![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
256 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MCC of erythroderma in adults
|
psoriasis
Usually due to withdrawal of CS, cyclosporine, efalizumab, MTX |
|
|
MCC of erythroderma in kids
|
Drug reaction #1
Psoriasis #2 |
|
|
MC bullous dermatosis to progress to erythroderma?
|
pemphigus foliaceous
|
|
|
Characteristic additional findings in erythroderma associated with CTCL
|
Painful and fissured keratoderma
Leonine facies Diffuse alopecia |
|
|
Causes of neonatal erythroderma
|
Non-bullous CIE
Bullous CIE Netherton |
|
|
What genes are mutated in monilethrix?
|
K81, K83, K86
|
|
|
Where does acute GVHD first appear?
|
Acrally
|
|
|
What two LP variants are associated with SCC?
|
Hypertrophic
Ulcerative |
|
|
What is the most common location for ulcerative LP?
|
Palmoplantar, especially soles
|
|
|
What is the most common location for perforating GA?
|
Dorsal hand
|
|
|
Name the vitiligo susceptibility genes.
|
NALP1 (SLEV1): component of cytoplasmic inflammasomes which regulate caspase activation
AIS1-3: AIS3 from non-autoimmunity associated families |
|
|
Most common location for segmental vitiligo?
|
Face
|
|
|
MC significant ocular abnormality associated with vitiligo?
|
uveitis
Severe form seen in Vogt-Koyonagi-Harada (uveitis, aseptic meningitis, dysacousia, poliosis,vitiligo) |
|
|
What is Alezzandrini syndrome?
|
Unilateral whitening of scalp hair, brows, lashes
Unilateral depigmentation of skin of forehead, nose, cheek, upper lip, chin Same side as unilateral visual changes (atrophic iris, decreased visual acuity) |
|
|
Differences in childhood vitiligo vs adult
|
Segmental vitiligo more frequent in kids (although MC type is still vitiligo vulgaris)
Lower incidence of associated endocrinopathies Increased incidence of autoab production |
|
|
MC type of albinism in Japan?
|
OCA4
|
|
|
Besides MITF, what other gene defect is associated with Wardenburg's syndrome type 2?
|
SLUG: encodes a zinc finger transcription factor; involved in dev't of neural-crest derived cells
|
|
|
Three gene defects in wardenburg's syndrome type 4?
|
EDN3, EDNRB, SOX10
|
|
|
What is Tietz syndrome?
|
AD, MITF gene
Allelic to WS2 Generalized hypomelanosis of skin Deaf-mutism Hypoplasia of eyebrows Light blond hair, blue eyes Normal fundi, no photophobia or nystagmus |
|
|
Systemic findings in Hermansky-Pudlak
|
Bleeding tendency (absence of dense bodies in plts; prolonged bleeding time)
Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis Granulomatous colitis Less often, RF, CM |
|
|
Which Hermansky-Pudlak subtype is associated with immunodeficiency?
|
HPS2
AP3B1 mutation (involved in protein sorting to lysosomes and organelles) CD1b binds AP3 complex; may account for recurrent bacterial infections |
|
|
Histologic hallmark of Chediak-Higashi
|
giant melanosomes in melanocytes
|
|
|
Triad of dyskeratosis congenita
|
Lacy reticulated hyperpigmentation neck, upper chest
Nail dystrophy (pterygium) Premalignant leukoplakia (lateral tongue) |
|
|
Gene defect in dyschromatosis symmetrica hereditaria
|
DSRAD
double stranded RNA-specific adenosine deaminase |
|
|
Gene defects in SCID
|
XLR (40%): gamma chain of IL2 receptor
AR: 20% adenosine deaminasae, 6% JAK3 |
|
|
AutoAb in SLE that correlate positively with activity, associated with lupus nephritis
|
dsDNA
|
|
|
AutoAb associated with neuropsychiatric SLE?
|
rRNP
|
|
|
What is typical clinical presentation of hypergammaglobulinemic purpura of Waldenstrom?
|
Recurring crops of burnin or stinging macula hemorrhage on LE
|
|
|
What is MC association in pts with hypergammaglobulinemic purpura of waldenstrom?
|
autoimmune CTD, especially Sjogren's
|
|
|
Associations with recurrent superficial thrombophlebitis
|
trousseau's (underlying malignancy, esp. pancreatic or lung)
Hypercoagulable state Inflammatory ds (Behcets) |
|
|
Typical skin finding with vasocclusive disease?
|
retiform purpura
|
|
|
Ddx of microvascular occlusiion
|
Platelet plugging
Cold-related gelling or agglutination Vessel-invasive organism Embolization Systemic coagulopathies Vascular coagulopathies Miscellaneous (spider bite) |
|
|
Cardinal physical exam findings in cryoglobulinemia?
|
Retiform purpuric or necrotic lesions at acral sites of cold exposure
|
|
|
Treatment for disseminated stronglyoides?
