![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which structure is the penis attached to? What attaches the penis to this structure?
|
The right and left ischiatic tuberosities of the pelvis is attached by the right and left crura.
|
|
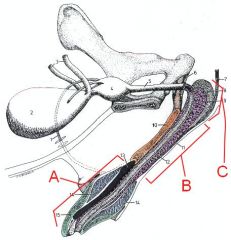
Name the 3 divisions of the penis. What are the subdivisions of A?
|
A - Glans (Bulbus Glandis and Pars Longa Glandis)
B - Body C - Root |
|
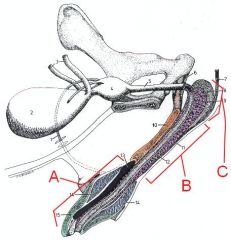
Identify these structures
What is the enlarged part of A called? |
A - Corpus spongiosum penis (Urethral bulb of the penis)
B - Corpus cavernosum penis C - Os penis D - Corpus spongiosum of the bulbus glandis E - Copus spongiosum of the pars longa glandis F - Bulbospongiosus m. |
|
|
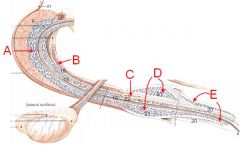
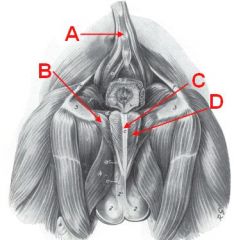
Identify these muscles.
Which are skeletal/smooth? What does B cover? |
A - Rectococcygeus m. (smooth)
B - Ischiocavernosus m. (covers crus of the penis) C - Bulbospongiosus m. D - Retractor penis m. (smooth) |
|
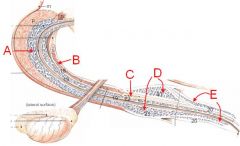
Identify these muscles.
Which are skeletal/smooth? What does B cover? |
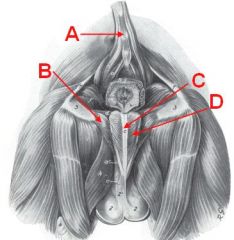
A - Rectococcygeus m. (smooth)
B - Ischiocavernosus m. (covers crus of the penis) C - Bulbospongiosus m. D - Retractor penis m. (smooth) |
|
|
T or F:
The spongy urethra is surrounded by corpus cavernosum. |
False you dill-weed!
The SPONGY urethra (penile urethra) is covered by the corpus SPONGIOSUM!! |
|
|
T or F:
Castrated male cats never have keratinized spines on their penis. |
True!
These spines are testosterone dependent and disappear soon after castration. |
|
|
What is the structure covering the glans penis? What are the layers of this structure?
|
Prepuce
External lamina (haired skin) Internal lamina Penile lamina (covering of penis) |
|
|
What are the plethora of little bumps on the internal lamina of the prepuce?
|
Lymphoid nodules
|
|
|
T or F:
That damn tomcat peed on the drapes ON PURPOSE! |
True! Punt that cat (just kidding)!!!
Toms can direct their urine spray wherever they want. |
|
|
Why should one be careful when applying traction to a cat testicle during a neuter?
|
As the ductus deferens wraps over the ureter, too much traction could possibly wip the ureter.
|
|
|
What is the primary source of blood to the penis?
|
Internal pudendal artery.
|
|
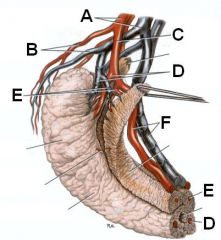
Identify the arteries.
|
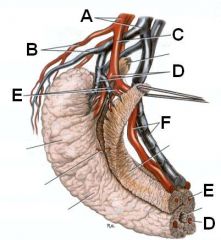
A - Internal pudendal a.
B - Ventral perineal a. C - Artery of the penis D - Artery of the bulb of the penis E - Deep artery of the penis F - Dorsal artery of the penis |
|
|
Which nerve stimulates erection? What type of stimulation is this?
|
Pelvic n.
Parasympathetic |
|
|
T or F:
The bulbus glandis is the last structure to become engorged in an erection. |
True! It receives no arterial bloodflow.
|
|
|
What denotes the proximal and distal extent of the body of the penis?
|
Where the 2 crura come together is the proximal extent. The glans penis is the distal extent.
|
|
|
T or F:
The os penis is the distal continuation of the corpus spongiosum penis. |
False!
It is the distal extent of the corpus cavernosum penis. |
|
|
Through which aspect (dorsal or ventral) does the urethra pass through in the os penis?
|
Ventral
|
|
|
What artery is the primary source of blood to the penis? What specific branches of this artery supply blood to the penis?
|
Internal pudendal a.
Artery of the penis gives rise to artery of the bulb of the penis deep artery of the penis dorsal artery of the penis |
|
|
What nerve or nerves innervate the penis?
|
Pudendal nerve
gives rise to: Deep perineal brs. and dorsal n. of the penis |
|
|
What is a less crude term for "nature's cockring"?
|
Ischiourethralis m.
|
|
|
What is the clinical term describing a narrowed preputial orifice?
|
Phimosis
|
|
|
Oh no! Fido ate a bottle of viagra! What condition does he have now?
|
Paraphimosis
|

