![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
178 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn?
|
A severe form of anemia caused in a fetus or newborn infant by incompatibility with the mother's blood type.
|
|
|
In the second pregnancy with the mother's blood type incompatible, what happens if their blood comes in contact during the 2nd trimester (mid-pregnancy)?
|
It is as though there is "organ rejection" and both mom and baby could die.
|
|
|
In the second pregnancy with the mother's blood type incompatible, what happens if their blood comes in contact during the 1st trimester (early pregnancy)?
|
The baby will be miscarried.
|
|
|
In the second pregnancy with the mother's blood type incompatible, what happens if their blood comes in contact during the 3rd trimester (late pregnancy)?
|
The baby will be born anemic and turns bright yellow with bilirubin 1 to 2 days after birth.
|
|
|
Lymph vessels lead to what two ducts?
|
Thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct
|
|
|
What is the lymph node made of?
|
1. Germinal Center
2. "background tissue" |
|
|
What is the Germinal Center made up of?
|
B-cell lymphocytes that make and release antibodies, if primed, and macrophages that present what was killed to the B-Cells
|
|
|
What is the background tissue in the lymph node made up of?
|
More macrophages waiting to be mobilized by inflammation and fibroblasts that make ECM, repair injury and make the scar
|
|
|
What are the 3 different kinds of lymph nodes and where are they located?
|
1. Cervical located in the neck
2. Axillary located in the arm pit 3. Inguinal located in the femoral triangle |
|
|
What is a swollen lymph node?
|
A lymph node that is busy fighting infection. The B-cells are multiplying to respond to the infection. They are usually swollen and hurt. If they are swollen and don't hurt, it could be leukemia.
|
|
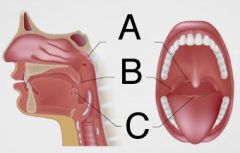
What is A, B & C ?
|
A. Pharyngeal tonsil (or adenoid)
B. Palatine tonsil C. Lingual tonsil |
|
|
What does the Spleen do?
|
Removes and recycles old and weird blood cells making bilirubin and stores iron
|
|
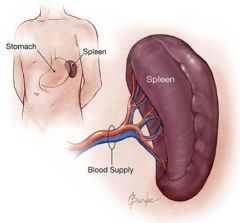
What is the spleen?
|
A dense bag (dense irr. C.T.) filled with a gelatinous substance made up of 2 types of tissue: White pulp (lymphatic tissue) and red pulp (sinuses - spaces for blood to travel made of cuboidal epithelium)
|
|
|
Where will it be felt if the spleen is ruptured and why?
|
In the shoulder because the nerves from the diaphragm enter the spinal cord near the shoulder.
|
|
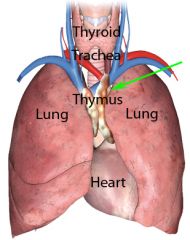
What does the Thymus Gland Do?
|
It is involved in enabling T-cells (Lymphocytes) to mature so they can become active.
Seems to prevent self-reaction. Shrinks with age (may be why cancer risk increases with age) |
|
|
What are the barriers against infection?
|
1. Intact skin
2. Mucus Membranes 3. Washing effects |
|
|
Name some places for mucus membranes
|
Mouth, nose, genitals, ear canals
|
|
|
Name some washing effects
|
Mucus - nasal cavity, digestive tract, genitals
Saliva, tears, urine, sweat and chemical protection (stomach acid, skin oil and lysozyme) |
|
|
What is Lysozyme?
|
An antibacterial in tears and saliva
|
|
|
What is interferon?
|
A chemical warning signal produced by a virus-infected cell warning other cells to protect themselves.
|
|
|
What is a fever?
|
An increase in body temperature which increases metabolism, which increases WBC activity in an attempt to "cook" some temperature-sensitive bacteria.
|
|
|
What are the triggers for a fever?
|
Inflammation and bacteria-made chemicals - endotoxins (pyrogen)
|
|
|
What does the hypothalamus do with an increase of prostaglandins?
|
-Increases thyroid hormones to increase metabolism
-makes you shiver increasing metabolism even higher (creating heat) - makes you vasoconstrict and pales (creating heat) - puts epinephrine on the arteries to help retain the heat being made |
|
|
What does inflammation do?
|
Releases interleukins, which call other WBCs to come fight the infection on site and calls fibroblasts to come fix the injury.
