![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the parts of a Microscope? |
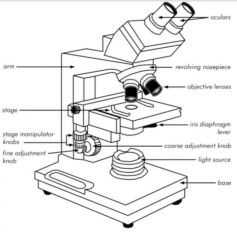
Oculars: Eye pieces
Revolving nosepiece: select lens Arm: support Stage: for holding object Stage knobs: move stage up and down Objective lens: focus on objects |
|
|
What would you see under a microscope?
|
Detailed lines... Magnified heavily objects.
|
|
|
How to measure an objects under a microscope?
|
See how many of the object will fit in the diameter.
|
|
|
Parts of the cell theory.
|
1. All living things are made of cells. |
|
|
What did the discoveries made help with regards to microscopes and cells.
|
They help to give an understanding as to how and why cells work/function.
|
|
|
SEM vs. TEM Microscopes
|
SEM: |
|
|
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
|
Pro:
Do not enclose DNA in nuclei. Eu: Enclose DNA in nuclei. |
|
|
Cell parts:
|
Mitochondria: Power
Nucleus: Control center Vacuole: Storage Cell wall: Rigid wall Cell membrane: Selectively permeable membrane Lysosome: Get rid of waste E.R.: Rough wall Ribosomes: Make proteins. |
|
|
Plant vs Animal cells.
|
Plant cells:
Have cell wall Have centrioles Chloroplasts Large vacuole Animal cells: None of first 4 Small vacuoles |
|
|
Prokaryotic cell structure:
|
Small cells, no nuclei with DNA.
|
|
|
How much weight of a cell does water account for?
|
70 percent
|
|
|
Phospholipid bilayer parts:
|
Hydrophobic tail (bottom)
Hydrophobic head (top) |
|
|
Chlosterols role in the plasma membrane:
|
Integrity and fluidity maintainence
|

