![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
116 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which is true regarding action potential? |
2 of above |
|
|
Which type of muscular tissue is characterized by many nuclei per fiber, striations, & voluntary control? |
Skeletal |
|
|
Which is true regarding a resting neuron? |
Cytoplasmic fluid contains more potassium ions than interstitial fluid |
|
|
Which neurotransmitter governs emotional states, body temp, sleep patterns, & endocrine activity? It's a neurotransmitter that makes us feel happy. |
Seratonin |
|
|
The part of the neuron that contains the nucleus is____? |
Cell body |
|
|
Smooth Muscle: |
is found in the gut |
|
|
Which serves as a method to clean up the synaptic cleft following release of neurotransmitters? |
3 of above |
|
|
____ disease results in tremors caused by a dopamine shortage. |
Parkinson's |
|
|
Which is a stimulant? |
Crystal meth |
|
|
Which neurotransmitters helps the body respond to stress? |
Epinephrine |
|
|
Which of the following stem cell types are totipotent? |
Fertilized egg undergoing LESS than 4 divisions |
|
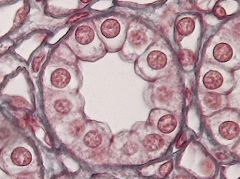
Name the tissue: |
Simple Cuboidal |
|
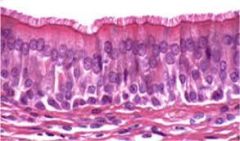
Name the tissue: |
Simple Columnar |
|
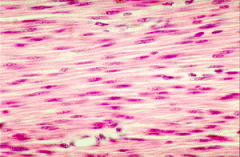
Name the tissue: |
Smooth Muscle |
|
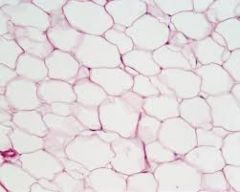
Name the tissue: |
Adipose Tissue |
|
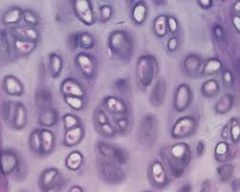
Name the tissue: |
Cartilage |
|
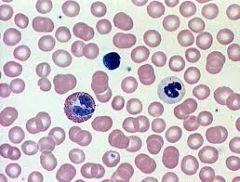
Name the tissue: |
Blood |
|
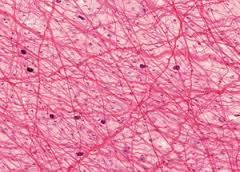
Name the tissue: |
Loose Connective |
|
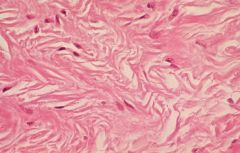
Name the tissue: |
Dense, Irregular Connective |
|
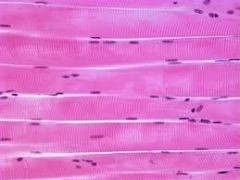
Name the tissue: |
Skeletal |
|
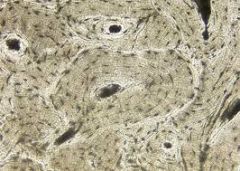
Name the tissue: |
Bone |
|
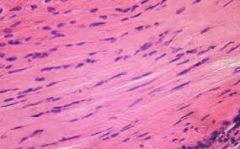
Name the tissue: |
Dense, Regular Connective |
|
|
Which statements regarding a resting neuron are true? |
2 of above |
|
|
The influx of ___ triggered by an action potential that reaches the output zone leads to the release of neurotransmitter vesicles |
Calcium |
|
|
Conduction from node to node: |
is quicker type of nerve conduction & involves jumping of impulses |
|
|
Which part of the PNS relays info from receptors in skin to CNS, then delivers commands to brain to skeletal muscle? |
Somatic |
|
|
Which part of the brain governs respiration, sleep, wake cycle, circulation, swallowing, & defecating? |
Medulla Oblongata |
|
|
Which half of the cerebrum contains centers for artistic appreciation, music, & abstract concepts? |
Right |
|
|
Which ion is most concentrated in the extracellular fluid of a resting neuron? |
Sodium |
|
|
Which structure is located in the dermis? |
2 of above |
|
|
Which disease is linked to destruction of melanocytes? |
Vitiligo |
|
|
Which of the neurotransmitters is commonly released at neuromuscular junctions? |
Acetycholine |
|
|
Which leads to the release of the egg from the ovary? |
LH |
|
|
Excessive amounts of GH released during adulthood leads to _____. |
Acromegaly |
|
|
Which lobe of the pituitary is characterized by the presence of axonal endings that originated in the hypothalamus? |
Posterior |
|
|
A sudden drop in blood pressure would lead to the release of ____? |
ADH |
|
|
Which are secretions of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland? |
None of above |
|
|
Which hormones cross plasma membranes & find receptors in the nucleus? |
Steroid Hormone |
|
|
What part of the brain is split during Sperry's Split Brain procedure? |
Corpus Collasum |
|
|
When is oxytocin released? |