|
|
|
What are the triggers for inflammation?
|
1. Cell contents - bacteria toxins, complement active
2. Basophils in blood or Mast Cells in tissue (that exocytose) 3. Release histamine (interleukins, prostaglandins) causing edema and vasodilation |
|
|
What does swelling or edema do?
|
Makes capillaries leaky and blocks lymph vessels which help WBCs leave and traps bacteria locally
|
|
|
What do we look for to see if swelling is infected?
|
1. Is the skin hot or is there a fever over 100.5?
2. Is it red? (if not could there be a deep infection) 3. Is it spreading? (the circle-drawing trick - check back) |
|
|
What is an antibody?
|
A special receptor protein made by
1. B-cells and released or 2. T-Cells and kept Many different types |
|
|
What do antibodies do?
|
Binds to antigens ("bad things") giving them a "handle", increasing the ability to endocytose the antigen.
Binding to an antigen turns on the complement proteins |
|
|
What are complement proteins and what do they do?
|
Proteins in the blood, made by the liver.
1. turns on and binds to the antigen, giving it another "handle" 2. drills a hole and Lyse (or kills) the antigen 3. goes to a local basophil or mast cell and triggers inflammation |
|
|
What is a Natural Killer cell and what does it do?
|
It is a T-cell cousin and it is always active, always looking at normal cells in the body, looks at the major histocompatibility protein, if it is altered or changed, it will kill it
|
|
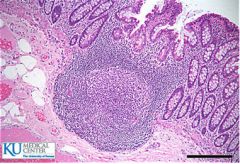
Identify this.
|
Lymph tissue of the large intestine - Peyer's Patch.
|
|
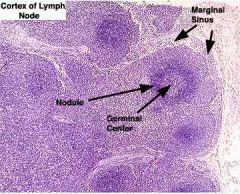
Identify this.
|
Cross section of a lymph node.
|
|
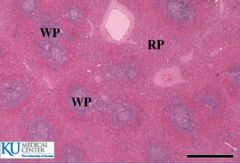
Identify this.
|
Spleen - red and white pulp
|
|
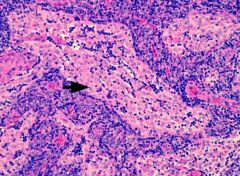
What kind of cells are here?
|
B-cells
|
|
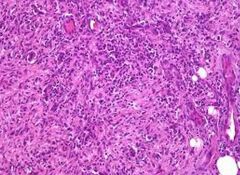
What kind of Connective Tissue is this?
|
Reticular
|
|
|
Define Immunity
|
Antibodies produced to an antigen and the resulting actions.
|
|
|
What is an active immunity?
|
The body reacting and making antibodies and using them.
|
|
|
What is Passive Immunity?
|
Using someone else's antibodies like an infant getting antibodies from his mother's breastmilk.
|
|
|
Describe the active immunity process of a B-cell in the lymph node.
|
Macrophage binds to the bacteria, endocytotes it and kills it with hydrogen peroxide then displays pieces of it on the MHC protein. If there are hurt cells or inflammation, it will display the B7 protein and the B-cell gets activated.
|
|
|
What does an activated B-cell do?
|
a. Clones itself, increasing mitosis - the lymph node will swell
b. releases antibodies into the lymph node and they make it into the blood stream - triggers inflammation and now the lymph node is sore. c. if a certain T-cell is active, a helper T-cell will make the active B-cell into a plasma cell where it becomes super active and dies in a few days d. Some active B-cells will rest and react to the next re-infection becoming a memory cell |
|
|
Describe the active immunity process of a T-cell in the blood.
|
Neutrophil binds to the bacteria, exocytotes it and kills it with hydrogen peroxide then displays pieces of it on the MHC protein. If bacteria is found near the inflammation, the neutrophil will display the B7 "danger" protein and the T-cell gets activated.
|
|
|
What does an activated T-cell do?
|
a. clones itself increasing mitosis
b. mature T-cells are i. helper T-cells CD4 which releases interleukins, will signal any active B-cells to become plasma cells, will encourage more WBCs to the area, and will encourage more NK cells to be created. ii. Cytotoxic T-cell CD8 which binds to the antigen-bearing cell and pokes holes in it. |
|
|
How does stress affect the body?
