![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the purpose of fatty acid synthesis? Where does it occur? What goes in/out? Regulation?
|
Energy Storage
Location: Cytoplasm of hepatocytes Acetyl CoA-->Fatty Acids Regulation: Rapid control via AcCoa carboxylase |
|
|
In what type of environment are fatty acids stored? What does this allow for?
|
Non-aqueous environment; allows for large stores
|
|
|
How do energy sources change from the fed state to post-absorptive state? 24 fast? 72 hour fast?
|
Fed: Energy from diet
Post-Absorptive: Glycogen breakdown 24 hour fast: Gluconeogenesis 72 hour fast: FA oxidation (not as glucose!) |
|
|
What are examples of esterified fatty acids? How are unesterified fatty acids transported in blood?
|
Esterified: TG's, cholesterol ethers, phospholipids
Must circulate while bound to ALBUMIN |
|
|
What are the essential fatty acids?
|
Linoleic Acid and Linolenic Acid
|
|
|
Describe the first step of fatty acid synthesis.
|
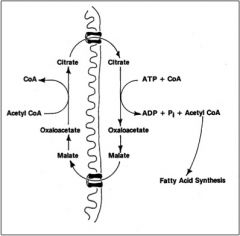
Acetyl Group Shuttle:
Acetyl CoA from inside mitochondria to cytosol via Citrate |
|
|
Describe the second step of FA synthesis.
|
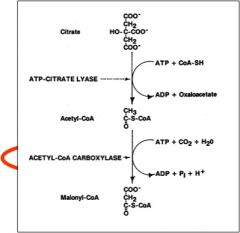
Malonyl CoA Synthesis:
RATE LIMITING STEP! Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase is RATE LIMITING ENZYME for FA Synthesis Regulated by insulin and counterregulatory hormones |
|
|
What's the rate limiting enzyme for FA synthesis? How is it regulated?
|
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase
Insulin, Norepi, Glucagon |
|
|
Describe the third reaction of fatty acid synthesis. What's the energy source that drives this reaction?
|
Malonyl-CoA + Acetyl CoA + NADPH-->Palmitate
Via Fatty Acid Synthetase Complex (REDUCTION REACTION!!!) Driven by NADPH (14 of them) from HEXOSE MONOPHOSPHATE PATHWAY |
|
|
What is the fatty acid synthase complex? What is its overall reaction? Requirements?
|
Complex of 7 enzymes that facilitate successive steps in FA synthesis
General: Lengthens FA by 2C's via REDUCTION REACTION!!! Requires acyl carrier protein (ACP) and Pantothenic acid (vitamin)--latter is what malonyl-coA binds |
|
|
What steps occur after formation of Palmitate? Where do these steps occur?
|

Elongation: ER and mitochondria in brain and adrenal gland
Desaturation: ER and catalyzed by oxidases |
|
|
If vertebrates lack the enzyme to convert oleic acid to linoleic acid, how is this acid obtained?
|
Through diet. It's an essential fatty acid. As is linolenic acid.
|
|
|
Describe the three fatty acids esterified to glycerol.
|
They're usually different, C1 saturated, C2 unsaturated, C3 can be either
It's complicated. |
|
|
What two functions do white fat cells serve?
|
Energy Storage
Metabolic functions: make cytokines (for inflammation) |
|
|
What is the purpose of fatty acid degradation? Where does it occur? What goes in/out? Regulation?
|
Purpose: Provision of energy
Location: mitochondria (it's oxidation) Dietary and Stored FA's-->CO2 + H2O + ENERGY (once completely oxidized) OR KETONE BODIES (in liver) Regulation: transport into mitochondria via carnitine shuttle |
|
|
Describe the first step in fatty acid oxidation.
|
Triacylglycerol (stored in fat cells)-->
Diacylglycerol + FFA--> Monoglyceride + FFA--> Glycerol + FFA All via Hormone-Sensitive Lipase: activated by cAMP-dependent kinase; inactivated by insulin |
|
|
Describe the second step in fatty acid oxidation.
|
Mitochondrial Transport in Liver Cell:
Outer mitochondrial membrane: RCOO- + CoA-SH+ATP-->RCO-S-CoA via Faty Acyl-CoA Synthase RCO-S-CoA + Carnitine--> RCO-Carnitine + CoA-SH Via CPT1 RCO-Carnitine + CoA-SH--> RCO-S-CoA in inner mitochondrial membrane via CPT II THIS IS THE REGULATORY POINT IN FATTY ACID OXIDATION!!!! |
|
|
Why are only long-chain fats subject to regulation?
|
Carnitine transport system is required for importing FA's of chain length longer than 12C's.
|
|
|
What is the third step of FA oxidation?
|
RCO-S-CoA + FAD-->Enoyl-S-CoA + FADH2
Via Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase |
|
|
Via what reaction is most energy derived from fat?
|
beta-oxidation
|
|
|
What do steps 4 to 7 of FA oxidation result in? Quantify this in terms of ATP.
|
Enoyl-S-CoA-->-->-->8 acetyl-S-CoA + 7FADH2 + 7NADH + 7H+
2ATP per FADH2 3 ATP per NADH =35 ATP 8 acetyl=CoA-->96 ATP Total: 131 ATP per mole |
|
|
Describe the steps of ketogenesis. When and where do these reacitons occur?
|
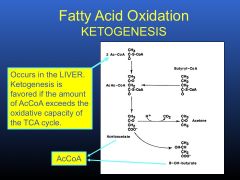
|
|
|
How is ketogenesis triggered?
|
In fasted state, have net flux of OAA-->Glucose (gluconeogenesis)
Decrease in OAA --> decreased acetylCoA used for citrate formation acetyl CoA then preferentially convereted to acetoacetate (AcAcCoA) So ketogenesis behaves as an overflow PW for AcCoa |
|
|
What's the effect of carbohydrate availability on ketogenesis?
|
Low cab availability-->increased hepatic ketogenesis
|
|
|
Explain diabetic ketoacidosis.
|
Lack of insulin stimulates lipolysis in periphery
Released TG's transported to liver where ketogenesis is fully activated Results in diabetic ketoacidosis |
|
|
What's the purpose of alpha-oxidation? Location? In/out? Regulation? Clinical relevance?
|
Purpose: metabolize Fa's that can't undergo direct beta-oxidation
Location: Peroxisomes FA (alpha-carbon is substrate for hydroxylation)-->alpha-OH FA's Regulation: Substrate-driven Clinical Note: Defective in REFSUM'S DISEASE |
|
|
What's the purpose of omega-oxidation? Location? In/out? Regulation? Clinical notes?
|
Purpose: Alternative metabolism of FA's
Location: Extra-mitochondrial (microsomal) In/Out: FA (omega-carbon)-->Dicarboxylic FA's REgulation: Substrate-driven Notes: Upregulated if beta-oxidation defective |
|
|
What are symptoms of MCAD?
|
Medium Chain Acyl-CoA DH Deficiency:
Fatty Liver No ketonuria Hypoglycemic Accumulation of medium chain fatty acids (octanedioic, nonanedioic, decanedioic acids) |

