![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
155 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is kinetics? |
*Study of forces that cuase motion |
|
|
So far what has kinematics been? |
Linear or angular |
|
|
What is kinematics? |
Study of forces that cause motion |
|
|
Momentum is a product of
A) mass and acceleraiton B) Force and acceleration C) Mass and velocity D) Force and velocity |
C |
|
|
What is the conservation of momentum |
The total momentum of a system of objects is constant if the net external force acting on the system is zero |
|
|
Does the conservation of moment have to do with Newton's 1st, 2nd or 3rd law? |
All of them |
|
|
Can you do a conservation of energy in addition to conservation of momentum |
Yes |
|
|
What is the equation for the conservation of momentum |
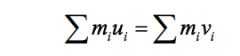
u is the inital velocity V=final velocity |
|
|
How do we conserve momentum in terms of velocity |
Have the same velocity on each end |
|
|
What are the two types of collisons? |
Elastic and inelastic |
|
|
What is an eleastic collsiion |
All of the energy is conserved (full energy conservation, complete recoil) |
|
|
What is an example of an elastic collision |
Two foot ball players hit and split apart |
|
|
What is an inelastic collison? |
When objects combine together
(two things clump together and stay together) |
|
|
What is an example of an inelastic collision? |
Two football players hit then fall down together |
|
|
Are collisions mainly elastic or inelastic or are they in between |
In between |
|
|
An elastic collision needs a conservation of what? |
Energy |
|
|
What is the equation for conservation of momentum |
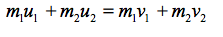
|
|
|
What is the equation for the conservation of energy? |
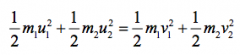
|
|
|
During an elastic collision what do you lose energy in the form of? |
Strain energy (main reason why a breakage occurs) or heat (byproduct) |
|
|
During an inelastic collision, what happens to the objects? |
Objects that are moving combine together and move at the same velocity after collison |
|
|
Is energy conserved in an inelastic collision? |
No, energy is not conserved, eventually the energy will dissipate |
|
|
What happens to the energy that is not conserved in an inelastic collsion? |
It will be sotred for a bit but then will be lost in the surrounding tissues in the form of strain energy
(or in the tendons) |
|
|
What are the equations for the inelastic equation |
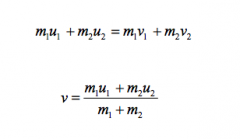
|
|
|
What is Payton's velocity given these conditions:
Mass = 92 kg velocity = 3m/s
Defensive Back mass: 100 kg velocity = -4 ms |
(92)(3)+(100)(-4)=(92+100)(v)
v= -0.634 m/s
Payton loses |
|
|
What is the Fridge's velocity given these conditions?
Mass: 148 kg Velocity= 3 m/s
Defensive Back mass = 100 kg velocity = -4 m/s |
(148)(3)+(100)(-4) = (148+100)(v)
v= 0.18 m/s
The fridge wins |
|
|
What is the way to solve for coeeficient of restitution? |
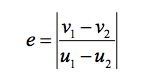
One object's initial velocity minus final veloicty over the opposite object's initial velocity over final velocity |
|
|
For an object that has a coefficient of restitution of 1 what does that tell us about the impact? |
It was purely elastic (velocity strike with in 100% of return velocity) |
|
|
What is the coefficient of resitution equation for a ball drop equation |
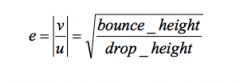
|
|
|
WHERE DOES THE BALL DROP EXPERIMENT EQUATION COME FROM? |
PE VS KE |
|
|
For F = ma what newton's law does it have to do with? |
2nd |
|
|
What is the inverse dynamics of newton's 2nd law? |
given a, m
Find: f |
|
|
What is the direct dynamics of the F =ma equation? |
given f, m
find: a |
|
|
What is the force required to life a 20 kg box in a static (a=0) case? |
(m)(g) |
|
|
What is the force required to lift a 20 kg box in a dynamic case (a=5 m/s2) |
F=(20)(5) + (20)(g)
(Exerting more force) |
|
|
(Need to calculate) |
|
|
What is the impulse equation |
Impulse = change in momentum
FΔt = m(final velocity - inital velocity) |
|

|
Crumple Force: F=(2700 + 150)(70 mph/0.06)
Find answers |
|
|
What are the biomechanics of safety devices
|
*Helmets: Decrease energy strain in head *Airbags: How/when drop affects how much force to expand it *Car seats *Cushioned seats |
|
|
What makes a muscle cell different than other cells of the body?
