![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Group 2 |
All of the compounds in group 2 have an Electron withdrawing atom or group that is attached to an SP3 carbon |
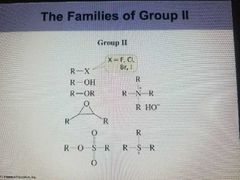
|
|
|
Substitution Reaction |
The electronegative group is replaced by another group. |

|
|
|
Elimination Reaction |
The electro negative group is eliminated along with a hydrogen |

|
|
|
Alkyl Halides |
Have relatively good leaving groups.
|

|
|
|
Substitution reaction |
More precisely called a nucleopholic substitution reaction because the Atom replacing the halogen is a nucleophile. |
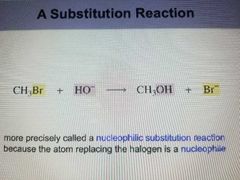
|
|
|
Rate Law |
Tells us what molecules are involved in the transition state of the rate limiting step. |
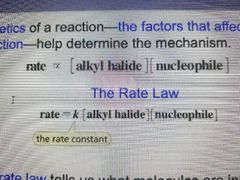
|
|
|
Inverted Configuration |
If the halogen is bonded to an asymmetric center, the product will have the inverted configuration. |
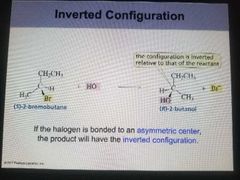
|
|
|
SN2 Reaction Mechanism |
1. Both the alkyl halide and the nucleophile are in the transition state of the rate limiting step. 2. The relative rates are primary alky halide, secondary, then tertiary. 3. The configuration of the product is inverted compared to the configuration of the reacting Chiral alkyl halide. |

|
|
|
Base |
Shares its lone pair with a proton |
|
|
|
Nucleophile |
Shares its lone pair with an Atom other than a proton. |
|
|
|
Negatively charged atoms |
Are a stronger base and a better nucleophile then the same Atom that is neutral. |
|
|
|
Polarizeability |

the larger the atom, the more polarizable it is. |
Can move more freely toward a positive charge |
|
|
Nucleophilicity |
If they are in an aprotic polar solvent I- is still the poorest nucleophile. If they are in a protic polar solvent I- is the best nucleophile. |
|
|
|
Non polar solvent |
Hexane, benzene |

Negatively charged species cannot dissolve in polar solvents |
|
|
Protic Polar Solvents |
Have a hydrogen attacjes to an O. (Water, alcohols) |

I- is the best neucleophile |
|
|
Aprotic Polar Solvents |
Do not have a hydrogen attached to an O. They can solvate a cation(+) better than they can solvate an anion (-) |
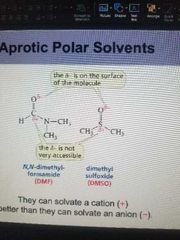
F- is the best neucleophile. |
|
|
Sovolysis |
The solvent is the nucleophile. Most SN1 reactions are sovolysis reactions. |

The leaving group departs before the nucleophile approaches. The slow step is carbocation formation. |
|
|
Product is Enantiomers |
If the halogen is bonded to an asymmetric center, the product will be a pair of enatiomers. |
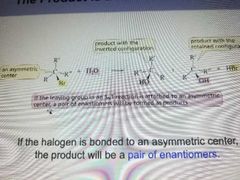
|
|
|
Partial Racemization |
Most SN1 products lead to partial racemization. Generally more inverted product is formed, because the front side is partially blocked. |

|
|
|
Mechanism of SN1 |
1. The rate of the reaction depends only on the concentration of the Alkyl halide. 2. Tertiary alkyl halides, but not primary or secondary alkyl halide undergo SN1 Reactions. 3 If the halogen is attached to an asymmetric center, the product will be a pair of enantiomers. |
|
|
|
Rate Law for Rxn of Alkyl Halide with Nucleophile |

|
|
|
|
Elimination Reaction |

A halogen is removed from one carbon and a hydrogen is removed from an adjacent carbon. A double bond is formed between the 2 carbons from which the atoms were removed. |
|
|
|
E2 Reaction |

The alkyl halide and the base are in the transition state of the rate-limiting step. |

Primary and secondary alkyl halides undergo E2 reactions. Tertiary undergo boe E2 and E1. E2 favored by a strong base and high temperatures. |
|
|
E2 is Regioselective |

The major product is the most stable alkene. The most stable alkene is generally obtained by removing a hydrogen from the Beta carbon that is bonded to the fewest hydrogens |
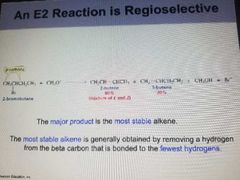
Reaction is favored by a low contentration of a weak base. |
|
|
E1 reaction |

Only the alkyl halide is in the transition state of the rate limiting step. |

|
|
|
E2 Stereoselective |
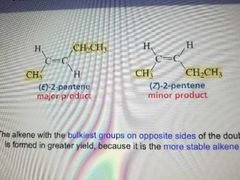
The alkene with the bulkiest groups on opposite sides of the double bond is formed in greater yield, because it is the more stable alkene |

|
|
|
Anti Elemination |
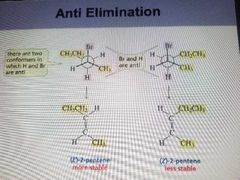
|
|

