![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List the 9 Functions of the Skin
|
1. Protection
2. Prevents penetration 3. Perception 4. Temp Regulation 5. Identification 6. Communication 7. Wound Repair 8. Absorption/Excretion |
|
|
What layer is the epidermis and what does it entail?
|
The thin, outermost layer
-the stratum corneum (outermost or horny cell layer) -stratum germinativum (inner or basal cell layer that contains keratin and melatonin |
|
|
What is the Dermis and what layer is it?
|
Dense connective tissue layer forming the middle bulk of the skin. Also contains the nerves that innervate the skin.
|
|
|
What is in the subcutaneous layer and where does it occur?
|
Inner most layer
Chiefly composed of adipose (fatty connective) tissue |
|
|
What determines the difference in skin color?
|
We all have the same number of melanocytes but the concentration of melatonin, keratin and the blood vessels that lie under the skin.
|
|
|
What is produced from Eccrine Sweat glands?
|
Dilute saline solution. Matures by the age of 2 months.
|
|
|
What is produces from Apocrine glands?
|
Sweat glands in the axila, hair, sticky solution. Active during puberty. Arises from sexual or emotional excitement. Musty Body odor.
|
|
|
What are Sebaceous glands?
|
Produce Sebum
|
|
|
What is most important to do when looking at the subjective history during the skin examination?
|
If any questions asked are answered yes then you must do PQRSTU.
|
|
|
Give some examples of Subjective Data for a skin exam
|
-Previous History of Skin Disease.
-Changes in pigmentation -Change in mole (color or size) -Excessive dryness or moisture -Pruritus (itching) -Excessive Bruising -Rash and lesions -Medications -Hair loss -Change in nails -Self care behaviors (sunscreen) -Environment or occupational hazards |
|
|
What are some considerations for objective data during a skin exam?
|
-Need proper equipment.
-Color -Moisture -Temp -Texture -Mobility and Turgor -Any lesions |
|
|
What is pallor and when can it occur?
|
Pallor is a washing out of the skin.
-can occur because of anemia, stress, fear, or if the exam room is too cool. -Raynaud's disorder-areas of pallor and others w/erythema (can be a rheumatological disorder) |
|
|
What is erythema and when does it occur?
|
Temporary reddening of the skin.
-can occur from embarrasment, over heating, exercise, or localized infection. |
|
|
What are some considerations for objective data during a skin exam?
|
-Need proper equipment.
-Color -Moisture -Temp -Texture -Mobility and Turgor -Any lesions |
|
|
What is Cyanosis and when does it occur?
|
When the skin turns a Blue color.
-can occur because of an decrease in O2 -poor vascular condition -shock or heart failure -chronic lung disease |
|
|
What are Mongolian Spots and which population(s) are more susceptible to them?
|
Hyperpigmentation
-Bluish, black, usually on the buttocks and usually fades away after 1st year. -Occurs primarily in Black, Mexican and Asian populations -Only 9% occur in White |
|
|
What Jaundice and when can it occur?
|
Yellow undertone of the skin
-Rise of bilirubin in the blood -Can occur from Hep, Sickle Cell, cirosis of the liver. Pancreatic cancer -Can be seen in the eyes or on the hard and soft palate of the mouth. |
|
|
What skin conditions are common in older adults?
|
-Senile Purpura- bleeding under the skin (dark spots)
-Dry Skin (xerosis) -Senile lentigines- liver spots from sun exposure and are not cancerous. |
|
|
Describe some moisture abnormalities in the skin
|
Diaphoresis: profuse sweating. May be MI or excessive sweating
-Panic attacks may cause clamminess -Dehydration- look at oral mucous membranes |
|
|
What skin disorder is a sign of pre-diabetes?
|
Hyper pigmentation around the neck.
|
|
|
What skin conditions are common in older adults?
|
-Senile Purpura- bleeding under the skin (dark spots)
-Dry Skin (xerosis) -Senile lentigines- liver spots from sun exposure and are not cancerous. |
|
|
Describe some moisture abnormalities in the skin
|
Diaphoresis: profuse sweating. May be MI or excessive sweating
-Panic attacks may cause clamminess -Dehydration- look at oral mucous membranes |
|
|
List some general observations when examining skin lesions
|
-Distribution, configuration, Morphology
-universally spread? -symmetrical? -localized? -color -sharpness (well or ill-defined) -surface contour (dome-like) -geometric shape |
|
|
Describe a Macule and give examples
|
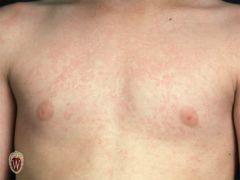
Circumscribed, flat,Non-palpable, change in skin color.