During labor contractions |
|
|
When does a cell become pluripotent? |
When it undergoes more than 4 divisions |
|
|
What is a tissue? |
Group of cells performing a common task |
|
|
What does Lining Tissue (epithelial) cover? |
Outside of body and internal areas |
|
|
What does Connective tissue do? |
Binds things together and supports them |
|
|
What does muscular tissue do? |
Moves body parts (contracting & detracting) |
|
|
What does Nervous tissue do? |
Reacts to stimuli |
|
|
What is an organ? |
Group of tissues working together |
|
|
What is an organ system? |
Group of two or more organs
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization? |
Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism |
|
|
In ____tissue, one surface is free and the other adheres to a basement membrane. |
Epithelial Tissue |
|
|
___ epithelium is one-cell thick and may have flat squamous, cuboidal, or columnar cells |
Simple |
|
|
Simple _____ epithelium allows substances to diffuse through readily in areas like the lungs |
Squamous |
|
|
Simple _____ and simple _____ epithelium may contain cilia to move substances along, as in the oviducts |
Cuboidal & Columnar |
|
|
_____ epithelium has many layers and is found in regions that get much wear and tear-as in human skin |
Stratified |
|
|
What are glands? |
secretory organs derived from epithelium |
|
|
_____ glands often secrete through ducts to free surfaces; they secrete mucus, saliva, wax, milk, etc. |
Exocrine |
|
|
_____ glands secrete hormones directly into intercellular fluid by distribution by the blood. |
Endocrine |
|
|
_____ accounts for 95% of all cancers |
Carcinomas |
|
|
_____ supports epithelia and organs, and surrounds blood vessels and nerves; it contains fibroblast cells and fibers plus macrophages |
Loose Connective Tissue |
|
|
____ has thicker fibers and more of them, but fewer cells; it forms protective capsules around organs |
Dense, Irregular Connective Tissue |
|
|
____ has its fibers in parallel; this is the arrangement found in tendons and ligaments |
Dense, Regular Connective Tissue |
|
|
____ contains a dense array of fibers in a jellylike ground substance |
Cartilage |
|
|
Where do tendons connect? |
Muscle to bone |
|
|
Where do ligaments connect? |
Bone to bone |
|
|
____ muscle is composed of short, striated, branching cells that can function in units. |
Cardiac |
|
|
____muscle tissue contains spindle-shaped cells; it lines the gut, blood vessels, and glands |
Smooth |
|
|
____ are excitable cells, organized as lines of communication throughout the body |
Neurons |
|
|
____neurons receive stimuli and send messages to the brain |
Sensory |
|
|
____ store information and coordinate responses |
Interneurons |
|
|
____ neurons send signals to muscles or glands |
Motor |
|
|
____ are diverse cells that protect and metabolically support the neurons |
Neuroglia |
|
|
The ____divides the coelom into the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity |
Diaphragm |
|
|
When a stimulus reaches a certain _____ gated channels open and sodium rushes in |
minimum threshold |
|
|
Action potentials are _____ events-at any given time, a neuron is either resting or excited |
All-or-Nothing |
|
|
When _____ in one region is ended, the sodium gates close and potassium gates open |
Depolarization |
|
|
The ____ membrane pumps also become operational to fully restore the resting potential |
Sodium-Potassium |
|
|
Action potential is ______ and moves away from the stimulation site to adjacent regions of the membrane undiminished |
Self propagating |
|
|
A brief _____ period follows at each depolarization site-sodium gates shut, potassium gates open |
Refractory |
|
|