|
Emotional or physical stress like pain will alert the hypothalamus which alerts the sympathetic NS, which releases epinephrine on the organs, increasing the HR, and increasing vasoconstriction which increases BP, slows the digestive system, dilates the pupils, causing sweats and on the liver will cause the liver to release glycogen as glucose causing high blood sugar.
|
|
|
How does stress affect the immune system?
|
Decreases the number of WBCs which increases the risk of infection and it decreases inflammation, which also increases the risk of infection.
|
|
|
Name one way stress affects the hormones.
|
The hypothalamus alerts the pituitary gland which will release an anti-diuretic hormone on the kidneys which will then retain H20 and vasoconstrict the arteries which will cause BP to go up. Cortisone will increase causing the liver to release glycogen as glucose and also fats & proteins as glucose increasing the blood sugar. And the adrenal gland also makes opposite sex hormones.
|
|
|
Name another way stress affects hormones.
|
The hypothalamus alerts the pituitary gland which sends the signal to activate the adrenal gland increasing aldosterone on the kidneys that will now retain H2O and Sodium (Na+) increasing BP.
|
|
|
What is ventilation?
|
Air Movement
|
|
|
What is Internal respiration?
|
Air to Blood
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration?
|
Using O2 at the mitochondria
|
|
|
Why do we breath?
|
To get O2 to the mitochondria and get CO2 out of our system
|
|
|
what kind of epithelia lines the upper respiratory tract?
|
Pseudo-stratified, ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
|
Describe the upper respiratory tract
|
lined with mucosa
makes mucus cilia sweep mucus to the pharynx where it is swallowed and hopefully bacteria is killed by the digestive fluids |
|
|
What kind of epithelia lines the eustachian tubes?
|
pseudo-stratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium
|
|
|
what affect does cigarette smoke have on the upper respiratory tract?
|
Smoke paralyzes the cilia
|
|
|
What does the nasal cavity do?
|
Warms and moistens the air we breath
filters past mucus (and nose hairs) gives resonance for speech gives olfaction (smelling) |
|
|
What kind of epithelium lines the pharynx?
|
Stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What's included in the nasopharynx?
|
Internal nares
eustachian tube adenoids |
|
|
What's included in the oropharynx?
|
Fauces (opening to the mouth)
Palatine tonsils lingual tonsils (depending on where the lines is) |
|
|
What's included in the Laryngealpharynx?
|
(lingual tonsils depending on where the line is)
larynx larynx/esophagus split epiglottis |
|
|
What is the larynx?
|
Home of the vocal folds (voice box)
|
|
|
Where is the trachea?
|
Behind the heart and in front of the esophagus
|
|
|
Describe the tracheal cartilage.
|
It is a C-shaped hyaline cartilage.
|
|
|
What is the name of the ridge between the right and left bronchi?
|
Carina
|
|
|
Describe the bronchi
|
The right side has 3 main branches, is wider and is angled downward. The left side is more horizontal and has 2 main branches and more narrow.
|
|
|
What kind of epithelium lines the larynx?
|
pseudo-stratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What kind of epithelium lines the bronchi and bronchioles?
|
pseudo-stratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What is the path of air from the trachea?
|
Bronchus, primary bronchiole, secondary bronchiole, (tertiary bronchiole), respiratory, terminal, alveoli
|
|
|
What happens if any bronchioles are blocked?
|
You can't breathe.
|
|
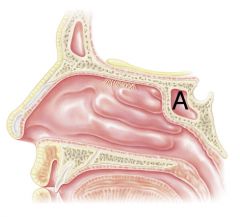
What is A?
|
Sphenoid sinus
|
|
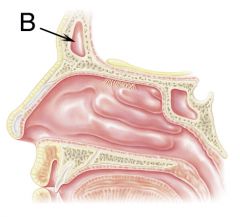
What is B?
|
Frontal sinus
|
|
|
What are the layers of the alveoli?
|
1. mucosa- pseudo-stratified, ciliated, columnar epith.
