![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Flow-stimulated NO production |
1) shear stress causes change in glycocalyx movement 2) glycocalyx attached to cytoskeleton hence causes change in cytoskeleton 3) activation of calcium channels = high intracellular calcium |
|
|
|
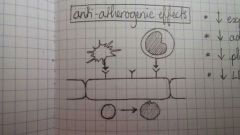
Effects of NO |
- less SMC contraction / proliferation - less vasoconstrictor production
Anti-Atherogenic Effects - less expression of adhesion molecules - less adhesion of monocytes / platelets - less platelet aggregation - less LDL oxidation |
|
|
|
Oxidative stress |
1) drop in eNOS substrate / cofactor 2) eNOS produces superoxide 3) NO + superoxide = peroxynitrite 4) peroxynitrite interacts with lipids, DNA, proteins... 5) oxidative stress |
|
|
|
Vasoconstrictor or vasodilator? (Prostanoids, EETs, angiotensin II, H2O2) |
prostanoids = vasoconstrictors EETs = vasodilators angiotensin II = vasoconstrictor H2O2 = both |
|
|
|
Normal BP and HBP |
Normal: 120/80 HBP: 140/90 |
|
|
|
Free cholesterol v cholesterol ester solubility |
Free cholesterol = amphiphilic Cholesterol ester = hydrophobic |
|
|
|
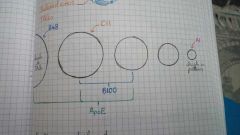
ApoA1. ApoB48. ApoB100. ApoC11. ApoE. |
ApoA1 = receptor ligand on HDL ApoB48 = receptor ligand on chylomicron ApoB100 = receptor ligand on VLDL and LDL ApoC11 = cofactor for LPL on VLDL ApoE = receptor ligand on chylomicron, VLDL and LDL |
|
|
|
What mutations can cause FH? |
Mutation in ApoB Mutation in LDL receptor Mutation in PCSK9 |
|
|
|
Resting coronary BF and BF during vigorous exercise |
Resting = 225 ml/min Exercise = 800+ ml/min |
|
|
|
Ischaemia on ECG |
ST depression on V1, V2, V3 |
|
|
|
Coronary BF equation |
Coronary BF = pressure difference/ resistance |
|
|
|
How does pericarditis cause SOB? |
1) heart is compressed 2) lower EDV 3) fluid stays backed up in lungs |
|
|
|
Pericarditis on ECG |
PR depression ST elevation |
|
|
|
Causes of viral pericarditis |
Coxsackie B HBV Influenzae Rubella Mumps |
CHIRM |
|
|
High platelet count but low Hb usually means... |
Bleeding or inflammation |
|
|
|
Difference between health selection and social selection |

|
|
|
|
Effect of vagal stimulation on coronary blood vessels |
No effect |
|
|
|
Range of cerebral autoregulation |
60 - 140 mmHg |
|
|
|
Autonomic control of blood vessel calibre |

|
|
|
|
Normal QRS |
< 0.12s |
|
|
|
Intervals and segments on ECG |

|
|
|
|
Blood vessels typically used in coronary a. bypass grafts |
Internal thoracic a. Great saphenous v. Radial a. |
|
|
|
Effects of peroxynitrite |
- less anti-oxidant effects - impairs enzyme cofactors - inhibits membrane channels - protein aggregation |
|
|
|
Effects of disturbed flow |
- less eNOS production (vasoconstriction) - inflammation - less endothelial repair - more ROS - permeability to lipoproteins - WBC adhesion - apoptosis - SMC proliferation - collagen deposition - less cytoskeletal / cellular alignment to direction of flow |
|
|
|
Percentage drop in MI risk following smoking cessation, drop in BP and reduction of HbA1c |
Quitting: 50 - 70%
BP: 2 - 3% per 1mmHg
HbA1c: 14% per 1% drop in HbA1c |
|

