![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What arteries supply the cerebral hemispheres and deep cerebral structures with blood? |
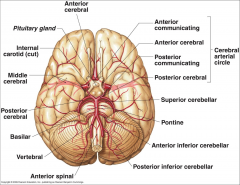
- Internal Carotid A.
- Vertebral A. |
|
|
How are the internal carotid and vertebral arteries connected?
|
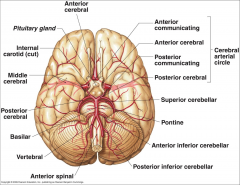
Cerebral Arterial Circle (of Willis)
|
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Internal Carotid A?
|
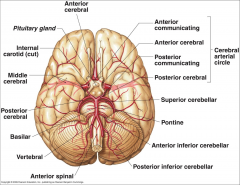
- Middle Cerebral A.
- Anterior Cerebral A. |
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Internal Carotid A?
|
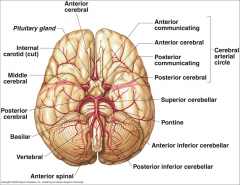
- Posterior Communicating A.
- Anterior Choroidal A. - Basal Ganglia, Diencephalon, Limbic system, optic tract - Ophthalmic - orbit and optic n. |
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Anterior Cerebral A.?
|
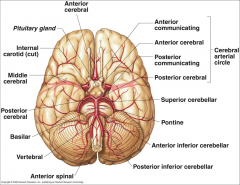
- Cortical branches to medial aspect of frontal and parietal lobes
- Arteries to corpus callosum (callosomarginal a. and pericallosal a.) |
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Anterior Cerebral A.
|
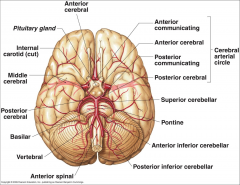
Medial Striate A. / Recurrent A. of Huebner
|
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Middle Cerebral A.
|
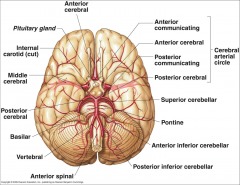
Cortical branches to frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
|
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Middle Cerebral A.
|
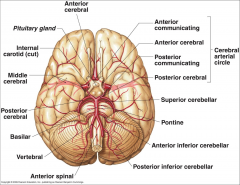
Lenticulostriate arteries - basal ganglia and internal capsule
|
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Vertebral A.?
|
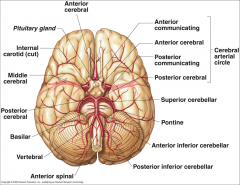
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar A. (PICA) - inferior surface of cerebellum, lateral part of rostral medulla, and choroid plexus of 4th ventricle
Posterior Spinal Aa. - supplies posterior 1/3 of cervical spinal cord and posterior part of caudal medulla |
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Vertebral A.?
|
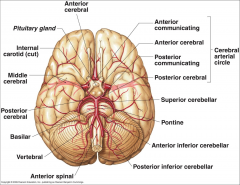
Anterior Spinal A. - runs along anterior median fissure and supplies anterior 2/3 of cervical spinal cord and anterior and medial medulla (including medullary pyramids)
|
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Basilar A.?
|
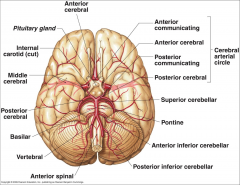
- Superior Cerebellar a. - cerebellum, lateral part of middle pons and pineal gland
- Pontine aa. (long) - pons - Anterior Inferior Cerebellar a. (AICA) - cerebellum and lateral part of caudal pons - Labyrinthine / Internal Auditory aa. - inner ear |
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Basilar A.?
|
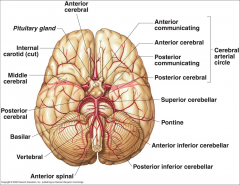
Pontine arteries (short) - pons
|
|
|
Long / Circumferential branches of Posterior Cerebral A.?
|
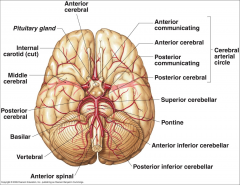
Cortical branches to occipital lobe and medial aspect of temporal lobe
|
|
|
Short / Penetrating branches of Posterior Cerebral A.?
|
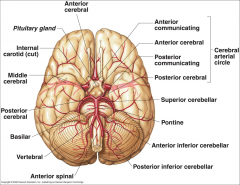
Posterior choroidal a.
Arteries to thalamus (thalamoperforating) |
|
|
Terminal branches of internal carotid artery?
|
Anterior Cerebral A. - smaller
Middle Cerebral A. - larger |
|
|
Arteries running in longitudinal fissure?
|
Anterior Cerebral aa.
|
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Behavior changes - Contralateral leg and foot weakness - Contralateral leg and foot sensory loss |
- Anterior Cerebral A.
- Behavior changes = frontal lobe - Lower limb weakness = precentral gyrus - Lower limb sensory loss = postcentral gyrus |
|
|
Which artery runs in lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure)?
|
Middle Cerebral a.
|
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Weakness and/or sensory loss of left face, hand, arm and trunk |
Right superior division of Middle Cerebral A.
|
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Weakness and/or sensory loss of right face, hand, arm and trunk - Broca's Aphasia (non-fluent speech) |
Left superior division of Middle Cerebral A.
|
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Sensory loss of left face, hand, and arm - Left hemineglect (unaware of L side of body) |
Right Inferior division of Middle Cerebral A.
|
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Sensory loss of rightface, hand, and arm - Wernicke's Aphasia (fluid speech but no comprehension of language) |
Left inferior division of Middle Cerebral A.
|
|
|
Route of Vertebral A.?
|
- Branch from subclavian aa.
- Pass through transverse foramina - Enter cranial cavity via foramen magnum |
|
|
Basilar A. bifurcates to form what?
|
2 Posterior Cerebral Aa.
|
|
|
Which arteries curve around the midbrain?
|
Posterior Cerebral Arteries
|
|
|
Posterior Cerebral Aa. supply what?
|
- Midbrain
- Medial and inferior surfaces of temporal and occipital lobes (visual areas of cerebral cortex) - Thalamus and globus pallidus (penetrating branches) |
|
|
Following symptoms fit infarction of what artery?
- Visual Field Defects (occipital lobe) - Contralateral hemiparesis or contralateral hemianesthesia if thalamus and internal capsule are affected |
Posterior Cerebral Aa.
|

