![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In Tuberous Sclerosis, what are the genetic mutations most commonly seen and what protein associated with?
|
Autosomonal dominant
75% = new spon't mutations TSC2>1 (3:1) Mutation of tumor suppressor genes: 1) TSC1 = chr9q34, hamartin 2) TSC2 = chr 16q13, more severe, encodes tuberin |
|
|
What does 'Epiloia' stand for?
|
Epilepsy
Low intelligance Angiofibroma *in TS |
|
|
For TS, what is the progress of symptoms?
|
1) hypomelanotic macules (at birth),
2) Facial angiofibromas (approx 2yo), 3) Shagreen patches (4-6yo) 4) Periungual fibromas (6-8yo) |
|
|
What dx criteria for TS?
|
Definite TS = 2 MAJOR or 1 M + 2minor
Probable TS = 1 M + 1m Possible TS = 1 M or 2+m |
|
|
What are the Major dx criteria for TS?
|
12
4 = cutaneous FAST TAN CLaRK Facial angiofibromas/forehead plaque Ash leaf spot (>3) Shagreen patch Tumors (koenen, toe>fingers) Tubers, cortical Astrocytoma, subependyma giant cell Nodules, subependymal Cardiac, rahbdomyoma Lymph... angioleiomyomatosis Retinal hamartomas Kidneys, angiomyolipoma |
|
|
What are the minor dx criteria for TS?
|
9
Dental pits Bone cysts Gingival fibromas Confettis skin lesions Rectal polyps Cerebral raditiona migration lines Multiple renal cysts Non-renal hamartomas Retinal achromic patch |
|
|
What is the most common type of arrhythmia in TS?
|
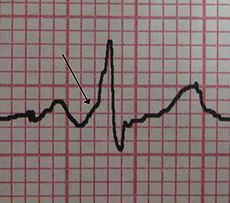
Woff Parkinson white syndrome
-0.1-0.3% population has --> sudden death -asymptomatic -can be dizzy, SOB, syncope -delta wave! (see ECG) -bundle of kent |
|
|
What are the 4 most common TS lesions?
|
Enamel pits (almost all)
Cardiac rhabdo (infants) Hypopigmented macules Facial angiofibromas Multiple cortical tubers |
|
|
Ddx of TS?
|
o MEN1
o hypopigmented macules: nevus depigmentosus, piebaldism, vitiligo o shagreen patch: congenital smooth muscle hamartoma, congenital melanocytic nevus o FAFs: acne, trichoepitheliomas |
|
|
Explain the work up for tuberous sclerosis?
|
• Hx
• P/E for skin lesions (Wood’s lamp), biopsy lesions •Neuro: o neurodevelopmental testing o CT/MRI brain (cortical tubers, SEN, lateral ventricle calcification), US in infants through fontanelle o EEG (if seizures) Cardiac: o EKG o echocardiography for cardiac rhabdomyomas (< 1y.o.) Renal: o renal US at baseline & q3–4 years Chest: o CT chest (women) for lymphangioleiomyomatosis Eyes: as needed o ophthalmologic exam for retinal hamartomas Genetics: o prenatal genetic testing or fetal echo For assessing family members: 1) CT brain, 2) renal US, 3) genetic testing |

