![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
|
|
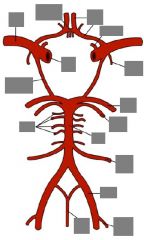
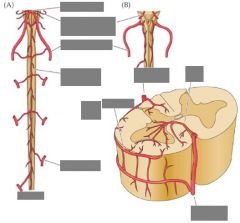
= name? |
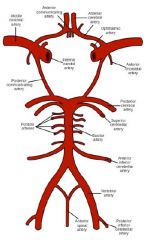
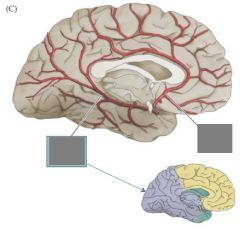
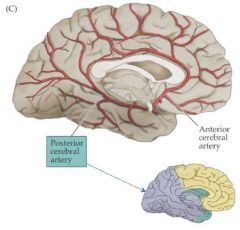
Circle of Willis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
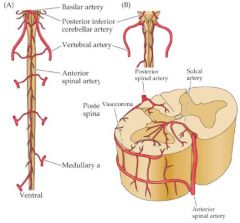
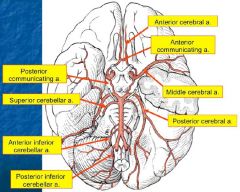
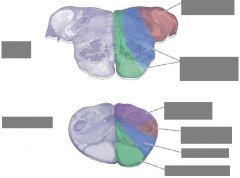
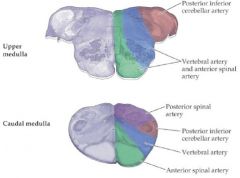
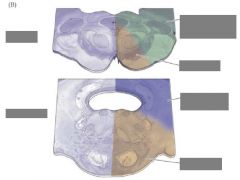
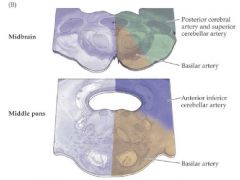
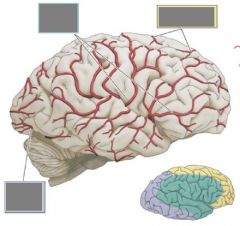
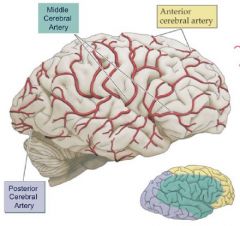
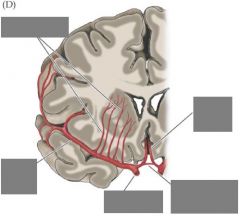
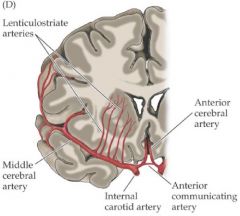
Supply of the pons? |
AICA = Anterior inferior cerebellar artery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
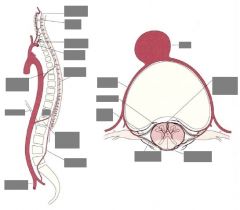
Watershed |
Areas of the brain in between vessel distributions that are particularly vulnerable to damage by low BP. |
|
|
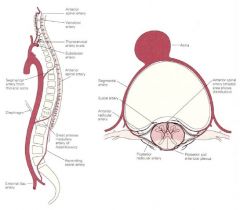
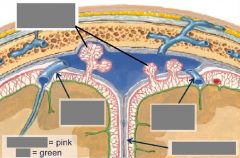
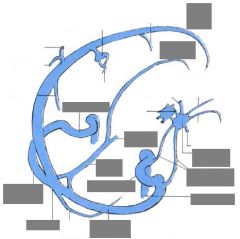
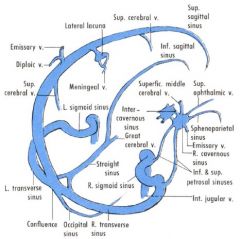
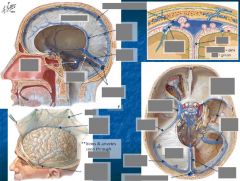
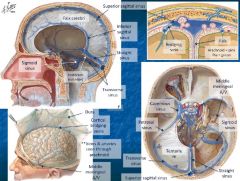
Meningeal vessels |
Meningeal a. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gray vs. white matter BF |
Gray > white matter (~2x) |
|
|
Minimum BF |
15 mL/100 g > stroke/cerebrovascular accident |
|
|
Regulation of cerebral BF |
Autoregulation (vessel capacitance) Chemical (CO2, metabolic coupling) Neuronal control (sympathetic & sesory, fx unclear) Blood viscosity (BF & O2 coupling; affected by hematocrit, RBC flexibility, plasma protein, etc.) |
|
|
Pericytes location |
Capillaries -> constriction |
|
|
Cerebral vessels' innervation |
Sympathetic, Parasympathetic Sensory - release vasoactive substances (headache); @ arteries & capillaries: - raphe nuclei -> serotonin - locus ceruleus -> norE - nucleus basalis -> ACh |
|
|
CBF Autoregulation |
Myogenic reflex (BF constant b/w 70-160 mmHg) Chronic HTN -> limits set @ a higher lvl |
|
|
CO2 reactivity in BF |