2. submucosa - CT, mucus glands & elastin 3. smooth muscle 4. cartilage |
|
|
What are septal cells and why are they important?
|
Septal Cells make surfactant. It breaks up water tension making it easier to breath, particularly for newborns.
|
|
|
What kind of epithelia makes up the alveolar wall?
|
Simple squamous
|
|
|
How many lobes on each lung?
|
3 on the right and 2 on the left
|
|
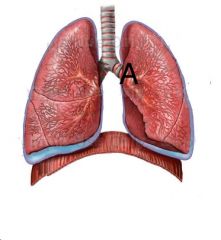
What is located at A?
|
The hilus
|
|
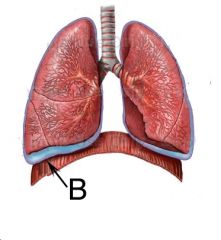
What is B? (the OUTSIDE pleura) and what is it attached to?
|
The parietal pleura is attached to the ribcage.
|
|
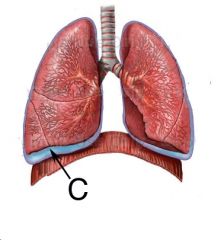
What is C (the INSIDE pleura) and what is it attached to?
|
The visceral pleura is attached to the lung.
|
|
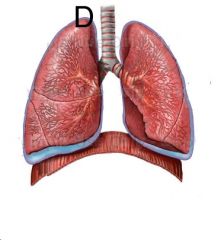
What is D?
|
The apex
|
|
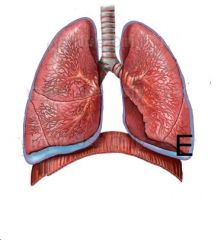
What is E?
|
The base
|
|
|
What kind of air pressure is between the two pleura?
|
Low air pressure
|
|
|
Define Boyle's Law.
|
For a given amount of gas, if you increase the volume then you decrease the pressure. If you increase the pressure, then you decrease the volume. Volume and pressure are opposite.
|
|
|
What happens when you inhale?
|
The ribcage is raised, the intercostals, the scalenes are lifted and the diaphragm is lowered. This is increasing the volume around the lungs and decreasing the pressure around the lungs. You suck on the lungs from the outside inflating them further, decreasing pressure in the lungs, pulling in air.
|
|
|
What happens when you exhale?
|
The ribcage, the intercostals and the scalenes relax. The ribcage drops down with gravity. The diaphragm relaxes and the abdominal organs push back up. This is decreasing the volume around the lungs and increasing pressure around the lungs which makes them recoil and get smaller. The increased pressure on the lungs forces the air out.
|
|
|
What happens when you force exhale?
|
To get the diaphragm even higher, you tighten the abdominals and push the abdominal organs against the diaphragm.
|
|
|
What happens when you force inhale?
|
You have to fix the arms and use the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor to lift the ribcage further.
|
|
|
What happens with a collapsed lung?
|
If a rib punctures a lung or a chest wound causes air to fill up the space between the pleura. The air pressure building up causes the lung to recoil and collapse because you can't increase the volume by decreasing the pressure.
|
|
|
Define Dalton's Law
|
For a mix of gases, at predetermined volume, the concentration of the mix is called "Total Pressure" and total pressure equals the sum of all the partial pressures of the ingredients.
|
|
|
What happens if you increase the partial pressure of one gas?
|
You increase the solubility of that gas.
|
|
|
What happens if you increase the total pressure by 2?
|
You double the pressure of all other ingredients.
|
|
|
Define Henry's Law.
|
The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid.
|
|
|
To predict a gas dissolving or not in a liquid, what two things do you need to know?
|
1. Partial pressure of that gas
2. Solubility coefficient of that gas for that liquid |
|
|
What are the 3 main ingredients of air?
|
Nitrogen, Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide.
|
|
|
Of the 3 main ingredients of air, which is the least soluble?
|
Nitrogen
|
|
|
Of the 3 main ingredients of air, which is the MOST soluble?
|
Carbon Dioxide. It LOVES hemoglobin!
|
|
|
What's normal breathing rates?
|
12 to 20 breaths per minute.
|
|
|
What is hypocapnea?
|
Breathing less than 12 breaths per minute. Also called hypoventilating.
|
|
|
What is hypercapnea?
|
Breathing faster than 20 breaths per minute. Also called hyperventilating.
|
|
|
What is Dyspnea?
|
Having trouble breathing or having pain while breathing.
|
|
|
What is apnea?
|
Stopping breathing as in Sleep Apnea (stopping breathing while sleeping).
|
|
|
What is pulmonary volume?
|
The volume of air associated with different phases of the respiratory cycle.
|
|
|
What is Tidal Volume?
|
Normal relaxed breathing volume. Approximately 500 ml.s in and 500 ml.s out
|
|
|
What is minute volume of respiration?
|
Average breathing rate X Tidal Volume.