-up to 1 cm exs. Freckles -fat nevi (little red spots) -measles (flat rash) -petechiae -scarlet fever |
|
|
Describe a patch and give some examples
|
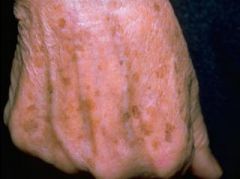
-A macule larger than 1cm
-Senile lentigo (liver spots) -Mongolian spot -vitiligo -cafe au lait -spot -measles rash |
|
|
What is a Papule and what are some examples?
|
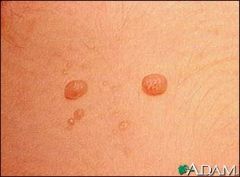
-A palpable, elevated, circumscribe, solid mass
-caused by superficial thickening in the epidermis -up to 0.5cm -Ex. Elevated nevus (mole), lichen planus, wart, molluscum |
|
|
What is a Plaque lesion?
What are some examples? |
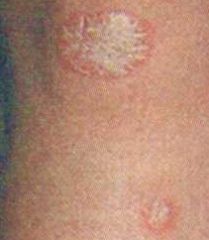
-A flat, elevated surface
-Larger than 0.5cm -Often formed by coalescence of papules -Ex. Psoriasis, lichen planus, xanthoma, xanthelasma |
|
|
What is a nodule? Give an example
|
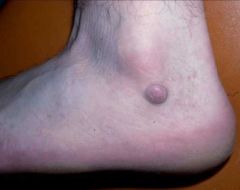
-A solid, elevated, firm or solft mass less than 1-2 cm
-May be firmer and extend deeper into dermis than papule -Ex. Fibroma intradermal nevi |
|
|
What is a tumor and what are its characteristics?
|
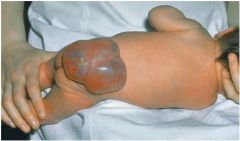
-A solid elevated firm or soft mass larger than 1-2 cms
-Extending deeper into dermis -Benign or malignant -Lipoma, hemangioma |
|
|
What type of lesion is known as a WHEAL?
Exs? |
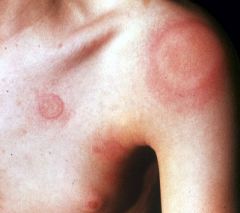
-A superficial, raised, erythemotaous, TRANSIENT lesion with irregular borders due to localized edema
-Fluid is held diffusely in the tissues -Ex. Mosquito bite, allergic reaction -can be a drug reaction |
|
|
What is the lesion know as URTICARIA? What is an example
|
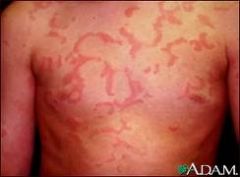
-Wheals that have coalesced to form and extensive rash.
-can be from scratching -caused by intrinsic pruritic (itching) ex. Hives |
|
|
What is a vesicle? Give some examples
|
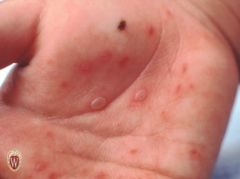
A circumscribed, superfical, elevated CAVITY
-contains free fluid -Clear fluid flows if wall ruptured -Up to 1 com in size -Ex. Herpes simplex, chicken pox, contact dermatitis. |
|
|
What is a Bullae? Give some examples
|
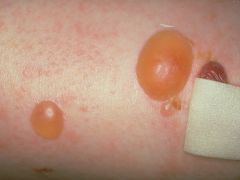
-A larger vesicle
-Usually single chambered -Superficial in epidermis -Thin walled so ruptures easily -Larger than 1cm -ex. Friction blister, pemphigus, burns, contact dermatitis |
|
|
What is a Cyst?