|
thiabendazole
|
|
|
What is most likely diagnosis in pt with h/o renal stones with sudden-onset livedo reticularis or retiform purpura?
|
Hyperoxaluria--oxalate embolus
|
|
|
Etiology of postinfectious purpura fulminans?
|
Acquired severe protein S deficiency
Seen in kids 2 weeks after recovering from GAS or VZV Infection-triggered Ab interfere with protein S function |
|
|
Antiphospholipid antibodies sensitivity and specificity
|
Anticardiolipin Ab (screening)
Detects Abs with affinity for negatively charged membrane phospholipids Better sensitivity Lupus anticoagulant (confirmatory) Ab interferes with coagulation during measurement of PTT measured with Russell viper venom test Better specificity |
|
|
What are precipitating factors associated with catastrophic antiphospholipid Ab syndrome?
|
Infections
Meds (sulfa containing diuretics,captopril,OCPs) D/c anticoagulant Surgical procedures |
|
|
Clinical features of Sneddon's syndrome?
|
Livedo reticularis or racemosa
Labile HTN CNS symptoms due to cerebal vascular disease (CVA, TIA) recurrent fetal loss raynaud's |
|
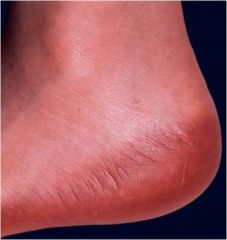
Medication?
|
Ara-c erythrodysesthesia
|
|
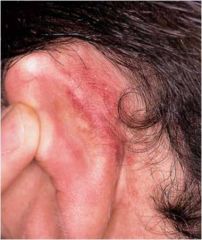
Medication?
|
Toxic erythema of chemo
Ara-C ears Petechiae due to thrombocytopenia |
|
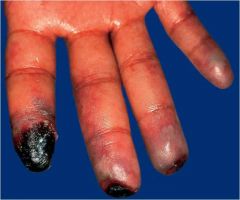
Medication?
|
Raynaud’s phenomenon with digital necrosis due to systemic bleomycin
|
|
|
What defect in patients with HIV is thought to increase their risk of cutaneous reactions to TMP-SMX?
|
acquired glutathione deficiency
|
|
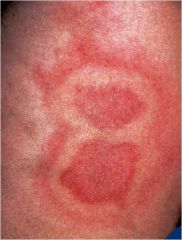
Etiology?
|
Reaction to vitamin K injection
|
|
|
What toll like receptor is activated by beta-defensin?
|
TLR-4
|
|
|
alpha-defensins increase expression of which cytokines?
|
TNF alpha, IL1
|
|
|
What mediates adhesion of langerhans cells to keratinocytes?
|
E-cadherin
|
|
|
Endogenous antigens complex with MHC1 or 2?
Exogenous antigens? |
Endogenous: MHC1
Exogenous: MHC2 |
|
|
What region of the TCR do streptococcal antigens bind-to to cause Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome?
|
beta variable
|
|
|
Th1 cytokines
|
IL12, TNFalpha, interferon gamma
|
|
|
Th1 diseases
|
psoriasis
ACD tuberculoid leprosy cutaneous (self-limited) leishmaniasis |
|
|
Th2 cytokines
|
IL4,5,6,10
|
|
|
Th2 diseases
|
atopic dermatitis
CTCL lepromatous leprosy disseminated cutaneous (chronic) leishmaniasis |
|
|
CD markers on Treg cells?
|
CD4+
CD25+ Foxp3+ (TF) |
|
|
What genodermatosis is associated with foxp3 gene defect?
|
IPEX
Immune dysregulation Polyendocrinopathy Enteropathy X-linked syndrome |
|
|
Which immunoglobulin fixes complement most efficiently?
|
IgM
|
|
|
Which IgG subcalsses activate complement the best?
|
IgG1 and IgG3
Less effective IgG2 IgG4 does not fix complement |
|
|
What is the name of the test used for assessing the presence of lupus anticoagulant activity?
|
Russell viper venom test
|
|
|
Triad in Sneddon syndrome?
|
livedo reticularis
labile HTN CNS disease May have fetal loss Tx: coumadin |
|
|
What type of T cells are involved in allergic contact dermatitis?
|
CD8+
|
|
|
What are the main markers currently used to detect B cells?
|
CD19,20,22
|
|
|
Subtype of EB with:
PPK with advancing age Oro-esophageal involvement Natal teeth Clumped tonofilaments on EM |
EBS-Dowling Meara
Most severe of EBS |
|
|
Type of EB associated with:
Sloughing of nails Perioral involvment with lip sparing |
Junctional EB
|
|
|
Gene defect in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia with skin fragility
|
plakophilin 1
Generalized erythroderma with blistering at birth short, sparse hair Thick, dystrophic nails |
|
|
Function of gene defective in Kindler's syndrome
|
Kind-1
Mb-associated signaling protein linking actin cytoskeleton to ECM |
|
|
EB associated with greatest risk of SCC development?