12-20/ min. X ~500 ml.s = about 6,000 ml.s per min. |
|
|
What is inspiratory reserve?
|
Forced inspiration. Air dragged into the lungs in addition to tidal volume.
|
|
|
What is expiratory reserve?
|
forced expiration in addition to tidal volume.
|
|
|
What happens with emphysema?
|
There is loss to the elasticity of the alveoli. The expiratory volume is less because there is less "spring" to force the air out and the residual volume increases.
|
|
|
What is Vital Capacity?
|
ER + IR + TV
|
|
|
What happens with pneumonia?
|
Pneumonia is an infection where fluid accumulates in the lungs decreasing the total useable volume, decreasing Vital Capacity.
|
|
|
What happens with asthma?
|
Decreases expiratory reserve
|
|
|
What is Endocrinology?
|
The study of hormones, blood-traveling chemical signals. They only react with cells that have a receptor for that hormone.
|
|
|
How do hormones from the endocrine glands enter the blood stream?
|
Directly into the blood stream. The glands are wrapped around small arteries or capillaries.
|
|
|
How many endocrine glands have simple cuboidal epithelia?
|
All but one.
|
|
|
How many cells in the body react to epinephrine?
|
About half.
|
|
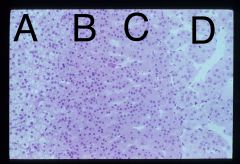
Which endocrine gland is this? Name the 4 layers and what hormone they secrete.
|
This is the Adrenal Gland.
A. Medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine B. The reticular layer produces androgens C. The fascicular layer secretes cortisone D. The glumerular layer produces aldosterone |
|
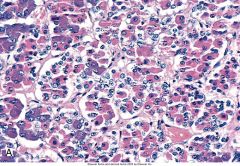
Which gland is this?
|
Anterior pituitary
|
|
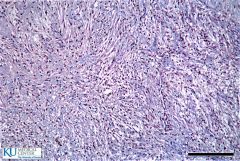
Which gland is this?
|
Posterior pituitary
|
|
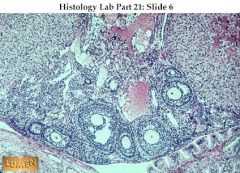
What is this a slide of? Mention something unique about it.
|
This is an ovary slide. There are many eggs here. Would either be a mouse, rabbit or a women on fertility drugs.
|
|
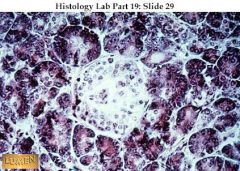
What gland is this? What is the lighter thing in the middle?
|
This is a pancreas slide and the lighter thing is an islet.
|
|
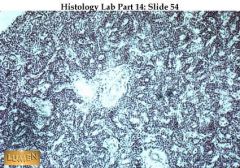
What gland is this and what hormone does it produce?
|
Parathyroid gland only produces parathyroid hormone.
|
|
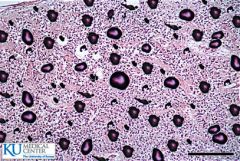
What gland is this? What are the larger dark circles?
|
This is a slide of the pineal gland and the dark circles are calcium crystals.
|
|
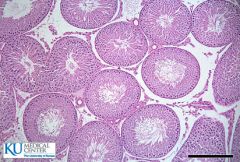
What is this a slide of?
|
The testes.
|
|
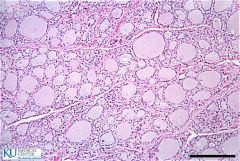
What is this a slide of?
|
Thyroid gland.
|
|
|
Name the molecule types of hormones.
|
1. Amine hormones
2. Protein, or peptide chain, hormones 3. Steroid hormones (true hormones) 4. Prostaglandins 5. Interleukins 4 & 5 are not officially hormones |
|
|
Describe amine hormones and give examples.
|
They are variations of the amino acid tyrosine. They are water soluble, small molecule and fast acting. Examples include epinephrine, adrenaline and thyroid hormones.
|
|
|
Describe protein or peptide chain hormones and give examples.