|
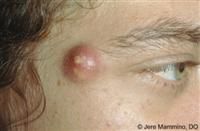
-An encapsulated fluid or pus-filled cavity in dermis or subcutaneous layer
-Tensely elevating the skin -Larger than 1cm Ex, Sebaceous cyst |
|
|
What are pustules?
|
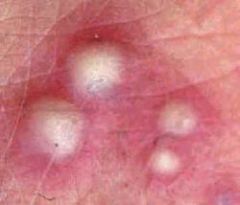
-A circumscribed, superficial, elevated cavity
-Contains turbid fluid (pus) -Up to 1 cm Ex. Impetigo, acne |
|
|
What is a crust?
|
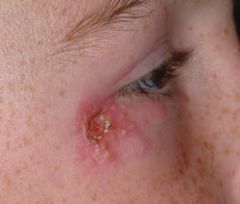
-Thickened, dried residue of burst vesicles, pustutles or blood
-can be red-brown, honey-colored, or yellow depending of the fluid's origin -exs. excema, impetgo, crust phase of herpes simplex |
|
|
What is scaling of tinea pedis?
|
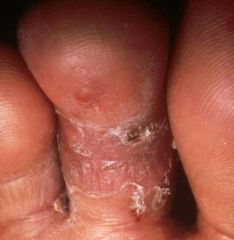
-Tinea: is the fungus that causes this type of scaling
-Athletes's foot -compact desiccated flakes of skin -Dry or greasy -Silvery or white -from shedding of dead excess keratin cells -visible exfoliation of the dermis |
|
|
What are fissures?
|
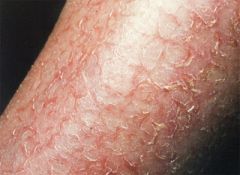
-A linear crack with adrupt edges
-Extends into the dermis -Can be dry or moist -ex. cheilosis, athlete's foot, anal fissure, renal failure |
|
|
What is erosion? Give some examples
|
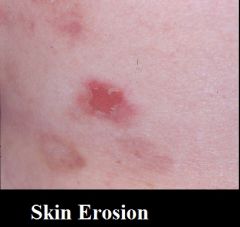
-A superficial circumscribed loss of epidermis
-Leaves a scopped-out but shallow depression -Moist but no bleeding -Heals without a scar because does not extend into the dermis -Ex, stage 2 pressure sore |
|
|
What is an Ulcer? Give some examples
|
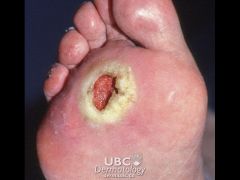
-A circumscribed depression extending into the dermis
-Irregular shape -May bleed -Leaves a scar when it heals -Ex stasis ulcer, pressure sore, chancre |
|
|
What is excoriation? What are some examples?
|
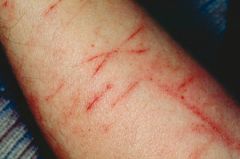
-A scratch mark
-Superficial -Can be self-inflicted abrasion secondary to intense itching -Ex. Scratch from foreign body, insects bites, scabies, dermatitis, varicella |
|
|
What is a scar?
|
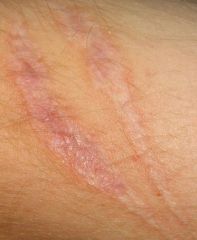
-After open reduction of fracture
-Replacement of destroyed normal skin tissue by fibrous connective tissue -A permanent change |
|
|
What is skin atrophy?
|
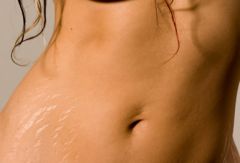
-Depressed skin level resulting from loss of tissue
-a thinning of the epidermis with loss of normal skin furrows, resulting in shiny, translucent skin -ex. Striae, senile skin, arterial insufficency |
|
|
What is Lichenification? What are some examples?