A) Mitochondria B) Myofibrils C) Nucleus D) Cell membrane |
Answer: B
Myofibrils are only present in muscular tissue |
|
|
A motor unit is:
A) A single motor neuron and a single muslce fiber
B) Multiple motor neurons and single muscle fiber
C) A single motor neuron and multiple muscle fibers
D) Multiple motor neuron and multiple muslce fibers |
Answer: C
*Receiving more of neurons
*All neurons innervate some number of fibers |
|
|
What is stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
A) Sodium B) Calcium C) Hydrogen D) Potassium |
Answer: B
Calcium is stored and released during a contraction |
|
|
What does botox block?
A) Action potential B) Release of ACH into neuromuscular junction C) Release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum D) Binding of acting and myosin |
Answer: B
*ACH is the connection point between the nerve and the muscle fibers -ACH is the interface |
|
|
What is the smallest contractile element of a muscle?
A) Fascicle B) Muscle Fiber C) Myofibril D) Sarcomere |
Answer: D
A--> C are all contractile units, they all just happen to be larger than a sarcomere |
|
|
What does the sliding filament theory of contraction state? |
Sarcomere shortening results from the relative movement of the acting attached to the vertical planes and getting pulled
The myosin have heads that bind to the action and that is the one that is moving |
|
|
The energy (in the form of ATP) is used to
A) Break actin-myosin bonds B) Form Actin-myosin bonds C) Release calcium form the sarcoplasmic reticulum D) Return calcium to the sarcoplasmic reticulum |
Answer: ?? |
|
|
What is the organization of muslce? |
Muscle --> Fascicle --> Muscle fiber --> Myofibril --> sarcomere
(They are all tubes) |
|
|
The maximal active force generating capacity of a skeletal muscle occurs when the muscle is at its
A) minimal length B) mid-range length C) Maximal length D) Force capacity is independent of length |
Answer: B
|
|
|
What does the length-tension curve look like? |
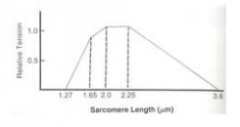
|
|
|
What are the lengthened, optimal and shortened sarcomere lengths look like? |

|
|
|
_______ will help to determine the properties of a muscle |
The number of sarcomeres in series or in parallel |
|
|
Having sarcomeres in series will allow for high what? |
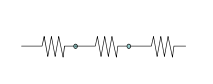
High velocity and ROM orientation |
|
|
What does three sarcomeres in parallel produce a high of? |
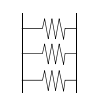
High force orientation |
|
|
Does having three sarcomeres in sereis or in parallel produce a bulkier muslce? |
In parallel |
|
|
The longer the tendon-to-tendon length, the greater number of sarcomeres in _______ |
Series |
|
|
The greater the physiological cross-sectional area (PCSA) the greater number of sarcomeres in ______ |
Parallel |
|
|
What mechanism is generally employed by the CNS to regulate muscle force?
A) Temporal summation B) Spatial summation |
Spatial summation
[Recruit one motor neuron then keep recruiting it and if need to produce more force will go to temporal summation of those neurons] |
|
|
What is temporal summation |
"call often" |
|
|
What is spatial summation |
"Call friends"
|
|
|
Maximal muscle force is proportional to
A) Cross-sectional area B) Resting sarcomere length C) Fiber length D) Tendon width |
Answer A
[Force produced increases when CSA increases
The resting sarcomere lenght have to do with the force and length optimal relationship
The resting sarcomere length and fiber lenght have relationship to it] |
|
|
What equation can you use to find the force of the muscle with the physiological cross sectional area? |
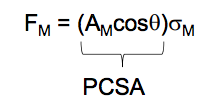
AM = Area of muscle
Cos θ = Cosine of penation |
|
|
What is the PCSA equation equal to |
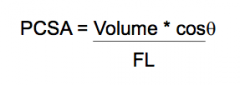
|
|
|
Can you get more muscle in with angle of pennation? |
Yes, when have angle, you have more surface area to play on to get more muscles in |
|
|
Draw a diagram of fibers with no pennation and without pennation |
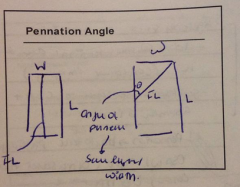
|
|
|
Maximal force can be generated during what type of muscle contraction?