|
Chains of amino acids. They are water soluble and fast acting. Examples include insulin, growth hormone, glucagon and oxytocin.
|
|
|
Describe Steroid hormones and give examples.
|
These are true hormones. They are lipid based, variations on cholesterol. The are not water based and not fast acting. They turn off or on genes. Can be made into creams like cortisone creams and testosterone cream.
|
|
|
Describe prostaglandins.
|
Though not officially a hormone, it is lipid based, has a local affect and triggers fever.
|
|
|
How does a steroid turn on or off a gene?
|
The steroid hormone enters the cell and meets the receptor, then binds to the waiting area of the gene in the DNA of the nucleus and turns on or off the gene, and in a few hours, there are new proteins and new RNA.
|
|
|
Water soluble proteins and amines, describe the pathway A.
|
There are two pathways depending on what the cell is set up to do in response and if there is a receptor. Pathway A. is Cyclic AMP. It happens outside the cell. The hormone binds to the receptor protein and activates an enzyme. ATP removes 2 phosphates and becomes cAMP, which turns on another enzyme, Protein kinase A, which adds phosphates to protein group A and turns the protein on. It is superfast and short lived.
|
|
|
Water soluble proteins and amines, describe the pathway B.
|
Called the IP3 pathway. The receptor binds to the hormone. Inside end binds to and activates and enzyme. The enzyme will act on a lipid and breaks it into 2 pieces.
1. DAG - activates enzyme Protein Kinase C which adds a phosphate to protein group C. and turns them on. 2. IP3 - goes to the smooth ER which releases Ca+ - can trigger exocytosis, start pathway for cell division, can bind to calmodulin, or trigger other paths like smooth muscle contraction. Very, very fast - seconds. |
|
|
There is a very strong connection between what 3 things?
|
Hormones, nervous system and interleukins.
|
|
|
What hormones does the anterior pituitary control?
|
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Growth Hormone Prolactin Follicle Stimulating Hormone Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Luteinizing Hormone |
|
|
What hormones does the posterior pituitary control?
|
Anti-diuretic Hormone
Oxytocin |
|
|
What does the Thyroid stimulating hormone do?
|
Goes to the thyroid gland, increases production of metabolic hormones and release .
Hypothalamus monitors the levels of metabolic hormones and monitors body temp. If you're cold, the hypothalamus will tell the pituitary gland to increase TSH |
|
|
What does Growth Hormone do?
|
Goes to the cartilage where it increases mitosis (growth plate growth). Goes to the liver, muscle & bone. Liver & muscle together make an insulin like growth factor which a. increases protein synthesis (muscle building) b. releases fatty acids as fuel and c. releases glycogen as glucose. Pituitary releases GH with exercise, as children and during trauma and starvation.
|
|
|
What happens if there's too much Growth Hormone for someone? Too little?
|
Child will be a giant and insulin resistance is possible. An adult will have acromegaly (enlargement of hands, feet, nose, lips, ears), a lowered voice, a pronounced brow protrusion.
Too little and the child will have pituitary dwarfism and it would have an effect on their brain - GH is needed. |
|
|
What does Prolactin do?
|
Goes to the mammary glands of the breasts. Increases the number of receptors for insulin (insulin causes the cells to take in sugar). Increases milk production. Inhibits ovulation. Inhibits testosterone production.
|
|
|
What does Follicle Stimulating hormone do?
|
Relates to fertility in men and women. Women - goes to the follicles in the ovary. Stimulates follicle cell to mature, the mature cells make estrogen and prepare the ovum for release. Men - increases the number and growth of the sperm. Increases production of food and estrogen by sertoli cells in seminiferous tubules.
|
|
|
What is ACTH and what does it do?
|
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone goes to the adrenal gland cortex, releases more steroid hormones. The hypothalamus monitors the levels of steroids and increases ACTH for any sort of stress, including high Blood pressure.
|
|
|
What does Luteinizing Hormone do?
|
In women, after an ovum is released, the rest of the cells in the ovary stop making estrogen and start making progesterone and turn yellow. In men, it converts estrogen to androgen including testosterone - along with prolactin.
|
|
|
What would too much Luteinizing hormone do? Too little?
|
Too much luteinizing hormone will cause premature puberty and too little with cause infertility, not going through puberty and in adults will lower sex drive.