|
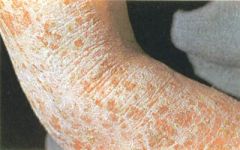
-Thickening and roughening of the skin usually as a result of intense scratching
-Results from a tightly packed set of papules -Causes increases visibility of the superficial skin markings -Ex long standing eczema, atopic dermatitis |
|
|
What is a keloid scar?
|
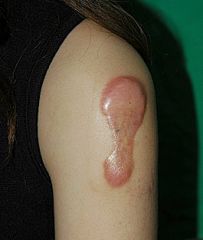
-Hypertrophic scar
-The resulting skin level is elevated by excess scar tissue, which is invasive beyond the site of the original injury |
|
|
What is meant by annular configurations?
|
the lesion occurs in circular pattern
|
|
|
What are confluent lesions?
|
Lesions that run together
|
|
|
What is a discrete lesion?
|
A lesions that is individual
|
|
|
What are grouped lesions?
|
Ones that are grouped in a particular place ie contact dermatitis
|
|
|
What is a target configuration of a lesion?
|
Described as an iris ex. lime disease.
|
|
|
What is the gyrate shape of a lesion?
|
The lesion looks twisted or snake like. ie scabies
|
|
|
What is a linear configuration?
|
striped lesions ie scratches
|
|
|
What are polycyclic lesions?
|
Annular lesions that grow together
|
|
|
What are zosteriform lesions?
|
linear along a nerve route. Ex. Herpes Zoster
|
|
|
What the the vascular lesions?
|
-Petechiae
-Purpura -Ecchymosis -Cherry Angioma -Spider Angioma -Telangiectasia -Nevus Flammeus-Port wine stain |
|
|
Describe Petechiae
|
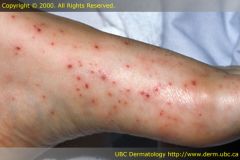
-Color-red
-Pin sized macules of blood in the skin |
|
|
Describe a Purpura
|
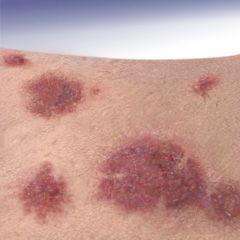
-A large macule or papule of blood in the skin
-Such blood-filled lesions do not blanch |
|
|
What is Ecchymosis?
|

-Larger extravasations of blood into the skin.
-bruises |
|
|
What are Cherry Angiomas?
|
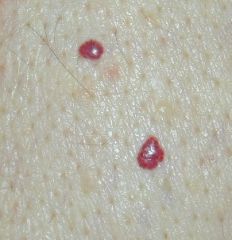
-aka Campbell de Morgan spots
-small bright red papules and of no consequence -Benign angiomas common on the trunks of the middle-aged and elderly |
|
|
What are spider Angioma?
|
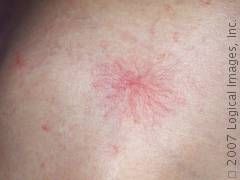
-Satellite telangiectases that look like spiders with legs radiated from a central, often palpable feeding vessel
-if diagnosis in doubt, press the center with slide and lesion will disappear -If many on trunk check liver function. May be normal in faces of children or erupt in pregnancy |
|
|
Telangiectasia?
|
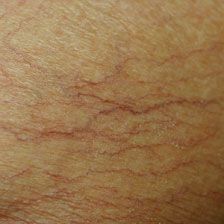
-Term refers to permanently dilated and visible vessels in the skin
-They can appear as linear, punctate stellate crimson-purple markings Can be caused by nifedipine |
|
|
What is Nevus Flammeus?
|
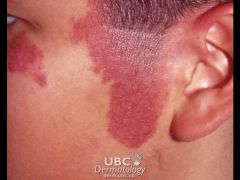
-Present at birth
-Caused by dilated dermal capillaries pale, pink to purple macules -Mostly on face and trunk |
|
|
What are the Skin Cancer Warning signs?
|
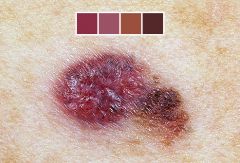
-Asymmetry in shape: one half unlike the other half
-Border is irregular: edges are irregularly scalloped -Color is mottled- haphazard display of color; shades of brown, black, gray, red and white -Diameter is unusually large: greater than the tip of a pencil eraser (6mm) -Elevations is almost always present: surface distortion is assessed by side-lighting. Melanoma in situ may be flat Enlargement: history of an increase in the size of lesion is perhaps one of the most important signs of malignant melanoma |
|
|
What is the most common skin cancer?