↑ CO2 -> vasodilation, evv. Probably pH-mediated pCO2 related to intracranial BV |
|
|
Cushing response |
Elevation of MAP as a response to increased CBP |
|
|
CBF regulation due to neural activity |
Via adenosine, A, prostaglandins, Glu, NO, etc. (fMRI) |
|
|
BBB |
Selective regulation of substances in/out of brain Maintains homeostasis & constant intracranial V Endothelium - tight jxns, mitochondria, few pinocytic vesicles - induced by astrocytic foot processes - presence of CNS vesicular enzyme systems |
|
|
Crossing the BBB |
Passive - lipid solubility, size, serum protein binding, polarity H2O - simple diffusion based on osmolarity Facilitated transport - metabolic substrates Ion transport - E-dependent & co-transport (tight regulation) |
|
|
Areas lacking the BBB |
Subfornical organ - osmolarity detection & regulation Area postrema - detection of blood substances, autonomic responses & vomiting Median eminence - release of hormone inhibiting & releasing factors -> AP Delienation: tanycytes prevent diffusion |
|
|
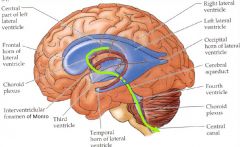
Choroid plexus |
- Located in the ventricles - Capillaries are normal; produce CSF outside of ventricles, behind - - Epithelium lining of choroid plexus has a barrier (blood/CSF) - No barrier b/w CSF & brain! |
|
|
CSF vs. blood concentrations |
CSF / blood: Protein (mg/dL): 35 / 7000 Glucose (mg/dL): 60 / 90 Na(mEq/L): 138 / 138 K (mEq/L): 2.8 / 4.5 Ca(mEq/L): 2.1 / 4.8 Mg(mEq/L): 0.3 / 1.7 |
|
|
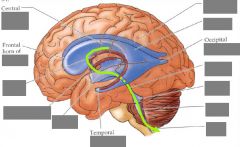
CSF -> subarachnoid space? |
Caudal end of cerebellum: 4th ventricle -> via foramina of Luschka & Magendie |
|
|
|
|
|
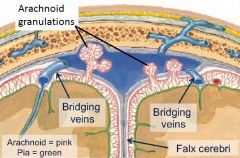
Arachnoid granulations |
- Portions of arachnoid mater that mushroom into sinuses, where they are surrounded by venous blood - site of CSF resorption into blood, via bulk transport (temporary openings) ->> IJV |
|
|
Bypassing BBB |
- Taking advantage of pathological disruption (penicillin in meningitis; cancerous angiogenesis) - Intra-arterial osmotic agents -> temporarily disrupt BBB by vasoactive substances (mannitol, adenosine, leukotrienes, radiation, ultrasound) - Direct administration into CSF (lumbar puncture, ventricular catheters) |

