![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell Division |
The reproduction of cells. "Every cell from a cell". |
|
|
Cell Cycle |
The life of a cell from the time it is formed during division of a parent cell until it's own division into two daughter cells. |
|
|
Genome |
A cell's endowment of DNA, its genetic information. |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Structures that DNA molecules are packaged into to make the replication and distributions of the large amount of DNA possible. |
|
|
Chromatin |
The entire complex of DNA and protiens that is the building material of chromosomes. It varies in its degree of condensation during the process of cell division. |
|
|
Somatic Cells |
All body cells except the reproductive cells. |
|
|
Gametes |
Reproductive cells. Sperm and eggs. |
|
|
Sister Chromatids |
A duplicated chromosome that are joined copies of the original chromosome. |
|
|
Sister Chromatid Cohesion |
Where two Chromatids, each containing an identical DNA molecule, are initially attached all along their lenghts by protien complexes called cohesions. |
|
|
Centromere |
A region of the chromosomal DNA where the Chromatid is attached most closely to its sister Chromatid. The attachment is mediated by protiens bound to the centromeric DNA. |
|
|
Arm |
The portion of a Chromatid to either side of the centromere. |
|
|
Mitosis |
The division of the genetic material in the nucleus in somatic cells. One cell becomes two, each the genetic equivalent of the parent cell. |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
The division of the cytoplasm immediately following Mitosis. |
|
|
Mitotic (M) Phase |
The shortest part of the cell cycle that includes both mitosis and cytokinesis. |
|
|
Interphase |
This phase accounts for 90% of the cell cycle that can be separated into 3 subphases in which the cell performs intense growth and metabolic activity. |
|
|
G1 Phase |
A subphase of Interphase where a cell grows. |
|
|
S Phase |
A subphase of Interphase where the cell continues to grow as it copies its chromosomes. |
|
|
Mitosis Phases |
Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
G2 |
Subphase of Interphase where Cell grows more as it as it completes preparations for cell division. A nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus Two centrosomes have formed by duplication of a single centrosome. Chromosomes duplicated during S phase cannot be seen individually because they have not yet condensed. |
|
|
Mitotic Spindle |
Consisting of fibers made of microtubules and associated protiens it begins to form in the cytoplasm during prophase. |
|
|
Centrosome |
Regions in animal cells that organize the microtubules of the spindle. Contains two centrioles. |
|
|
G2 of Interphase |
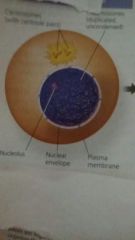
|
|
|
Prophase |

|