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
Describe Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
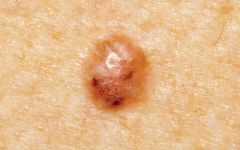
-Locally invasive and destructive
-Slow growing rarely metastasized -Almost translucent, dome-shaped papule with overlying telangiectasias |
|
|
What are actinic keratosis of the Scalp?
|
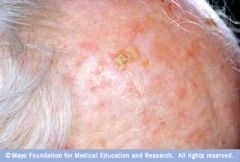
Keratotic lesions with malignant potential
|
|
|
Describe Squamous cell Carcinoma
|
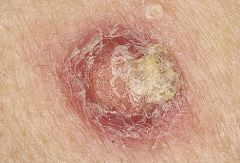
-Invasive malignancy
-Commonly found on the head, neck or hands -May arise from actinic keratosis or de novo |
|
|
What is malignant melanoma?
|
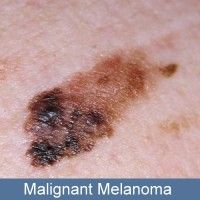
-The most serious of skin cancers
-whenever it is very black or raised |
|
|
What are the 2 types of hair?
|
Vellis hair: the thin hair that is all over the body
Terminal hair: hair on the scalp, eyebrows, axila, pubic or chest |
|
|
Why does hair turn white?
|
-Melanin in shaft gets replaced by colorless hair bubbles
|
|
|
What is Alopecia Areata?
|
-Non scarring hair loss, typically of rapid onset in a sharply defined, usually round or oval area
-The loss may be diffuse or patchy or band-like at the margins of the scalp -Most likely immunological phenomenon |
|
|
Hirsutism?
|
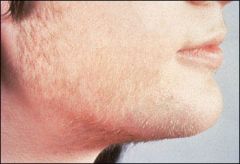
-More hair in areas that are not normal
-May be normal for heritage or certain diseases polycystic ovarian syndrome=more hair |
|
|
What is nail clubbing?
|
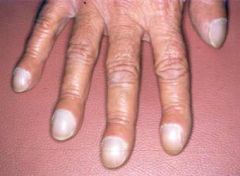
Flattening of the nail at the bed
-can be a sign of cancer of the lungs or lung disease |
|
|
What is capillary refill?
|
-Color should return to the nail between 1-3 seconds
|
|
|
What is impetigo?
|
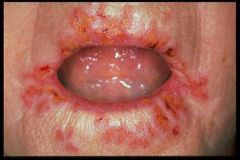
It is a staph or strep infection
|
|
|
What is paronychia?
|
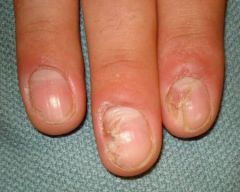
-Acute bacterial infection of the proximal and lateral nail fold
-Rapid onset of pain and swelling -Pus accumulates behind the cuticle -Chronic irritant exposure |
|
|
Name the structures of the nail
|
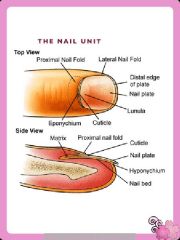
-Nail plate: actual nail
-Lanula: crest shaped half moon -Lateral nail fold -Nail matrix: where nail grows from -Posterior nail fold -Nail Bed |
|
|
What is pitting?
|
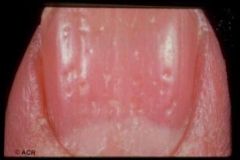
Pits in the nail
|

