![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what organism is the olfactory bulb the most prominent structure and why? How does their brain compare to ours? |
Rats and rabbit because they rely on smell for survival Their brains are smoother and less convoluted |
|
|
How does a dolphin brain compare to a human brain? |
More convolutions |
|
|
Where are blood vessels found in the skull? |
Arachnoid layer |
|
|
What nerves regulate hormone release? |
PNS nerves |
|
|
Where would one find CSF? What is it's function? |
Found in the subarachnoid space, ventricles, and spinal cord Acts as a dumping ground for metabolites and as a cushion to absorb impact |
|
|
Why would someone have enlarged brain ventricles? |
Neurodegenerative disease or drug abuse such as alcohol |
|
|
The forebrain surrounds what CSF containing structures? |
Lateral and third ventricles |
|
|
The midbrain surrounds what CSF containing structures? |
Cerebral Aqueduct |
|
|
The hindbrain surrounds what CSF containing structures? |
Fourth ventricle |
|
|
The forebrain contains what divisions of the CNS? |
Telencephalon (Cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, and limbic system) and diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) |
|
|
The midbrain contains what divisions of the CNS? |
Mesencephalon (Tetum and Tegmentum) |
|
|
The hindbrain contains what divisions of the CNS? What is the other name for the hindbrain? |
Metencephalon (Cerebellum and Pons) and Myelencephalon (Medulla Oblongata) Hindbrain = Rhombencephalon |
|
|
What is the only CNS division not surrounding a CSF containing strucutre? |
Myelencephalon = Medulla |
|
|
What is the function of the primary cortices? |
They receive information from sensory organs or directly control movement
|
|
|
What 3 major structure can be found in the telencephalon? |
Cerebral cortex, limbic system, and basal ganglia |
|
|
What are the divisions of the cerebral cortex? |
Neocortex - Motor, Somatosensory, visual, auditory processing Limbic cortex - Cingluated gyrus |
|
|
What are the parts of the limbic system? |
Hippocampus Amygdala Mammillary bodies Fornix Septum aka septal nuclei Anterior Thalamic nuclei |
|
|
The hippocampus, mammillary bodies, and anterior thalamic nuclei work together to achieve what goal? How do they communicate? What role does the hippocampus serve that the other structures don't? |
The hippocampus, mammillary bodies, and anterior thalamic nuclei are responisible for short-term memory formation/learning. The hippocampus also makes cognitive maps. They communicate via Fornix, which takes hippocampal output to mammillary bodies then to thalamic nuclei |
|
|
Damage to the amygdala would elicit what symptoms? Thus, what is the role of the amygdala? |
Hypersexuality and docileness The amygdala is involved in emotional responses particularly negative ones |
|
|
Chronic alcoholism can inhibit short-term memory formation by damaging which limbic structure? |
Mammillary bodies! |
|
|
Compare the hippocampus of a rodent that that of a human |
Way larger |
|
|
Where are the limbic system's septal nuclei and what structures do they communicate with. |
Lie below the rostal end of the corpus callosum and communicate with the olfactory bulb (but have no relation to sense of smell), hippocampus, amygdala, and diencephalon. |
|
|
In rats, the basal ganglia has only 2 structures, whereas in humans, we have 3. What are these structure? What is the overarching function of the basal ganglia? Where is the basal ganglia? |
Striatum (Caudate nucleus and putamen) Globus pallidus These are involved in the control of movement and correction of movement. This lies just under the anterior portion of the lateral ventricles. |
|
|
Describe the connectivity of the basal ganglia |
They receive no direct input spinal input and have no direct motor output, rather they recieve extensive input from the motor regions of the cerebral cortex and extensive output to thalamic nuclei. |
|
|
Degeneration of what telencephalon structure is characteristic of parkinsons? |
Basal gangli |
|
|
The forebrains diencephalon consists of what 2 major structures? What are their primary functions? |
-Thalamus recieves sensory info and transmits it to the cortex for sensory and motor integration -Hypothalamus integrates special-typical behaviors and control of the autonomic nervous system and pituitary gland |
|
|
What substructures can be found in the thalamus? |
1) Medial geniculate 2) Lateral geniculate 3) Thalamocortical projection 4) Massa intermedia |
|
|
Where would one find the ventromedal, lateral, and paraventricular nuclei? |
