![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a non-nutrient?
|
A substance that occurs in the diet that has advantageous health benefits but is not essential for survival. Can be toxic at high doses.
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols
|
- products of secondary metabolism of plants.
- produced in response to stress (as pathogen defence against fungi/bacteria, UV light protection, antioxidants) - can cause astringency due to binding to salivary glands which makes some plant inedible. Also binds metal ions which can cause deficiency. - structure: one or more benzene rings with phenol (OH) side chain. |
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Flavanols
|
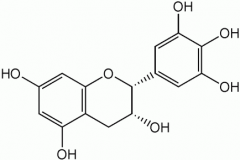
- found in redwines, apples, black tea.
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Flavonols
|
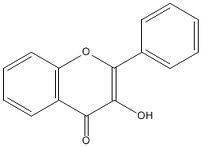
- found in onions, broccoli, apples, green and black tea
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Flavone
|
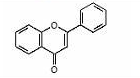
- found in celery, pepper, olives, citrus fruit, parsley.
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Anthocyanidins
|
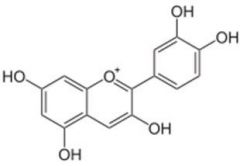
- found in strawberries, raspberries, eggplant, red wine, red grapes
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Isoflavones
|
- found in soy products (flour, beans, milk, souce etc), tofu
|
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - Daily intakes
|
- flavanols 100mg/day
- flavonols 3-64mg/day - anthocyanidins 200mg/day - isoflavones 50mg/day in east, as low as 1mg/day in UK |
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - adsorption
|
- attach to sugars to present as glycosides which can interact with transporters in the gut to get absorbed by the small intestine
- if the sugar is too large they become non-interacting and pass into large intestine where they are broken down by bacteria in gut flora. |
|
|
Phenols and polyphenols - epidemiology
|
- use info from cross sectional and longitudinal studies to identify any health benefit.
- eg Elderly's study found polyphenols inversely associated with CHD with a 68% reduction in risk with people consuming over 19mg/day. Reduction in stroke risk of 54% with 18-28mg/day consumption, and 73% for over 28mg/day - thought to act as antioxidant by scavenging free radicals and supporting/protecting other antioxidants (vitamins etc) - also bind metal ions which can cause lipid oxidation - lowers intake of carbohydrates which can lower risk of type II diabetes. - helps maintain a healthy gut flora. |
|
|
Terpenes
|
- fat soluble unbranched 5c chain which join together to form large structures
- triterpenes: 6 unit C30 structure, eg carotenoids - tetraterpenes: 8 unit C40 structure eg sterols/stanols - coffee diterpenes: C20 structures eg caffestol, kahweol. |
|
|
Sulphur containing compounds
|
- Alliaceae containing foods eg onions, chives, garlic
- organic disulphides responsible for hot taste and watering of the eyes, produces enzymatically when tissue is damaged, can be decreased by pickling/cooking to inhibit enzymes - Brassicas foods such as cabbage, broccoli, sprouts, cress etc - glucosinolates and isothiocyanates produced enzymatically when tissue is damaged, causes taste and odour, also thought to reduce risk of some cancers (sulphorophan) |
|
|
Alkaloids (nitrogen containing)
|
- caffeine, mild stimulant in tea, coffee, chocolate, cola etc. Prevents sleep and encouraged wakefulness, can elevate blood pressure. not recommended for pregnant women as can cross placenta.
- quinine, antimalarial properties, found in tonic water, high dose can have negative effect on eyes - solanum alkaloids, in green potatoes, typically 1-15mg/100g, aids in pest and disease resistance in the plant, can make bitter taste and high dose can cause GI symptoms, cardiovascular/respiratory depression and occasionally death. |

