![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nutrition |
Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up |
|
|
Diet |
Herbivores: mainly plants and algae (cattle sea slugs termites) Carnivores: eat other animals (sharks,hawks, and spiders) Omnivores: consumes animals, plants or algae (cockroaches crows bears humans) Most are opportunistic feeders (cattle and deer) |
|
|
3 nutritional needs |
1. Diet must provide chemical energy for cellular process (atp) 2. Organic building blocks for macromolecules (organic carbon-sugar and nitrogen protein) 3. Essential nutrients we can’t synthesize |
|
|
Essential nutrients |
Material that an animal cannot assemble from simpler organic molecules |
|
|
4 classes essential nutrients |
1. Amino acids 2. Fatty acids 3. Vitamin 4. Minerals |
|
|
Amino acids |
isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylaline, threonine, tryptophan, valine, histidine (infants) |
|
|
Fatty acids |
Linoleic, linolenic acid, omega-3 fatty acid |
|
|
Vitamins |
A B C D E K |
|
|
Minerals |
Calcium, Magnesium, sodium, iron, zinc, potassium, etc |
|
|
Proteins and amino acids |
Require amino acids to produce new proteins (retention) and replace damaged ones (maintenance) No protein storage possible Complete protein sources for all 20 amino acids: meat, milk, and poultry |
|
|
Plant protein |
Usually incomplete in amino acid vegetarians need to eat specific plant combinations to get all amino acids ie: corn lacks tryptophan and lysine Beans lack methionine |
|
|
Conditionally essential |
Not normally required in diet Must be supplied to specific populations that do not synthesize in adequate amounts ie: PKU: cannot synthesize tyrosine from phenylalanine so T becomes essential |
|
|
Essential fatty acids |
Obtained from diet Include certain unsaturated fatty acids bc humans can not synthesize fatty acid due to double binds on carbon 9 |
|
|
Polyunsaturated oils |
Contains essential fatty acids that can only be obtained through diet Linoleic and linolenic acid (needed for hormone production and plasma membrane of cells) Omega 3: olive oil or canola monosaturated |
|
|
Vitamins |
Organic molecules required in the diet in very small amounts 0.01 mg to 100 mg daily 13 vitamins are essential 2 categories: water soluble and fat soluble |
|
|
Water soluble vitamins |
B vitamins (8 subclasses)- coenzymes involved in cellular respiration Vitamin C (absorbic acid)-required for connective tissue production Excreted in urine |
|
|
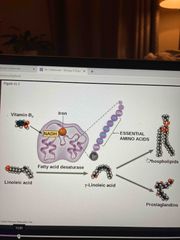
Fat soluble vitamins |
Vitamin a: retinol, visual pigment of eye Vitamin k (phylloquinine) blood clotting Vitamin d (calcitrol): calcium absorption and bone formation Vitamin e (tocopherol): antioxidant Not excreted. Deposited in body fat |
|
|
Vitamin chart |
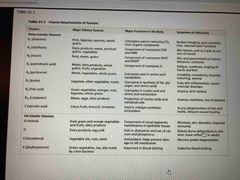
A |
|
|
Minerals |
Simple inorganic nutrients Usually required in small amounts (less than 1mg to 2500 mg daily) Cofactors built into the structures of coenzymes |
|
|
Major minerals |
Constituents of cell and body fluids, electrolytes , Structural components Ca, Mg, P, Na, S, K, Cl |
|
|
Trace minerals |
Components of larger molecules Cu, Cr, I, Fe, Mn, Se, Zn |
|
|
Sodium, potassium, chloride |
Nerve function, muscle contraction, osmotic balance btw cells and interstitial fluids |
|
|
Iodine |
Thyroid hormones Regulate metabolism rate |
|
|
Calcium and phosphorus |
Construction and maintenance of bone, ATP, phospholipids |
|
|
Magnesium, iron |
Iron: hemoglobin Mg: enzyme function |
|
|
Zinc, Cu, Mn |
Enzymes Zn-finger like proteins bind to DNA |
|
|
Minerals image |

A |
|
|
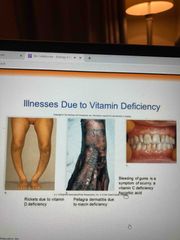
Malnutrition |
Failure to obtain adequate nutrition Negative impacts on health and survival Obesity Bulimia nervosa Anorexia nervosa |
|
|
Deficiencies in essential nutrients |

Can cause deformities, disease, and death Cattle deer and other herbivores can prevent phosphorus deficiency by consuming concentrated sources of salt or other minerals |
|
|
Protein deficiency |
Diet that is insufficient in amino acids Most common type of malnutrition in humans ie: people on rice diet may suffer vitamin a deficiency which can cause blindness (golden rice is engineered with beta carotene which converts to vitamin a) |
|
|
Undernutrition |
Results when a diet does not provide enough chemical energy Individual will: Use up stored fats and carbs Breakdown protein Lose muscle mass Suffer protein deficiency of the brain Due or suffer irreversible damage |
|
|
Food guide pyramid |
Developed in Sweden in 1974 Updated in 2005 Shaped for healthy foods |
|
|
MyPlate 2011 |

Current nutrition guide in US Sections: 30% grains 30% vegs 20% fruits 20% protein Smaller circle for dairy |
|
|
Beriberi |
Nervous system problem caused by deficiency in vitamin B1(thiamine) in diet Include lethargy, fatigue, heart muscle nervous systems affected ie: population removed outer layer of rice (which contains thiamine) and developed this disease |
|
|
Pasteurization of milk |
Scurvy in infants due to milk Heat milk to kill bacteria but destroys vitamin c |
|
|
Epidemiology |
Identify nutritional strategies for the prevention and control of disease Neural tube defects come from deficiency in folic acid (vitamin B9) in pregnant mothers |