A) Eccentric B) Concentric C) Plyometric D) Isometric |
Eccentric |
|
|
What are the three componenets of a muscle-tendon model |
1) Contractile component 2) Parallel Elastic Componenet 3) Series Elastic Componenet |
|
|
What is the contractile componenet of the muscle-tendon model |
Active shortening of msucle through actin-myosin structures |
|
|
What is the parallel elastic component of the muscle-tendon model? |
Parallel to the contractile element
The connective tissue network |
|
|
What is the series elastic componenet of the muscle-tendon muscle? |
In series with the contractile element
Resides in the cross bridges between the actin and myosin filaments and the tendons |
|
|
What are the passive elements of the force-length characteristics of muscles? |
*Parallel elastic componenent *Series elastic componenent |
|
|
What is the parallel elastic component? |
*The connective tissue that surrounds and is parallel to the contractile element (IE muscle membranes or fascia) supplies resistence when a muscle is passively stretched
When the muscle is at resting length or less, the parallel elastic component is in a slack state with no tension |
|
|
What is the series elastic component |
(During dynamic situations)
All connective tissue in series with the contractile element (IE tendon) act as a spring to store elastic energy when a tensed muscle is stretched |
|
|
What componenets are part of the total tension? |
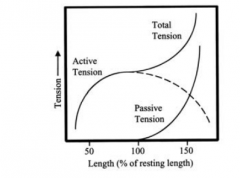
Active tension + passive tension
tension = force produced |
|
|
What is the force velocity characters of the muscles |
A decrease of tension as the muscle shortens and an increase as it lengthens |
|
|
What kind of skeletal muscle fiber types are there? |
*Slow twitch fiber *Fast twitch fiber |
|
|
What are slow twitch fibers? |
Type 1
A fiber that reaches peak tension relatively slowly |
|
|
What is fast twitch fiber |
Type IIa and IIb
A fiber that reaches peak tension relatively fast
Large diameter, fatigues more quickly and generates increased amount of torque |
|
|
What is a graph of fast twitch vs slow twitch muscle? |
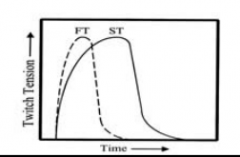
|
|
|
What type of fiber type is recruited first? |
Type I |
|
|
Can fiber type change with training? |
Yes |
|
|
What fibers are important contributers to performances requiring fast, power muscular contraction; eg. sprinting and jumping |
Fast twitch |
|
|
What fiber types are good for endurance performances such as distance running, cycling and swimming require effective functioning of more fatigue resistant fibers? |
Slow twitch |
|
|
What is the equation for work? |
W = F * d |
|
|
What is the equation of work for angular kinematics? |
W = Torque * θ
(Torque times angular displacement |
|
|
What is the units for torque? |
Joules |
|
|
Is work scaler? |
Yes |
|
|
What does positive work mean? |
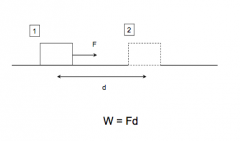
Force in the same direction as the distance moved |
|
|
What does negative work mean? |
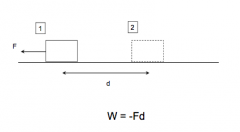
Work done in the opposite direction of displacement of an object |
|
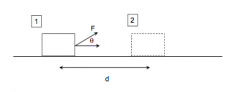
How do you find work when the force is not aligned with displacement?
|
W=Fcos(θ)d |
|
|
What is work equal to in the terms of energy |
W = ΔKE + PE
KE = Energy of momentum PE=Stored energy |
|
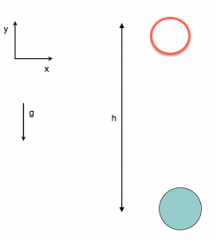
What is the work equal to in this situation where it starts from the top and is at the bottom?