Hypothalamus, in the diencephalon, part of the forebrain |
|
|
All sensory systems except _____ stop at the ______ before reaching the cortex |
Olfaction, thalamus |
|
|
The main output of the _____ is to the cortex, and the main output of the ______ is to the thalamus |
thalamus, cortex |
|
|
What substructure of the diencephalon can you be born without yet still live a healthy life? |
Massa intermedia of the thalamus which connects both lobes of the thalamus via a gray matter bridge |
|
|
What autonomic functions does the hypothalamus regulate? |
-Fighting, feeding, fleeing, fornicating -Drinking, sleeping, thermoregulation |
|
|
What is the primary function of the 2 geniculate nuclei? Where are they found? What is the name of the 2 nuclei and their specific functions? |
They recieve sensory information and transmit it to primary cortices. They are found in the thalamus. The lateral geniculate receives visual info and project to the primary visual cortex. The medial geniculate receives auditory information and transmits it to the primary auditory cortex. |
|
|
The midbrain is also called the ________ and consists of the ______ and _______ |
mesencephalon, tectum, and tegmentum |
|
|
What structure do we find in the dorsal portion of the midbrain? What structure is ventral to this? |
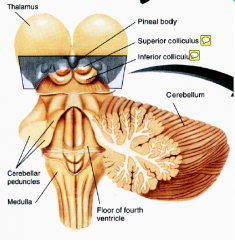
Tectum is dorsal, tegmentum is vental |
|
|
What is the function of the superior and inferior colliculi? Where are they found? |
The superior colliculi process visual information whereas the inferior process auditory information. The superior is directly above the inferior and both are in the dorsal part portion of the midbrain. |
|
|
What are the 3 most important structures of the mesencephalon's tegmentum? What are their functions? |
Substantia Nigra- projects to striatum an is involved in movement Rostral end of the reticular formation- Involved in directed attention, motor control, and sleep Periaqueductal gray matter- Controls species-typical movements such as fighting and mating |
|
|
Degeneration of what projection pathway is characteristic of parkinsons? |
Nigro-striatal pathway which connects substantia nigra to striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) |
|
|
Motor control, directed attention, sleep, and arousal are all found together in what division of the CNS? What ventricle do they surround? |
This is all found in the metencephalon surrounding the 4th ventricle |
|
|
In what metencephalon substructure would we find the structure responsible for directed attention, motor control, and sleep? |
We find the reticular formation in the pons. |
|
|
What hindbrain structure controls sleep and arousal? How does this structure communicate with the other major metencephalon structure? |
Pons, which communicate with the cerebllum via 3 dorsal cerebellar peduncles |
|
|
I integrade individual muscle movement in order to modify motor outflow for coordinated movement and motor learning. What am I? |
Cerebellum |
|
|
What hindbrain division has only 1 structure? What is this structure and what is it's function? |
Myelencephalon |
|
|
Damage to what structure would result in jerky, poorly coordinated, and exhaggerated movement? |
Cerebellum |
|
|
The medulla contains within it a structure that spans the forebrain's diencephalon, the midbrain's mesencephalon, and the hindbrain's myelencephalon and metencephalon. What is that structure and what is its function? |
Reticular formation who is responsible for directed attention, motor control, and sleep |
|
|
What do the nuclei of the medulla regulate? |
Vital autonomic muscle functions such are the cardiovascular system, breathing, and skeletal muscle tone |
|
|
What CNS division and structure is the only one continuous with the spinal cord? |
Myelencephalon |
|
|
What do you call a peripheral nerve attached to the spinal cord? |
Spinal nerve. |
|
|
Where do we find the cell bodies of afferent sensory neurons? |
Dorsal root ganglion |
|
|
How many vertebrae are in the spinal cord? What is the name of the opening in each vertebrae? |
24 vertabrae and the opening is a foramen |
|
|
Where do we find the bodies of efferent motor neurons? |
Ventral root |
|
|
How many cranial nerves and how many spinal nerves are there? Hint: 43 in total |
12 cranial 31 spinal Total 43 |
|
|
Compare and contrast a nucleus (in terms of neuroanatomy) to a ganglion |
Both are a collection of cell bodies Nucleus are in the CNS whereas ganglion are in the PNS |
|
|
Compare and contrast nerve and tract |
Both are a collection of axons Nerves are in the PNS, tracts are in the CNS |