|
AR DEB-Hallopeau Siemens type
|
|
|
EB that can cause granulation tissue around the trachea leading to fatal asphyxia?
|
JEB-Herlitz type
|
|
|
Miliaria cystallina is caused by obstruction of the sweat glands at what level?
|
stratum corneum
|
|
|
Miliaria rubra: obstruction of sweat glands at what level?
|
malpighian layer
|
|
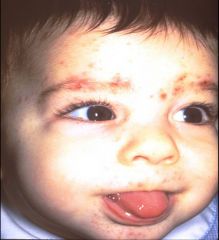
Diagnosis?
|
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis in infancy
Sterile pustules scalp and face, spares trunk/extremities |
|
|
MC eye abnormality in IP?
|
Strabismus
|
|
|
Gene defect and function in hyperIgE?
|
STAT3 gene
IL6 downstream mediator |
|
|
MC location of pyoderma gangrenosum in infants?
|
Perineal area
|
|
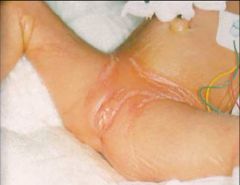
Rigid, taut, shiny translucent skin with linear splits in the flexural folds
Diagnosis and MCC death? |
Restrictive dermopathy
Pulmonary disease |
|
|
Gene defects in restrictive dermopathy?
|
LMN-A
ZMPSTE-24 (zinc metalloproteinase involved in post-translational modification of lamin A) |
|
|
3 genera under spirochaetales
|
Leptospira
Borrelia Treponema |
|
|
Signs of early congential syphilis
|
Marasmic syphilis
Typical secondary skin lesions (more bullous and erosive--pemphigus syphiliticus) Snuffles (bloody or purulent nasal discharge) Perioral and perianal fissures Lymphadenitis Skeletal involvement (pseudoparalysis) Reduced movement secondary to pain Pneumonitis, hepatitis, nephropathy, neurosyphilis |
|
|
Signs of Late congenital syphilis
|
Hutchinson’s Triad
Interstitial keratitis Hutchinson’s teeth Neural deafness |
|
|
Risk of transmission of congenital syphilis
|
100% when mom infected b/t conception & 7th month
<50% risk if mom infected more than 2 yrs prior to pregnancy Reduced risk of transmission after 7th month |
|
|
Treatment for primary, seconday, or early latent syphilis
|
Benzathine penicillin 2.4 MU IM
Alternate: doxy, TCN, E-mycin for 14 days |
|
|
Treatment for late latent syphilis
|
Benzathine penicillin 2.4 MU IM weekly x3
Alternate: doxy, e-mycin, TCN for 28 days. |
|
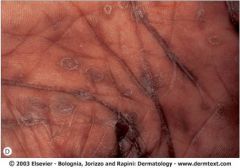
Diagnosis?
|
Collarette of Biett
Secondary syphilis |
|
|
Growth requirement for culture of Neisseria gonorrhea
|
iron
|
|
|
Culture media for Neisseria gonorrhea?
|
Thayer-Martin
|
|
|
Cause of acute painful genital ulcers w/ inguinal adenitis & buboes w/o systemic sxs
|
Chancroid
Hemophilus ducreyi |
|
|
Incubation period for chancroid?
|
3-10 days
|
|
|
Name of bodies in histiocytes in LGV?
|
Gamma-Favre bodies (Geimsa stain)
|
|
|
TOC for LGV?
|
Doxy x 3 weeks
Alternative: macrolides |
|
|
Incubation period for granuloma inguinale?
|
long: 2-12 weeks
|
|
|
Cause of non-tender genital sore without lymphadenopathy?
|
Granuloma inguinale (donovanosis)
Calymmatobacterium granulomatis |
|
|
Extragenital lesions in donovanosis?
|
Due to autoinoculation or dissemination
Most frequently to bone |
|
|
TOC for donovanosis?
|
Bactrim 1 tab bid x 3 wks
or Doxycyline 100mg bid x 3 wks |
|
|
HLA association with gestational pemphigoid?
Other associations? |
HLA-DR3, HLA-DR4
Graves disease Choriocarcinoma Hydatidiform moles |
|
|
What are fetal risks in herpes gestationis?
|
Increased risk of prematurity and SGA (small-for-gestatational age)
10% have skin lesions, usually mild No increase in fetal morbidity or mortality |
|
|
MC pregnancy dermatosis?
