![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is active membrane transport? |
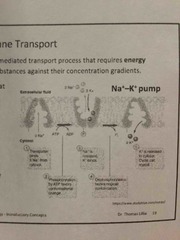
A mediated transport process that requires energy (ATP) moves substances against their concentration gradient |
|
|
|
What is the maximum rate ? |
Proceeds is limited by the ATP POWERED pumps in the plasma membrane and the amount of available ATP |
|
|
|
What is vesicular transport? |
It’s the movement of larger volumes of substances across the plasma membrane through the formation or release of vesicles Requires ATP |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of vesicular transport |
Endocytosis (in) & exocytosis (out) things in and out of cell |
|
|
|
Endocytosis are both what? |
Phagocytosis ( cell eating large solid particles & Pinocytosis (cell drinking small molecules dissolved in liquid) |
|
|
|
Does pinching off a vesicle use ATP ENERGY? |
Yes it does |
|
|
|
What’s CYTOPLASM? |
It’s inside the cell and outside the nucleus Inside plasma membrane |
|
|
|
What is cytoplasm composed of? |
Cytosol - fluid portion- dissolved molecules and colloid(proteins) in water Cytoskeleton- supports the cell but allows for movement lie changes in cell shape and mvmt of cilia Cytoplasmic inclusions- aggregates of chemicals such as lipid droplets ( not dissolved in water Organelles- other functioning cells |
|
|
|
What does nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles have in common ? |
Small specialized structures with particular functions Most have membranes that separate interior of organelles from cytoplasm Related to specific structure & function of the cell |
|
|
|
Tell me 4 things about the NUCLEUS? |
Membrane-bound Brain of cell- Centrally located Has the nucleoplasm, nucleolus, & nuclear envelope DNA-blue print for life |
|
|
|
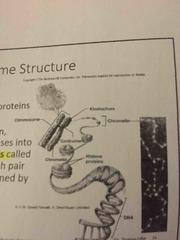
Explain Chromosome structure ... |
Chromatin- DNA complexed with proteins (histones) During cell division, chromatin condenses into pairs of chromatids called chromosomes Each pair of chromatids is joined by a centromere |
|
|
|
What does RIBOSOMES make? |
PROTEIN! Very small! strain of RNA |
|
|
|
There are 2 types of Endoplasmic Reticulum, what are they? |
Rough - has attached ribosomes & produced proteins & Smooth - NO attached ribosomes & manufactures LIPIDS & FATS |
|
|
|
Explain 2 things about Golgi Apparatus |
Modifies, Packages, & distributes proteins & lipids for lipids- sends them out of the cell - smooth Flattened membrane sacs stacked on each other |
|
|
|
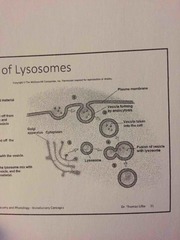
What does Lysosomes do? |
There are chemicals inside to break down substances Strong enzymes Keep substances encapsulated For digestion of substances (chemicals) Vesicle forms around material outside of cell Vesicle is pinched off from the plasma membrane & becomes a separate vesicle inside the cell Lysosome is pinched off the Golgi apparatus Lysosome fuses with the vesicle Enzymes from the lysosome mix with the material in the vesicle & the enzymes digest the material |
|
|
|
What is peroxisomes? |
Similar to Lysosome Smaller to lysosome Contain enzymes to break down fatty acids & amino acids Hydrogen peroxide (by-product of breakdown)
|
|
|
|
3 things about Mitochondria |
Make ATP INCREASE in number when cell energy requirements increase Contain DNA that codes for some of the proteins needed for mitochondria production Side note. Mitochondria is from ur mom |
|
|
|
5 things about Cilia |
Attached to the filia It’s anchored to the cell It moves things along on the cell surface In the respiratory track Hair - like projection Not mobile |
|
|
|
4 things about flagella |
Like cilia but longer -a tail Mobile Moves an entire cell - wave like fashion Normally there’s 1 per cell Eg. sperm cell is the only example of a flagella in the human body |
|
|
|
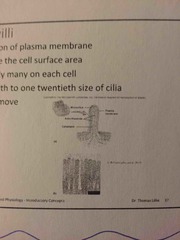
What are Microvilli? |
Extension of plasma membrane Fingerlike projection increase surface area Don’t move Ability to get stuff in & out of cell Maximizes surface area Eg. Small intestines |
|

