![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Who is the only one who can make the business Cycle less dramatic? |
Government |
|
|
Inflationary Gap |
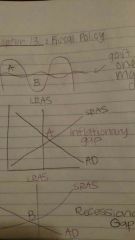
Total spending is greater than total planned spending |
|
|
Recessionary Gap |

|
|
|
Flexibility of prices |
Goes up & down until it reaches equilibrium |
|
|
The economy is driven by what? |
Total spending |
|
|
Employment Act of 1946 |
Maximize employment & maintain stable prices ; create a stable economy |
|
|
Fiscal policy |
Governments ability to tax & spend to achieve a specific Macroeconomy goal |
|
|
3 basic macro goals |
1. Inflation 2. Employment 3. Economic Growth |
|
|
Discretionary |
Deliberate act on the part of government |
|
|
Expansionary |
Reduce taxes & increase government spending Recessionary Gap |
|
|
Contractionary |
Taking actions to shrink the economy; Raising taxes or reduce government spending Inflationary Gap |
|
|
Stagflation |
Prices & unemployment is high at the same time |
|
|
Laisser Faire |
Leave it alone |
|
|
Richardian equivalence theorem |
Government cuts taxes, but they may not achieve their goal because people act with the opposite effect Proposition that an increase in government budget deficit has no effect on aggregate demand |
|
|
Where does the money from loans come from? |
From consumers when they save |
|
|
Who has higher MPS? |
Wealthy people |
|
|
Crowding-out |
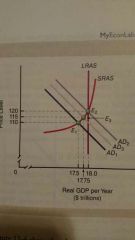
Tendency of expansionary fiscal policy. Causes a decrease in planned investment or planned consumption in the private sector. Decrease normally results from a rise in interest rates |
|
|
Inverse relationship |
Disposable income & tax rate |
|
|
Disposable income |
Personal income - personal income tax |
|
|
Marginal propensity to consume |
Extra % of each dollar you spend |
|
|
Supply side Economists |
Believe the best way to stimulate the economy is to reduce taxes, which increases aggregate supply & tax revenue |
|
|
Laffer Curve |

|
|
|
Tariff |
Tax on imports |
|
|
When people have an increase in income due to a decrease in taxes |
Substitution & Income Effect |
|
|
Substitution Effect |
When income increases, opportunity cost of not working is high (more vacation time) |
|
|
Income effect |
Make money you make, the more incentive you have to work |
|

|
Economy grows, but price level goes down |
|
|
Recession |
Decline in the real GDP for 6 months straight |
|
|
Lags |
1. Recognition 2. Action 3. Effectiveness |
|
|
Recognition |
When the economy falls for 6 months, causing a recession |
|
|
Action |
Tax cuts & spending agreements made by the government |
|
|
Effectiveness |
How long it takes for consumers to use their tax rebate |
|
|
automatic stabilizers meaning |
Fiscal policy tools that don't have to go through lags |
|
|
Automatic stabilizers |
Progressive Unemployment benefits |
|
|
Progressive |
Tax income increases due to a raise in income |
|
|
Unemployment benefits |
Ability to spend in an economy even with no job |
|
|
Recessions cause; |
An increase in government spending |
|
|
Deficit |
Government spending> government revenues during a given period of time |
|
|
Balanced budget |
Government spending= tax revenue |
|
|
Surplus |
Government spending is less than tax revenue |
|
|
Budget deficit |
Cumulative of government debt |
|
|
Budget |
How much the government has to spend |
|
|
Where does government revenue come from? |
Taxes |
|
|
Stock |
Debt, how much you owe at a particular time |
|
|
Flow |
Time between each pay period |
|
|
How to get out of a deficit |
Selling Treasury notes & bills Selling US saving bonds |
|
|
Gross Public Debt |
All cumulative debt of the federal government |
|
|
Net public debt |
Gross debt - interagency borrowing |
|
|
Fastest growing part of the budget |
Medicaid |
|
|
Twin deficits |
Trade & budget deficits happen together |
|
|
Proposals to deal with government debt |
1. Increase everyone taxes 2. Tax the rich 3. Reduce spending |
|
|
Barter |
Direct exchange of goods & services for other goods without the use of money |
|
|
1861 |
Money became |
|
|
3 functions money serves.. |
medium of exchange store of value unit of account |
|
|
What gives money value? |
1. Decree 2. Money is scarce 3. Acceptable 4. Liquidity 5. Predictable Value |
|
|
What is the most liquid of all your assets? |
Money |
|
|
Liquidity |
Asset into a medium of exchange |
|
|
Measure Money |
M1 & M2 |
|
|
M1 |
Most liquid Money you have in your checking account Demand deposit Traveler's checks |
|
|
M2 |
All of M1 + savings account + small time deposits + money mutual fund |
|
|
Businesses operate on ; |
Credit |
|
|
Central Bank |
Agency that supplies the country with money ; banker's bank |
|
|
Federal Reserve (FED) |
1913; America's central bank |
|
|
Federal Reserve Districts |
Have 12 in the US Quasi-Private Institutions We are district 11 |
|
|
Role of Federal Reserve |
1. Provides economy with money 2. Keep an eye on the banks (supervise) 3. Responsible for monetary policy |
|
|
Provides the economy with money |
Determined by the board 7 members Appointed by the president , approved by Congress Serve 1, 14 year term Chair is appointed |
|
|
Monetary Policy |
Use of money to maintain stable price levels |
|
|
FOMC |
Responsible for monetary policy 7 permanent members 5 rotating members |
|
|
Required Reserve |
(20%) how much deposit that must be kept in the bank |
|
|
Multiplier |
1÷ rr |