(Hold ball above head and let go)
|
w1 = mgh w2=-mgh (w=0+(0-mgh))
W=0 |
|
|
How can we measure work done on a treadmill?
A) Have the runner slow down B) Have the runner speed up C) Keep treadmill flat D) Tilt treadmill |
Answer: D |
|
|
An athlete pedals 60 revolutions on a cycle ergometer, against a resistance of 50 N, what is her work output (in Joules)
R=40 cm |
W =F*d
W=(50)(2*π*r)(60) = (50)(2)(π)(0.4)(60) = 7500 J
Means work done on the bike |
|
|
What does energy mean? |
The capacity of the system to do work on another system
Work is the change of energy of the systme |
|
|
What are the two comonenets of mechanical energy |
Kinetic energy Potential Energy |
|
|
What is kinetic energy |
Energy of motion |
|
|
What is potential energy |
Stored energy |
|
|
What is the equation for the linear kinetic energy? |
1/2*m*v^2 |
|
|
What is the equation for the angular kinetic energy |
KE = (1/2)(I)(ω)^2 |
|
|
What is the units of kinetic energy? |
kg*m^2/s^2
or
Joules |
|
|
Is energy scaler or a vector? |
Scaler |
|
|
Is torque a vector or a scaler? |
Vector |
|
|
What is the equation for PE |
mgh |
|
|
What is the untis for PE |
Joules |
|
|
Whati s the spring PE equation? |
PE = (1/2)(K)(x^2) |
|
|
What is the units for Spring PE |
Joules |
|
|
What parameter is measured in direct calorimetry
A) work B) Power C) Heat D) Oxygen |
C |
|
|
What is direct calorimetry? |
Measurement of heat production as an indication of metabolic rate
|
|
|
What is direct calorimetry measured in? |
calories |
|
|
What is one kcal equal to in Joules |
1 kcal = 4 186 J |
|
|
What gas is important for the measurements of indirect calorimetry? |
Oxygen |
|
|
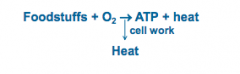
What is indirect calorimetry? |
Measurement of oxygen consumption (VO2) as an estimate energy expenditure
Food + O2 --> work + heat |
|
|
If there is an increase in VO2 what does that mean for work performance |
Increased |
|
|
What is the work-energy theorem |
W = ΔKE + ΔPE
The work done by the external forces ( other than gravity) acting on an object causes a change in energy of the object |
|
|
When there isn o work what does that mean for mechanical energy? |
Conservation of mechanical energy
ΔKE + Δ PE =0 |
|
|
What is power? |
Force * distance /time |
|
|
What is the units of power? |
Watts |
|
|
Is power scaler or vector? |
Scaler |
|
|
What is power in terms of F and velocity |
F*v
Because P=W/t = F*d/t |
|
|
What is power in terms of angular kinematics |
T*ω |
|
|
What is the relationship btween velocity and force? |
As velocity increases so does force |
|
|
An athlete pedals 60 revs per minute on a cycle ergometer against a resistance of 50 N, what is the power output in watts (r = 40 cm) |
p = 125 watts |
|
|
The tendon of which rotator cuff muscle is most commonly torn?