____ is a junction between a neuron and an adjacent cell, separated by a synaptic cleft into which a neurotransmitter substance is released |
Chemical synapse |
|
|
The neuron that releases the neurotransmitter molecules into the cleft is called the ______ cell. |
Presynaptic |
|
|
_____ causes the vesicle to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron |
Calcium |
|
|
Neurotransmitters may have ______ effects if they drive a cell's membrane to the threshold of an action potential |
Excitatory |
|
|
Neurotransmitters may have ______ effects if they help drive the membrane away from the threshold |
Inhibitory |
|
|
Both _____ and epinephrine are neurotransmitters that prime the body to respond to stress |
Norapinephrine |
|
|
_____ affects fine motor control and pleasure-seeking behaviors |
Dopamine |
|
|
____ is a small neurotransmitter derived from the amino acid tryptophan, which affects mood and memory |
Serotonin |
|
|
____ drugs stimulate the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in the sense of pleasure |
Addictive |
|
|
____increase alertness and attentiveness |
Stimulants |
|
|
____ and caffeine block Ach receptors |
Nicotine |
|
|
_____increases the sense of pleasure by blocking reabsorption of norapinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin |
Cocaine |
|
|
_____increase dopamine, serotonin, & norepinephrine, reducing appetite and energizing users |
Amphetamines |
|
|
______ (ecstasy) and crystal meth are ampethamines |
MDMA |
|
|
_____slow motor responses by inhibiting Ach output |
Depressants |
|
|
____ nerves (31 pairs) connect with the spinal cord and innervate most areas of the body |
Spinal |
|
|
_____ (12 pairs) connect vital organs directly to the brain |
Cranial |
|
|
___ nerves increase overall body activity during times of stress, excitement, or danger |
Sympathetic |
|
|
____ nerves tend to slow down body activity when the body is not under stress |
Parasympathetic |
|
|
What color matter contains the cell bodies, dendrites, unsheathed axons, and neuroglia? |
Gray |
|
|
What color matter contains myelin sheathed axons and neuroglia? |
White |
|
|
____ acts as a reflex center for maintaining posture and coordinating limbs |
Cerebellum |
|
|
___ integrates sensory input and selected motor responses |
Cerebrum |
|
|
____ relays and coordinates sensory signals |
Thalamus |
|
|
____monitors internal organs and influences responses to thirst, hunger, and sex |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
___ lobe contains the primary somatosensory cortex-main receiving area for signals from the skin and joints |
Parietal |
|
|
____ lobe has centers for vision |
Occipital |
|
|
____ lobe is a processing center for hearing and houses centers for influencing emotional behavior |
Temporal |
|
|
____ system governs our emotions and has roles in memory |
Limbic |
|
|
____ cortex allows us to correlate organ activities with self-gratifying behavior such as eating and sex |
Cerebral |
|
|
____is a pea sized gland connected to the hypothalamus by a stalk |
Pituitary gland |
|
|
____ of the pituitary gland consists of nervous tissue and releases two neurohormones made in the hypothalamus |
Posterior lobe |
|
|
___stimulates the adrenal cortex (ACTH) |
Adrenocorticotropin |
|
|
___ stimulates the thyroid gland (TSH) |
Thyroid Stimulating |
|
|
___stimulates egg formation in females and sperm in males (FSH) |
Follicle Stimulating |
|
|
___ also acts on the ovaries to release an egg and on the testes to release sperm (LH) |
Luteinizing |
|
|
____ acts on mammary glands to sustain milk production |
Prolactin |
|
|
___ acts on body cells in general to promote growth (GH) |
Growth Hormone |