Risk factors for development? |
PUPPP
increased maternal weight gain multiple gestation higher prevalence w/ male fetus, C-section delivery |
|
|
Clinical presentation of cholestasis of pregnancy?
|
Typically during 3rd trimester
Onset coincides with UTI in 50% intense, generalized pruritus typically recurs with OCP Risk to fetus:Undefined tendency toward meconium/premature labor, fetal stress, and fetal death which may be reduced by treatment |
|
|
What is maternal risk of cholestasis of pregnancy?
|
Vitamin K malabsorption/deficiency leading to bleeding anomalies
Tends to develop cholelithiasis, gb disease |
|
|
Treatment of autoimmune progesterone dermatitis?
|
Tamoxifen or danazol
Inhibit ovulation by estrogen-containing preparations Recurrent cyclic flares of dermatitis that correspond to luteal phase of the menstrual cycle |
|
|
Pregnancy dermatosis with increased risk of stillbirth and placental insufficiency?
|
Impetigo herpetiformis
Pustular psoriasis of pregnancy Associated w/ hypocalcemia |
|
|
Medication that can provoke Darier's?
|
Lithium
|
|
|
Name the 2 non-syndromic diffuse hereditary PPKs
|
Vorner (epidermolytic, K9 (KI) defect)
Unna-Thost (non-epidermolytic, K1) |
|
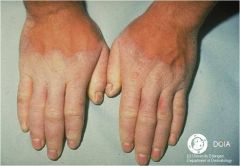
|
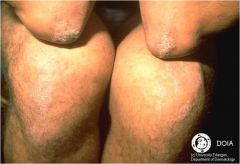
Mal de Meleda
Transgradient, malodorous PPK Elbows/knees involved Hyperhidrosis Periorificial lesions Thickened nails (koilonychia, subungual hyperkeratosis) |
|
|
Gene defect and eponym for transgradiens and progrediens PPK?
|
Greither's syndrome, AD, K1
Diffuse transgradient PPK with onset in infancy Hyperhidrosis Hyperkeratotic plaques on elbows and knees Histo: epidermolytic changes of granular layer (distinguishes from orthokeratosis and nl granular layer in mal de meleda) |
|
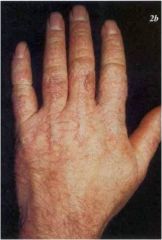
|
Vohwinkel's (Keratoderma hereditaria mutilans)
Pseudoainhum Starfish keratoses Honeycombed palms Variable hearing loss, ichthyosis, alopecia |
|
|
Clinical features of Bart-Pumphrey syndrome?
|
Knuckle pads
Leukonychia Sensorineural deafness Variable and mild PPK Connexin 26 (GJB2) |
|
|
Syndrome with mutilating PPK, ichythosis hystrix, normal hearing?
|
Curth-Macklin
K1 defect |
|
|
Eponym for PPK with scleroatrophy?
|
Huriez syndrome
Red, atrophic skin dorsal hands/feet mild PPK sclerodactyly Nail changes Almost complete absence of Langerhans cells At risk for SCC in atrophic skin |
|
|
Besides transgradient PPK and destructive periodontitis, other features in Papillon-Lefevre?
|
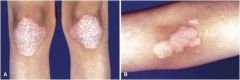
Psoriasiform lesions on extremities
Loss of teeth Pyogenic infections |
|
|
Syndrome allelic to Papillon-Lefevre?
|
Haim-Munk
Both due to cathepsin C defect PPK Periodontitis Arachnodactyly Atrophic nail changes Acro-osteolysis |
|
|
Eponym for mutilating PPK with periorificial plaques?
|
Olmsted syndrome
Keratoderma leads to flexion contractures Mutilation w/ digit constriction +/- autoamputation |
|
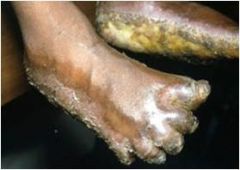
|
Olmsted syndrome
|
|
|
Clinical features of Naxos?
|
Diffuse NEPPK (erythematous border, non-transgradient): 1st yr of life
Woolly hair: birth R sided cardiomyopathy: puberty Plakoglobin gene, AR |
|
|
Gene defect in focal/striate nonsyndromic PPK
|
Desmoglein 1 (m/c), desmocollin, desmoplakin
AD |
|
|
Clinical features of Carvajal syndrome?
|
Striake EPPK (early infancy)
Woolly hair (birth) Left sided cardiomyopathy (adolescence) desmoplakin gene defect, AR |
|
|
In Howell-Evans, is late or early onset PPK associated with increased risk of esophageal cancer?
|
late onset PPK (age 5-10)
Esophageal cancer in 5th decade Other features of H-E: KP, dry skin, oral leukokeratosis |
|
|
Inheritance and gene defect in Howell-Evans?
|
AD, TOC gene
|
|
|
Inheritance and gene defect in Richner-Hanhart?
|
AR, hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase
|
|
|
PPK associated with degeneration of elastic fibers?
|
acrokeratoelastoidosis of costa
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of acute ICD?
|
Damaged keratinocytes
Increased TNFa, IL6, IL1b Upregulation of ICAM1 leading to T-cell inflammation |
|
|
What electrolyte abnormality can be found with exposure to hydrofluoric acid?
|
hypoMg
hypoCa |
|
|
What metal exposure can cause nasal septum perforation?
|
chromic acid
|
|
|
Which metal salt causes green hair discoloration?
