![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Catastrophism |
Believed that earths varied landscape developed from catastrophies |
|
|
Uniformitarianism |
Believed that physical, chemical and biological laws today operated in the geological past |
|
|
Types of dating: |
Relative dating and Absolute dating |
|
|
Relative Dating |
Related to one another; principle of original horizontality- NO AGE |
|
|
Law of Superposition: |
Younger rock is on top of older rock |
|
|
Cross Cutting Relationship |
Geological features that cut across rocks must form after the rocks they cut through |
|
|
Inclusions: |
Fragments of one rock unit have been enclosed with another |
|
|
Unconformities: |
Denotes erosion and/or non-deposition |
|
|
What are Three types of Unconformities? |
Disconformity, Non-conformity and Angular Unconformity |
|
|
Nonconformity |
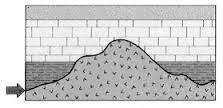
Younger sedimentary strata over-lie older metamorphic or intrusive igneous rocks. (non-disposition and erosion) |
|
|
Disconformities: |
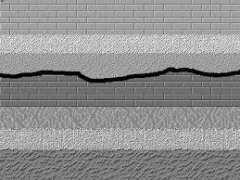
Represents a long period of time during which deposition ceased and erosion removed previously formed rocks and then deposition resumed. |
|
|
Angular unconformity: |
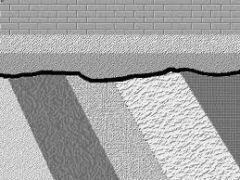
Tilted or folded sedimentary rocks that are overlain by younger, more flat lying strata |
|
|
Law of Fossil Succession: |
The kinds of animals and plants found as fossils change through time. When we find the same kinds of fossils in rocks from different places, we know that the rocks are the same age. |
|
|
Index of Fossils: |
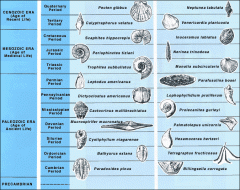
|
|
|
Absolute Dating |
Calculation of numerical dates |
|
|
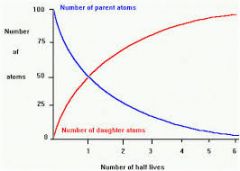
Radioactivity: |
Spontaneous breaking apart (decay) of the atomic nucleus. |
|
|
Parent/daughter products: |
The original radioactive material is called the parent; the stable product is called the daughter. |
|
|
Half-life of an isotope |
The rate of decay of the isotope |
|
|
Radioactive Decay Rates |
|

