![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the three principles of cell theory? |
1.) all living things are composed of cells 2.) cells are the basic unit of life 3.) new cells are produced by existing cells |
|
|
|
What are the differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells? |
Prokaryotes have NO nucleus Eukaryote HAVE nucleus |
|
|
|
What is cytoplasm? |
Is the portion of the cells outside the nucleus |
|
|
|
Nucleus is the what of the cell |
Control center |
|
|
|
What do ribosomes do? |
Make proteins Proteins are assembled on ribosomes |
|
|
|
What does the ER do? |
Helps finish assembling proteins makes membranes |
|
|
|
Rough ER and smooth ER |
Rough works on proteins Smooth makes membranes |
|
|
|
What does the Golgi apparatus do? |
Finishes sorts labels and ships proteins (ups or fed ex) ships proteins in vesicles (vehicles) |
|
|
|
What do lysosomes do? |
Digest food (used to make energy) clean up and recycle |
|
|
|
What does the vacuole do? |
Pumps excess water out fo the cell |
|
|
|
What does the mitochondria do? |
Power house of the cell Converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use |
|
|
|
What does the chloroplasts do? And what cell are they in? |
They capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis |
|
|
|
What does cytoskeleton do? |
A network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape. It is also involved in movement |
|
|
|
Where are centrioles found? And what do they do? |
Located near the nucleus Help organize cell division |
|
|
|
What does the cell membrane do? |
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection and support |
|
|
|
What does the cell wall do? |
Protects the cell |
|
|
|
What are solutes? |
Substances dissolved in solution |
|
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Particles in a solution tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated |
|
|
|
What is osmosis? |
The diffusion of water through selectively permeable membranes |
|
|
|
Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic |
Hypertonic above strength Hypotonic below strength Isotonic same strength |
|
|
|
What is endocytosis? |
The process of taking material into the cell |
|
|
|
What is exocytosis? |
Materials are forced out of the cell |
|
|
|
What is mitosis |
Division of the cells nucleus |
|
|
|
What is mitosis |
Division of the cells nucleus |
|
|
|
What is cytokinesis |
Division of the cell cytoplasm |
|
|
|
What are chromosomes |
Genetic information is passed from one generation to the next before cell division each chromosome is duplicated or copied- consists of two identical “sister” chromatid- each pair of chromoatifs is attached at an area called the centromere |
|
|
|
What is interphase |
The period of growth that occurs between cell division |
|
|
|
What is interphase |
The period of growth that occurs between cell division |
|
|
|
4 phases of cell cycle and define them |
G1- the cell increases in size synthesizes new proteins and organelles S phase- chromosomes are replicated DNA synthesis takes place once entered it usually completes the rest of the cycle G2- organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced once complete the cell is ready to start m phase M phase- mitosis |
|
|
|
What are cyclins? |
Group of closely related proteins that will regulate the cell cycle |
|
|
|
Mitosis 4 phases and define them |
Prophase-centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus chromatin- condenses into chromosomes and becomes visible - nuclear envelope breaks down Metaphase- chromosomes line up across the center of the cell Anaphase- the sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes- spindles directed by centrioles are used to pull the chromosomes apart Telophase- chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell and lose their distinct shape- a nuclear envelope forms around each cluster of chromosomes |
Pmat |
|
|
During cytokinesis what happens |
The cytoplasm punches in half- each daughters cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes |
|
|
|
Name the stuff in animal cells |
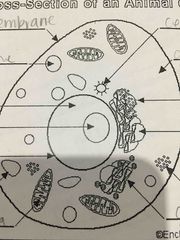
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Name the stuff in plant cells |
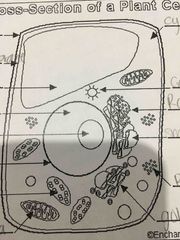
Back (Definition) |
|