|
copper
|
|
|
Which metal salt causes blue linear pigmentation of the tongue and gums?
|
inorganic mercury
(marker for systemic mercury poisoning) |
|
|
Metal salt causing ulcerating granulomas and possibly hypersensitivity reactions
|
beryllium compounds
|
|
|
Hematologic effect of benzene exposure?
|
aplastic anemia
|
|
|
What is the irritant in the plant Family Alliaceae?
|
thiocyanates
garlic, radish |
|
|
What is the irritant in the plant Family Amaryllidaceae?
|
calcium oxalate
daffodil, narcissus, hyacinth |
|
|
What is the irritant in the plant Family Euphorbiaceae?
|
Phorbol esters
In croton plant |
|
|
Gene defect in x-linked hypogammaglobulinemia?
|
BTK gene
tyrosine kinase that regulates conversion of pre-B cells to B cells |
|
|
Gene defect in x-linked hypogammaglobulinemia?
|
BTK gene
tyrosine kinase that regulates conversion of pre-B cells to B cells |
|
|
What viral infections are pts with X-linked hypogammaglobulinemia at increased susceptibility for?
|
hepatitis B
Enteroviral infections |
|
|
Gene defect in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease?
|
SH2DIA
Encodes signaling lymphocytic activation molecule associated protein critical for cytotoxic T cell function |
|
|
What viral infectino are pts with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease susceptible to?
|
Abnormal response to EBV infection
Stimulates rapidly progressive B cell lymphoma--death in 70% of affected boys |
|
|
MC ocular manifestation in kids with Behcet's?
|
bilateral panuveitis
associated with worse prognosis |
|
|
Prodrome in SJS/TEN?
|
fever
stinging eyes painful swallowing |
|
|
SCORTEN in SJS/TEN
|
Age > 40
Malignancy Tachycardia > 120 Initial surface of epithelial detachment > 10% Serum urea > 10 Serum glucose >14 Bicarb < 20 |
|
|
Skin finding in chronic rheumatic fever?
|
Subcutaneous nodules over bony prominences
|
|
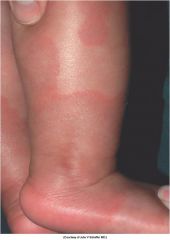
|
Annular erythema of infancy
|
|
|
Migration rate of erythema gyratum repens?
|
1cm/day
|
|
|
Associations with erythema gyratum repens?
|
85% w/ neoplasm (LUNG> breast, esophagus)
pulmonary TB icthyosis PPK hypereosinophilia |
|
|
Meds causing photoallergic reactions
|
MC: thiazides
sulfonamides sulfonylureas phenothiazines |
|
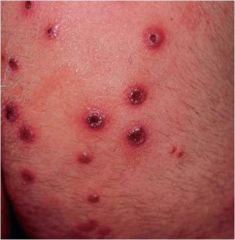
|
Iododerma
Erythematous, edematous vesiculopustules on the buttocks |
|
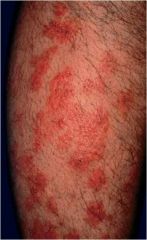
|
Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis
|
|
|
Predisposition to develop DRESS from anticonvulsants due to?
|
Defect in epoxide hydroxylase or the inability to detoxify arene oxide metabolites
Cross reactivity between phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital |
|
|
Predisposition to develop DRESS from sulfonamides due to?
|
Slow acetylators
Also susceptibility of lymphoid cells to toxic effects of the metabolite, hydroxylamine |
|
|
Meds causing DRESS
|
Anticonvulsants
Sulfonamides Dapsone Minocin Lamotrigine Allopurinol Abacavir |
|
|
Treatment with CS for DRESS when which organ systems involved?
|
Cardiac and lung
(Ineffective for liver or kidney involvement) |
|
|
MCC of pseudolymphoma?
|
Anticonvulsants
|
|
|
Skin findings in serum sickness like reaction?
|
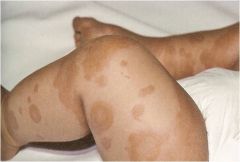
urticarial, EM-like with lilac center
|
|
|
Distinguishing features b/t serum sickness like reaction and serum sickness
|
SS-like: no hypocomplementemia, no immune complexes, no vasculitis, no renal involvement
Type II (cytotoxic) vs type III (immune complex) in SS |
|
|
Meds associated with telogen effluvium?
|
Anticoagulants: heparin> warfarin
β-blockers Lithium Retinoids |
|
|
Chemotherapeutic drug causing onycholysis?
|
paclitaxel
|
|
|
Mechanism of anagen effluvium from chemo agents?
|
Abrupt cessation of mitotic activity in the rapidly dividing cells of the hair matrix
|
|
|
Treatment for chemo-induced stomatitis?