*Subscapularis *Supraspinatus *Infraspinatus *Teres minor *Teres major |
Supraspinatus |
|
|
Why is the supraspinatus the most suseptible to tears? |
Because it is the sandwiched between two bones and the tendon can get compressed |
|
|
What directions can you dislocate the shoulder |
Every direction except superiorly because of acromion process
(If start to get superior forces, not good for tendon because of the tendon there) |
|
|
What is the single most common shoulder patholog? |
Impingement syndro |
|
|
What is the impingement syndrome? |
The rotator cuff tendon is between two bones |
|
|
What are some possible mechanisms for an impingement syndrome? |
*Biological
Related to anatomy (Some people have flat acromion others have swooped acromion
Inflammation of surrounding joints or spaces
Overuse |
|
|
What does intrinsic mean? |
How tendon used |
|
|
What does extrinsic mean? |
How tendon looks and biomechanical |
|
|
What do you think happens to the orientation of the glenohumeral joint reaction force when the deltoid force increases |
More superior |
|
|
Given:
-Weight of upper extremity (Fw) = 50 N -Moment Arm of upper extremity weight = 20 cm -Deltoid moment arm =Supraspinatus moment arm = 2 cm -Supraspinatus vector (Fs) aligned with horizontal axis -Deltoid vector (FD) at 60 degrees with respect to horizontal axi -Joint reaction force (R) unknown magnitude and direction
Step 1-FBD Step 2-Use SM = o to find an equation in the form Fs + FD = ? Step 3-Use SF = 0 to find an equation in the form Ry/Rx |
Answer on Week 6-2 lecture |
|
|
What is the positive feedback loop of Rotator Cuff damage |

|
|
|
What is the angular analogy of f=ma |
t= Iα |
|
|
For the moment of inertia, the further away the mass is from the axis of rotation, the (more or less) resistence to motion |
More |
|
|
What are the ways to determine the moment of inertia |
1) Add up the contributions of all mass elements
2)Radius of gyration
3) Known or assumed shapes
4) Parallel axis theorem
5)Give to you to look up |
|
|
What is the equation of inertia (I) in terms of the radius of gyration (l) |
I =m *(k^2) |
|
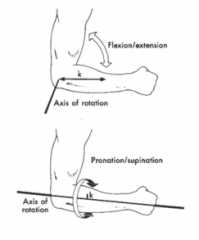
Which axis has a larger I?
A) flexion/extension B) Pronation/Supinatin C) Same |
Flexion//extension |
|
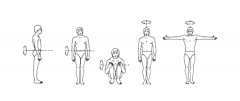
Which person would have the greatest moment of inertia |
The first two on the left |
|
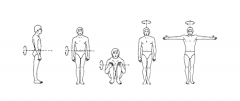
Which person would have the smallest moment of inertia? |
Fourth one |
|
|
What is the angular analog of Newton's 1t Law? |
A rotating body will continue to turn aobut its axis of rotation with constant angular momentum, unless acted upon by an external torque
(Conservation of angular momentum)
H = I * ω |
|
|
What is the angular analog of Newton's 2nd Law? |
The rate of change of angular momentum of a body is proportional to the toruqe causing it
T = I (ωf-ωi/t)
or
T = I * α |
|

|
Completed on lecture week 7-1
Answer: ω = 16 rad/s |
|

|
Answer on last page of lecture week 7-1
1) Fd = 236.5 N
2) FD=436.5 N |
|
|
What are the functions of skeletal muscles? |
*Movement and posture maintenance *Heat production *Protecture *Pressure alteration |
|
|
Basic contractile unit of a muscle |
Sarcomere |
|
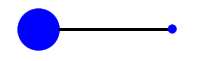
Where is the COM for this object? |
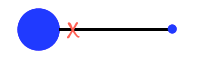
Lot more mass towards proximal
Need to know something about the mass to know where the COM would be located, it is not just in the middle |
|
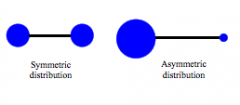
How does the COM differ for these two distributions? |
Symetric: COM in middle
Asymmetric Distribution: COM closer to larger mass |
|
|
What is the equation to find the x and y coordinates of the COM |
X (cm) = (all of the (m)(x) / all of the masses)
Y is the same except with y for all of the Xs |
|
|
What segment of the body has the most mass distribution? |
Trunk
Therefore, wherever the trunk goes, is where the person is headed |
|
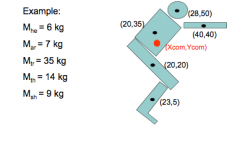
What is the y and x of the COM for this situation? |
X = 23 cm y=30 cm
(Work in lecture 7-2) |
|
|
What is the Whole Body Center of ass? |
Imaginary point that the whole body is concentrated at |
|
|
Where is the whole body center of mass approximately located ? |
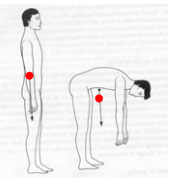
Located just in front of the lumbosacral junction during standing posture
And then when out of standing posture, may move outside of the body |
|
|
What is COG refered to in terms of the COM |
The COG refers to the horizontal position of the COM because only forces ogravity are considered
Effects of gravity are independent of vertical position |
|
|
What is the motion of COM during walking? |
Generally in the pelvic area and rises up and down |
|
|
How can elderly enhance stability |
But increasing base of support by adding a walker |

