •This method of conduction reduces the ATP requirements |
|
|
Neuron organization |
•There are 20 billion interneurons •Organized in neuronal pools: Groups of neuron specific to a function •Pools communicate through circuits |
|
|
Glossary: Synapse |
Junction where a neuron stimulates/ inhabits another |
|
|
Glossary: Proprioception |
Sensing ones own body/ knowing where you are in space |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
•Rest & digest |
|
|
Sympathetic |
•Fight or flight |
|
|
Circuit arrangements: Divergence |
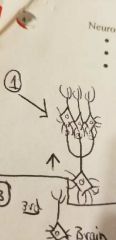
•Amplification •one neuron > many |
|
|
Circuit arrangements: Convergence |
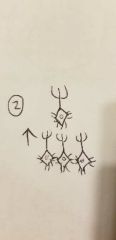
•Many to one |
|
|
Circuit arrangements: Serial |
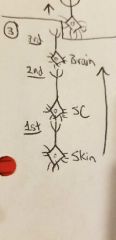
•In sequence (1st, 2nd, 3rd) |
|
|
Circuit arrangements: Parallel Processing |
•Simultaneous processing |
|
|
Circuit arrangements: Reverbernation |

•Stimulates the same process/ repeats •Positive feedback |