|
Palifermin (keratinocyte growth factor)
Binds keratinocyte GF receptor, stimulates cells to grow and divide |
|
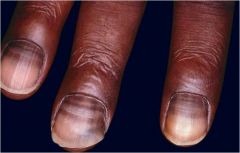
Medication?
|
5-FU
|
|
|
Drug associated with necrosis of psoriasis when overdosed?
|
MTX
|
|
|
Meds involved in drug-induced psoriasis?
|
Terbinafine, NSAIDs (<4wks latency)
Antimalarials, ACE inhibitors (4-12 wks) β-blockers and Lithium (>12 wks) |
|
|
Fungus associated with favic chandelier?
|
Trichophyton schoenlenii
|
|
|
Pectinate bodies
|
Microsporum audouinii
|
|
|
Spiral hyphae
|
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
|
|
|
Etiology of neonatal cephalic pustulosis
|
Malassezia sympodialis
|
|
|
Risk factors and etiology for Pityrosporum folliculitis
|
Chronic abx use, immunosuppression, local occlusion
Excessive growth of M. furfur & M. globosa |
|
|
MCC white piedra in pubic hair?
|
Trichosporon inkin--increased since HIV epidemic
|
|
|
MCC trichosporonosis?
|
T. asahii
serious systemic infection (fungemia, fever, skin lesions, pulmonary & renal disease) |
|
|
Typical locations for white and black piedra
|
White: face, axillae
Black: scalp, face |
|
|
Common causes of fluorescing ectothrix infection?
|
M. canis
M. audouinii M. distortum M. ferruginosum M. gypseum (Sometimes) |
|
|
Common causes of endothrix infection?
|
T. yaoundei
T. gourvilli T. rubrum T. tonsurans T. soudanese T. violaceum |
|
|
Most sensitive stain for dermatophytes?
|
calcofluour white
fluorescent stain specific for glucan chains in chitin and cellulose fungal cell walls |
|
|
What does chlorazol black stain?
|
E-chitin
|
|
|
Components of mycosel?
|
Sabaroud's dextrose agar with chloramphenicol (inhibits bacterial growth) and cycloheximide
|
|
|
What does cycloheximide inhibit?
|
Rapidly growing nonpathogenic moulds
Some pathogens: Scytalidium species, Cryptococcus neoformis, Some Candida species, Prototheca, Yeast forms of Histoplasma and Blastomyces |
|
|
Interpretation of DTM?
|
Dermatophytes utilize protein as a carbon source producing alkaline by-products causing the media to turn from amber to red
Nondermatophytes media to turn yellow due to acid by-products. |
|
|
MC webspace involved in erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica
|
3rd web space between MF and RF
One of cutaneous manifestations of DM |
|
|
MC endocrinopathy seen in APECED?
|
hypoparathyroidism
|
|
|
MCC mycetoma in US?
|
Pseudoallesheria boydii
Asexual state: Scedosporium apiosperum White grains Tx: miconazole |
|
|
Treatment for actnomycetoma
|
Nocardia species: sulfonamide
Actinomyces: penicillin |
|
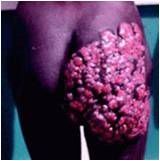
|
Actinomadura pelletieri
Red grains |
|
|
In the U.S. the Splendore-Hoeppli phenomenon is most commonly associated with what organism?
|
Botryomycosis: S. aureus or pseudomonas
|
|
|
Treatment for sporotrichosis?
|
SSKI (iododerma, GI upset, hypothyroidism)
Itraconazole(CHF)--NOT ketoconazole |
|
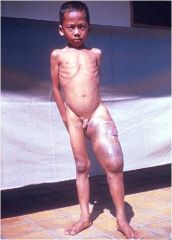
|
Basidiobolomycosis
Basidiobolus ranarum Saprophyte with worldwide distribution Infection m/c in kids in tropical/subtropical climates Solitary, indurated, painless, subcutaneous nodule or swelling of the thigh or buttock RX: SSKI, ketoconazole, TMP-SMX Surgical excision not recommended |
|
|
Characteritic clinical presentation of protothecosis?
|
olecranon bursitis
|
|
|
Treatment of lobomycosis
|
Antifungals not effective
Surgical excision, cryosurgery Possibly clofazimine |
|
|
MC cutaneous manifestation of histoplasmosis?
|
Oral ulcers
|
|
|
MC opportunistic infections in neutropenic pts?
|
Systemic Candidiasis
Aspergillosis |
|
|
Systemic mycosis seen most commonly in HIV?
|
Disseminated histoplasmosis
Coccidioidomycosis Penicillium marneffei Cryptococcosis |
|
|
MCC of disseminated aspergillosis with cutaneous involvement?
|
Aspergillus fumigatus
|
|
|
MCC primary cutaneous aspergillosis?
|
Aspergillus flavus
|
|
|
MC fungus in burn patients?
|
Fusarium
Aspergillus 2nd MCC |
|
|
What stains the capsule of cryptococcus?