|
|
|
What hormones does the posterior pituitary control?
|
Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin |
|
|
What does Antidiuretic hormone do?
|
ADH is produced in response to low blood water at the hypothalamus, or in response to low blood pressure at the brain stem. Will cause vasoconstriction (less space for blood, increasing BP) and will cause the kidneys to retain water, but not salt.
|
|
|
What does an excess of ADH do? How about too little?
|
An excess of ADH will cause water toxicity (High BP, excess of H2O, and low salt, which can make the brain swell. Not enough will cause one to pee freely, but will retain salt, causing hangover symptoms, hypernatremia, much less water than sodium. Will cause also cause diabetes mellitus - peeing pure H2O
|
|
|
What does Oxytocin do?
|
Causes contracting at the uterus for birth, causes contracting of milk storage ampulla in breasts for nursing. Causes strong emotional bonding in men and women and is also released during orgasm for both.
|
|
|
What hormones does the pineal gland make?
|
With the dark, makes and releases melatonin, which makes us sleepy, depressed, low energy and a decrease in sex drive. When it's light outside, the hypothalamus tells the pineal gland not to make it. During seasonal changes, it can cause Seasonal Effective Disorder, when there is less light.
|
|
|
What hormones does the Thyroid Gland control?
|
Calcitonin - a calcium regulator
Two metabolic hormones T4 and T3 |
|
|
What does Calcitonin do?
|
Regulates calcium. It is made in the interstitial cells of the Thyroid. If calcium is up, it increases calcitonin and puts calcium in the bones, so it lowers blood calcium and strengthens bone.
|
|
|
What is T4 and T3 what do they do?
|
Follicle cells produce these hormones and stores them in the colloid. When it's needed, it's removed and iodine is added to it before it is released. They increase metabolism and body temp.
T4 is Thyroxin and T3 is Triiodothyronine |
|
|
What is hypothyroidism?
|
When thyroid isn't making enough thyroid hormone. There will be low energy, cold, slow thinking, slow reflexes, hard edema on the shins and hair and skin get coarse.
|
|
|
What is hyperthyroidism?
|
Often called Grave's disease, it is an autoimmune disease with hyper metabolism, hyper reflexes, emotional labile, tachycardia, fine hair and skin and very prominent eyes (because fat builds up behind the eyes)
|
|
|
What hormone does the parathyroid gland control? What does the hormone do?
|
Parathyroid hormone - an "anti-calcintonial". It is self-regulated. If the calcium is low, it will release parathyroid hormone, it goes to the bone and increases the breakdown of bone by osteoclasts to release calcium. Has an effect on the kidneys, retains calcium at the kidneys. If Vitamin D is present, it will absorb from the gut.
|
|
|
What are the layers of the Adrenal Gland?
|
Medulla and the adrenal cortex which has three layers - reticular, fascicular and glumerular layers.
|
|
|
Describe the medulla layer of the adrenal gland.
|
It is derived from the neural crest of the fetus. Produces epinephrine and norepinephrine. The cells of the medulla are called chromaffin cells. A tumor in the medulla will cause too much epinephrine and therefore cause extreme stress.
|
|
|
Describe the Reticular layer of the adrenal gland.
|
The innermost layer of the adrenal cortex makes estrogen and androgens. Women under stress wil grow facial hair because they make extra androgen in the adrenal gland. An excess in men will create "man boobs". Excess in children will cause premature puberty or male looking genitals on a baby girl.
|
|
|
Describe the fascicular layer of the adrenal gland.
|
The middle layer of the adrenal cortex produces cortisone, goes to the liver, releases glycogen as glucose. It encourages the liver to convert amino acids and lipids as glucose and acetyl groups. Goes to the bone marrow, decreases WBC production and activity and it an anti-inflammatory.
|
|
|
Describe the glumerular layer of the adrenal cortex.
|
Outer layer of the cortex. Produces aldosterone, goes to the kidneys - retains sodium, H2O, and loses potassium, so BP is raised. It is often called mineralocorticoid.
|
|
|
What is Cushing's Disorder?
|
Excess steroids. 1. excess cortisone causes high blood sugar, adrenal diabetes, loss of muscle mass and skin thickness and breaks down protein. It increases yellow fat in the abdomen, face and back of neck and decreases immunity. Excess aldosterone causes high blood pressure and low potassium.
