![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ANP
|
28 AA polypeptide secreted in response to stretch
1. Dilates afferent arterioles in kidney, inhibits renin secretion, and limits Na+ resporption in proximal tubule and collecting duct 2. Restricts aldosterone secretion 3. relaxes vascular smooth muscles in arterioles & venules. ↑ capillary permeability to allow fluid extravasation. |
|
|
Describe the electrolyte movements which determine the membrane potential of the cardiac pacemakers
|
4: Funny Current: Gradual Inward Sodium Current
0: Upswing: Calcium Channels 3: Repolarization: K+ movement |
|
|
Holosystolic mumurs
|
Mitral Regurgitation: loudest at apex and radiates towards axilla
Enhanced by: ↑ TPR (Hand grip, sqyatting) or LA return (expiration) 2° to: ischemic heart dz, prolapse, LV dilation Tricuspid Regurgitation: loudest at Tricuspid area, radiates to right sternal border Enhanced by: ↑ RA return (inspiration) 2° to: RV dilation, endocarditis (Rheumatic fever can cause both) VSD: Holosystolic harsh sounding, loudest at tricuspid area |
|
|
Mitral Regurgitation
|
Holosystolic murmur loudest at apex and radiates towards axilla
Enhanced by: ↑ TPR (Hand grip, sqyatting) or LA return (expiration) 2° to: ischemic heart dz, prolapse, LV dilation |
|
|
Tricuspid Regurgitation
|
Holosystolic murmur loudest at Tricuspid area, radiates to right sternal border
Enhanced by: ↑ RA return (inspiration) 2° to: RV dilation, endocarditis (Rheumatic fever can cause both) |
|
|
VSD
|
Holosystolic harsh sounding murmur, loudest at tricuspid area
|
|
|
Systolic Murmurs following Clicks
|
Aortic Stenosis
click-crescendo-decrescendo-S2 -aortic area, radiates to carotids/apex puslsus parvus et tardus: late and weak 2° to: age related calicifcation or bicuspid valve Mitral Prolapse: click-crescendo-S2 2° to: myxomatous degeneration, rheumatic fever, chordae rupture enhanced with: ↓ venous return (standing, valsalva) |
|
|
Continuous machine like murmur
|
PDA, loudest at S2
2° congenital rubella or prematurity |
|
|
Aortic Stensosis
|
Aortic Stenosis
click-crescendo-decrescendo-S2 -aortic area, radiates to carotids/apex puslsus parvus et tardus: late and weak 2° to: age related calicifcation or bicuspid valve |
|
|
Mitral Prolapse:
Sound Causes Enhancing the Sound |
click-crescendo-S2
2° to: myxomatous degeneration, rheumatic fever, chordae rupture enhanced with: ↓ venous return (standing, valsalva) |
|
|
Mitral Stensosis
Sound Causes Enhancing the Sound |
Diastolic Murmur
Follows "Opening Snap" S2-silent--snap-murmur 2° rheumatic fever results in LA dilation enhanced by ↑ LA return (expiration) Best indicator of intensity: S2 to opening snap |
|
|
Regions of the Hypothalamus
|
Lateral Nucleus: Hunger.
--lesion → anorexia, failure to thirve. inhibited by leptin Venteromedial: Satiety. Stimulated by leptin; --lesion → extreme hunger and rage Dorsomedial: uninhibited → "sham rage" animal like biting, hissing, clawing --lesion → ↓ agression & anorexia Anterior: cooling, parasympathetic activation Posterior: heating, SNS activation Suprachiasmatic: circadian rhythm --lesion → no rhythm Supraoptic: ADH Paraventricular: Oxytocin (Oxys = quick, toxos = birth) |
|
|
Confirming Menopause
|
[FSH]
Normally LH: induces follicular progesterone prodxn FSH: induces granulosa conversion of progesterone to estradiol loss of estrogen feedback → unregulated FSH |
|
|
Coronary Arteries during Exercise: what limits flow rate
|
flow rate ↑ 5x during exercise from vasodilation/contraction forcing blood through system
limitation on flow rate is duration of diastole |
|
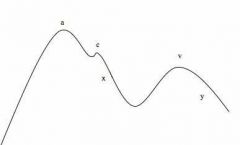
|
a: right atrial contraction
c: right ventricular contraxn (bulging tricuspid) x: right atrial relaxn v: continued inflow of blood y: passive emptying after tricuspid valve opening |
|
|
What hormone induces the secretion of bicarbonate
|
Secretin produced by the S cells in the duodenal mucosa in response to acidity
|
|
|
Gastrin
|
produced by G cells in the grastric antrum
induced by stomach distention, vagal stim, food decreased by acidity Fnx: ↑ histamine release from enterochromaffin-like cells → ↑ H+ pump fnx; ↑ gastric mucosal growth & gastric motility ↑↑↑ in Zollinger Ellison Sro |
|
|
G cells
|
Found in antrum of stomach, Produce gastrin
induced by stomach distention, vagal stim, food decreased by acidity Fnx: ↑ histamine release from enterochromaffin-like cells → ↑ H+ pump fnx; ↑ gastric mucosal growth & gastric motility ↑↑↑ in Zollinger Ellison Sro |
|
|
I cells
|
Found in Duoedenum and Jejunum
stimulated by fatty acids & AA's to produce cholecystokinin activates muscarinic pathways to ↑ pancreatic secretion ↑ gallbladder contraxn relax sphincter of oddi ↓ gastric emptying |
|
|
CCK
|
Produced by I cells found in duodenum and jejunum in response to fatty acids & AA's to produce cholecystokinin
activates muscarinic pathways to ↑ pancreatic secretion ↑ gallbladder contraxn relax sphincter of oddi ↓ gastric emptying |
|
|
D cells
|
pancreatic islets adn GI mucosa
produce somatostatin when stimulated by acid; inhiibted by vagal stimulation inhibitory hormone which decreases: gastric acid & pepsinogen secretion GI fluid secretions gallbaldder cotnraction insulin & glucagon release |
|
|
K cells
|
found in duodenum and jejunum
stimulated by fatty acids, amino acids and oral glucose to produce Glucose-dependent Insulotropic peptide (GIP) ↓ gastric H+ secretion ↑ insulin release NB: oral glucose uptaken by ts faster than IV glucose because of GIP effect |
|
|
Glucose depndent Insulinotropic peptide
|
GIP
produced by K cells found in duodenum and jejunum when stimulated by fatty acids, amino acids or oral glucose ↓ gastric H+ secretion ↑ insulin release NB: oral glucose uptaken by ts faster than IV glucose because of GIP effect |
|
|
Motilin
|
Produced by Small intestin in fasting state
produces migrating motor complexes (MMC's) ie peristalsis |
|
|
Which stomach cells produce what?
|
Parietal Cells: Intrinsic Factor and Gastric Acid
Cheif Cells: Pepsinogen (activated by H+) G cells: Gastrin |