|
Mucicarmine or Alcian blue
India Ink (PAS for organism) |
|
|
Fungi causing molluscum-like umbilicated papules
|
Cryptococcus
Histoplasmosis Penicilliosis Coccidioidomycosis |
|
|
Treatment for zygomycosis?
|
Ampho B
|
|
|
What two organism are most commonly isolated from subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis?
|
Exophiala jeanselmei
Exophiala dermatitidis |
|
|
What organism most commonly causes CNS phaeohyphomycosis?
|
Cladosporium trichoides (Cladophialophora bantiana)
|
|
|
All porphyrias are AD except which?
|
ALA-dehydratase deficiency
Gunther's (CEP) |
|
|
Factors precipitating acute porphyria attacks?
|
All increase increased synthesis of cytochrome P450 in liver:
alcohol, drugs, infections, fasting/diets, changes in steroid production (eg. menses, OCP’s, pregnancy) |
|
|
Difference in RBC fluorescence b/t EPP and CEP
|
EPP: transient
CEP: stable |
|
|
What are the acute porphyrias?
|
No skin findings: AIP, ALA-D deficiency
Skin findings: VP, HCP |
|
|
Receptors expressed by mast cells?
|
CD34, KIT & IgG receptors (FcγRII)
Do NOT express high affinity IgE receptors (FcεRI) |
|
|
What are preformed mediators in mast cells?
|
hepain, histamine, neutrophilic & eosinophilic chemotactic factors, trytase/chymase
|
|
|
MC location for mastocytoma?
|
distal extremities (dorsal hand near wrist)
|
|
|
What lab test correlates wtih systemic disease in mastocytosis?
|
alpha and beta tryptase
100% pts w/ levels > 75 ng/ml had proven systemic dz Preferred test over urinary histamine / metabolites |
|
|
Urinary findings in mastocytosis?
|
Urinary histamine
Urinary MeImAA (1,4-methylimidazole acetic acid) Metabolite of histamine Often persistently elevated Correlates to extent of disease |
|
|
What systemic mastocytosis pts can be treated with imatinib?
|
FIP1L1-PDGFRA translocation OR
Lack 816 c-KIT mutation (Does not work for pts w/ 816 c-KIT mutation) |
|
|
What embryonic week does nail appartus first appear?
|
9th week
|
|
|
Which part of epithelium of nail apparatus keratinizes with a granular layer?
|
Hyponychium
(Nail matrix and bed do not) |
|
|
Keratins in nail matrix keratinocytes?
|
K 6, 16, 17
|
|
|
Where in nail apparatus are melanocytes?
|
Distal matrix and suprabasal layers
|
|
|
Where in nail apparatus are Langerhans cells?
|
Suprabasal layers of matrix
More common in proximal vs. distal matrix |
|
|
Growth rate of finger and toenails?
|
Fingernails: 2-3mm/month
Toenail: 1mm/month Hair:1 cm/month |
|
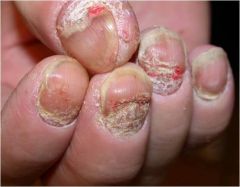
|
Onychomadesis
|
|
|
What causes nail pitting?
|
Abnormal keratinization of proximal nail matrix leads to clusters of parakeratotic cells in dorsal nail plate
AA, psoriasis, eczema |
|
|
Causes of trachyonycia?
|
"20 nail dystrophy"
AA, LP, Psoriasis, Eczema |
|
|
Drugs associated with multiple longitudinal bands of melanonychia?
|
AZT
5-FU Doxorubicin Psoralens |
|
|
Association with Muehrcke's lines?
|
Hypoalbuminemia (nephrotic syndrome)
chemotherapy Paired transverse white bands Apparent luekonychia |
|
|
Onychomadesis with pseudopyogenic granuloma of the proximal nail fold is a sign of what condition
|
Mild and transitory peripheral nerve injury
Seen in pts w/ phalanx, metacarpal or wrist bone fractures during or after cast immobilization |
|
|
Which type of dermatophyte-associated onychomycosis is highly associated with HIV-infected patients?
|
Proximal subungual onychomycosis
T. rubrum |
|
|
What drugs may be responsible for causing nailfold pyogenic granulomas?
|
Retinoids
Indinavir Lamivudine Methotrexate EGFR inhibitors* |
|
|
Chemotherapeutic agent causing subungual hemorrhages & absesses?
|
Taxanes (paclitaxel and docetaxel)
|
|
|
What is cheilitis glandularis?
|
PAINFUL hypertrophy of lower lip
Dilated/inflammed salivary secretory ducts Mucopurulent secretion can be expressed |
|
|
MC intraoral sites for lymphoma?
|
palate and vestibule
MC type : NHL, B-cell type |
|
|
MC intraoral location for melanoma?
|
Hard palate, maxillary gingiva
|
|
|
MC oral lesion in Crohns?
|
Linear fissures/ulcers
|
|
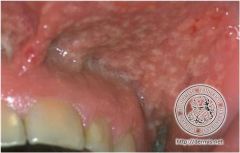
|
Pyostomatitis vegetans
Creamy-yellow “snail track” pustules & ulcers set against a background of diffusely red mucosa M/C labial, gingival and buccal mucosa Dorsum of tongue is SPARED |
|
|
Which proteins are found in reduced levels in humans with lipodystrophies?
|
1) Adiponectin: plays a role in regulating insulin sensitivity and glucose and lipid homeostasis
2) leptin: decreased level results in TG accumulation, insulin resistance, diabetes, hepatic steatosis 3) glut 4: when absent, leads to insulin resistance |
|
|
Potential cause of death in congenital generalized lipodystrophy?