|
|
|
What is Addison's Disease?
|
Lack of steroids. Could be adrenal or pituitary. There is low blood pressure, especially with stress - can go into shock. There is low blood sugar - with stress can go really low and go into sugar shock.
|
|
|
Kidneys, as a gland, make what hormones?
|
Renin and erythropoietin.
|
|
|
What does Renin do?
|
Only if blood pressure is low will it be made. It acts on angiotensin (a vasoconstrictor) - goes to the adrenal gland and raises aldosterone.
|
|
|
What does erythropoietin do?
|
When blood oxygen is low, it goes to the bone marrow to increase RBC production. The full effect takes a week to 10 days.
|
|
|
What hormones does the pancreas control?
|
Somatostatin, glucagon and insulin
|
|
|
What does somatostatin do?
|
Stops the movement of the gut in the digestive system during times of high stress and emotional trauma. Why the hospital needs to make sure you have a bowel movement before you're discharged after surgery - to make sure it's working again.
|
|
|
What does glucagon do?
|
Responds to low blood sugar. Glycogen is released as sugar and fats and proteins are released as sugar and acetyl groups.
|
|
|
What does insulin do?
|
Causes all cells with receptors to take glucose in from blood and body fluids. Uses glucose as fuel, stores excess as glycogen (in liver and muscle) or the liver will turn excess into fats and lipids. Uses amino acids as protein.
|
|
|
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
|
When blood sugar is too high or there is sugar in the urine. Type I is when cells can't take in sugar. No insulin is made. It is an autoimmune disorder. Blood sugar is too high and spills into urine. They urinate a lot but very thirsty. The cells have no fuel so they're starving. The person eats a lot trying to compensate, but still loses weight burning proteins and fats and acetyl groups. They become acidic causing ketoacidosis. If the person is in a coma, their heart rate will be fast and their breathing will be fast as well. Their breath will smell fruity.
|
|
|
What is type II Diabetes?
|
They are not yet insulin dependent. The patient does make insulin but the cells are not responding enough or not making enough insulin. It has a slow onset. Over time the blood sugar levels increase and eventually glucosuria, more infections (WBCs don't like high blood sugar), and blurred vision (high sugar dehydrates retina). People with metabolic syndrome are likely to develop it.
|
|
|
What is metabolic syndrome?
|
A disorder characterized by high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high risk of diabetes, and apple body type (lots of abdominal fat).
|
|
|
what kind of damage can high blood sugar do to arteries and nerves?
|
Can cause atherosclerosis - risk for heart attack and gangrene. Can also cause nerve damage, blindness and loss of sensation in the hands and feet.
|
|
|
What hormones do the gonads produce?
|
Ovaries produce estrogen, progesterone, androgens and inhibin.
Testes produce estrogen, testosterone, androgens and inhibin. The placenta makes Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone and Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin. |
|
|
What does estrogen do?
|
Estrogen causes subcutaneous fat (the curves in women), increases calcium in the bones, causes the lining of the uterus to grow, in a girl, it causes proper growth of uterus and length of vagina, and growth of ducts in the breasts. It is made and stored in the adipose tissue. For males, the sertoli cells make it for food for the baby sperm cells.
|
|
|
What does progesterone do?
|
Grows the lining of the uterus to secrete food for baby (and sperm for male), grows glands in the breasts, blocks contraction of the uterus during pregnancy.
|
|
|
What do androgens do?
|
Increases sex drive in women. One of them is testosterone in men and it increases muscle mass, increases size of genitalia, increases bone density, maturation in of sperm cells and increases sex drive in men as well.
|
|
|
What does inhibin do?
|
Controls the amount of FSH & LH levels. For women, it limits the amount of eggs fertilized (so humans don't have "litters")
|
|
|
What hormones does the placenta produce?
|
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Hormone (HCG) and
Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin |
|
|
What does Human Chorionic Gonadotropin do?
|
Placenta starts producing it at one week pregnancy and continues until the end of the 3rd month. It goes to the ovary and tells it to keep making progesterone because there is an embryo present.
|
|
|
What does Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin do?
|
It causes the mom's body to become insulin resistant increasing sugar for the baby. Makes mom a type II diabetic at about 6 months pregnancy. Mom's body compensates by making extra insulin bringing the sugar down to make sure baby is normal sized. This also ensures no artery or nerve damage.
|