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (fatal); avg age of death 32
|
|
|
Gene defects in congenital generalized lipodystrophy?
|
AGPAT2
BSCL2 (seipin) |
|
|
Distinguishing features between CGL and acquired generalized lipodystrophy?
|
AGL: women > men, more liver complications, often preceded by systemic illness, manifests later in childhood, involves palms/soles
|
|
|
Gene defects in Familial partial lipodystrophy?
|
Progressive loss of subq fat after normal childhood; predominantly extremities
FPLD1: Kobberling (spares face), unknown FPLD2: Dunnigan (most common), AD, LMNA gene, fat accumulation in head/neck FPLD3: PPARG mutation encoding PPARgamma |
|
|
Associated systemic diseases in acquired partial lipodystrophy?
|
mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, low C3, C3 nephritic factor, autoimmunity
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of acquired partial lipodystrophy?
|
presence of adipsin (identical to factor D, imp in alternative complement pathway)
Fat cells + C3NeF leads to unopposed activation of alternate pathway and fat lysis |
|
|
How is acquired lipodystrophy from NRTI different from PI-induced lipodystrophy?
|
No insulin resistance seen with NRTI
Pathogenesis linked to mitochondrial damage |
|
|
What is Donohue syndrome?
|
Look like generalized lipodystrophy
Severe insulin resistance, AN, hirsutism Elfin facies, severe IUGR, prominent nipples, loose skin, macrophalus, early death Insulin receptor gene mutation |
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Kidney disease + complement dysfunction |
Barraquer-Simons (acquired partial)
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Full body atrophy + cirrhosis + death due to variceal bleeds |
Lawrence (acquired generalized)
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Fat loss of the extremities + compensatory acromegalic facies |
Berardinelli-Seip (Congenital generalized)
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Myocardial infarction due to hyperlipidemia + increased omental fat |
Protease inhibitor-induced
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Diffuse fat atrophy except palms and soles + severe acanthosis nigricans |
Berardinelli-Seip (Congenital generalized)
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
High-pitched voice + short stature + acro-osteolysis + clavicular hypoplasia |
Mandibuloacral variety (familial partial)
|
|
|
Which lipodystrophy?
Fat loss of the extremities + NO facial fat compensation |
Kobberling variety (familial partial)
|
|
|
MC presentation of
cutaneous histoplasmosis & coccidiomycosis in HIV? |
Ulcers on face & mouth
|
|
|
Distribution of scabies in HIV + patients?
|
Distribution in HIV is ears, face & scalp
|
|
|
What test should be ordered if diagnosis of reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome) is made?
|
HIV
Strong association b/t the two |
|
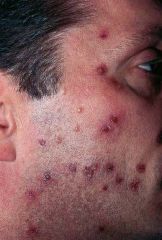
Diagnosis?
|
Eosinophilic folliculitis
Excoriated follicular papules & pustules on forehead & trunk |
|
|
HIV meds associated with alopecia?
|
nucleoside analogs
|
|
|
Which HIV protein upregulates expression of HPV?
|
tat protein
|
|
|
Which type of neoplasms are HIV + pediatric pts more at risk of compared to adults?
|
HIV kids: higher incidence of MALT
More smooth muscle tumors (leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas) |
|
|
What immunophilin does sirolimus bind?
|
FKBP12
|
|
|
MOA of enfuvirtide
|
Fusion inhibitors for HIV infection
Blocks HIV from entering target cells by inhibiting gp41 mediated viral-cell membrane fusion |
|
|
Dematiaceous organism causing dermatomycoses of the soles and toe webs, paronychia, onychomycosis
|
Scytalidium dimidiatum
|
|
|
Treatment for lobomycosis?
|
Surgical excision
Antifungals ineffective |
|
|
MC organ system affected in paracoccidiodomycosis after lung and skin?
|
adrenal glands
|
|
|
MC fungus in burn patients?
|
fusarium
|
|
|
Opportunistic organism causing white superficial onychomycosis?
|
scopulariopsis
|
|
|
Candida species implicated in oropharyngeal Candidiasis in HIV infected patients
|
C. dublinensis
|
|
|
Candida species causing chronic paronychia?
|
C. parapsilosis
|
|
|
Candida species resistant to fluconazole
|
C. glabrata
|

