![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
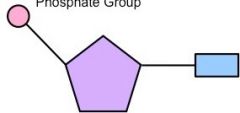
What part of the nucleotide is coloured purple in this image? |
The pentose sugar |
|
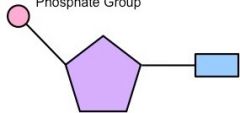
What part of the nucleotide is coloured blue in this image? |
The nitrogenous base |
|
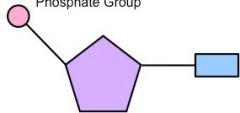
What part of the nucleotide is coloured pink in this image? |
The phosphate |
|
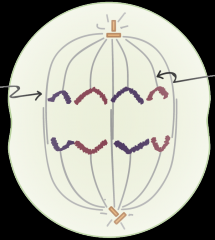
What stage of mitosis is this? |
Anaphase |
|
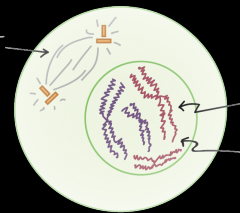
What stage of mitosis is this? |
Early prophase |
|
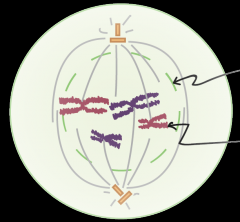
What stage of mitosis is this? |
Late prophase |
|
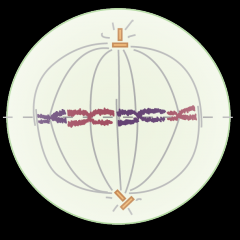
What stage of mitosis is this? |
Metaphase |
|
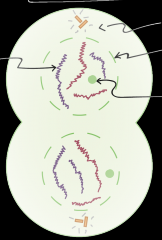
What stage of mitosis is this? |
Telophase |
|
|
What is the complimentary DNA sequence for: ATCG |
TAGC |
|
|
What is the complimentary RNA sequence for: ATCG |
UACG |
|
|
If DNA is grown in a N15 medium, and placed to replicate in an N14 medium, what will the density of the second generation DNA be when centrifuged? |
50% medium density and 50% low density |
|
|
What are the four nitrogenous bases of DNA? |
Adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine |
|
|
What are the four nitrogenous bases of RNA? |
Adenine, Guanine, Uracil, Cytosine |
|
|
What is homologous recombination? |
One chromosome from the mother and one from the father crossover and trade DNA from the same section of each chromosome |
|
|
Which of chromosomes (in males only) are not homologous? |
23rd Chromosome |
|
|
What is the difference between prophase I and prophase II? |
No DNA replication takes place in prophase II |
|
|
What happens in prophase I? |
Chromosomes join up with their homologous pairs and undergo recombination |
|
|
What happens in metaphase I? |
The chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell |
|
|
What happens in anaphase I? |
The chromosome pairs are separated from one another by spindle fibres and moved to the poles of the cell |
|
|
What happens in telophase I? |
The cell separates into two (each containing one chromosome from each homologous pair |
|
|
What happens in metaphase II? |
The chromosomes line up in single file at the middle of the cell (not in pairs) |
|
|
What happens in anaphase II?
|
Spindle fibres pull one chromatid from each chromosomes to separate poles of the cell
|
|
|
What are the two types of dominant and recessive trait? |
Autosomal and sex linked |
|
|
What is the difference between blood types |
They contain different antigens (except O which don't contain any) |
|
|
Which blood type can accept blood transfusions from anyone (regardless of their blood type) |
AB |
|
|
What does the '+' after a blood type mean? |
The person contains RH Factor on the surface of their blood cells |
|

What is circled in this image? |
A nitrogenous base pair |
|
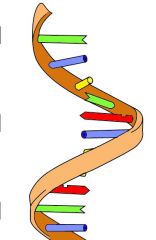
What does this image show?
|
RNA
|
|
|
What is an intron? |
A segment of a DNA or RNA molecule which does not code for proteins |
|
|
What do chromosomes consist of? |
DNA and proteins |
|
|
When is DNA replicated? |
During interphase |
|
|
How are chromosomes counted?
|
By the number of centromeres present |
|
|
'I pissed myself at Tesco', is a mnemonic for what? |
Interphase, Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
|
In which stage does the nuclear envelope break down? |
Prophase |
|
|
When do new nuclei begin to form? |
During telophase |
|
|
What is a zygote?
|
A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum |
|
|
On which part of the chromosomes do the spindle fibres attach? |
The centromeres |
|
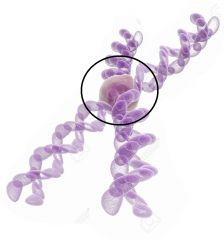
What part of this chromosome is circled? |
The centromere |
|
|
What happens during the G1 phase of interphase?
|
The organelles replicate |
|
|
What happens during the S phase of interphase? |
The DNA replicates and each chromosome now has two chromatids |
|
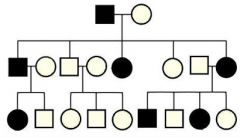
What do the black squares represent? |
Affected males
|
|
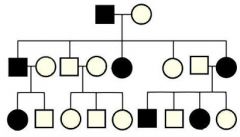
What do the white circles represent? |
Unaffected females |
|
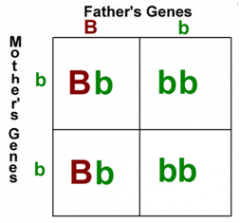
If lowercase b = blue eyes and uppercase B = brown eyes, what percentage of children will have blue eyes? |
50% |
|
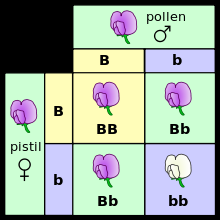
What genotype are the parent plants? |
Heterozygous |
|
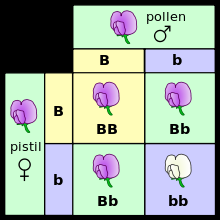
What percentage of flowers will definitely produce white flowers? |
75% |
|
|
Eye colour is an example of what? |
A phenotype |
|
|
Which two nitrogenous bases are purines?
|
Adenine and Guanine |
|
|
Which three nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines? |
Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine |
|
|
Where is the ribosome binding site in eukaryotic mRNA? |
5' cap |
|
|
Why does a eukaryotic mRNA have a poly-a-tail? |
To protect it from damaging enzymes as it travels from the nucleus into the cytoplasm |
|
|
Where is the ribosome bonding site on prokaryotic mRNA? |
SD sequence |
|
|
What is the five' cap? |
A guanine nucleotide |
|
|
What is the main enzyme that transcribes DNA into RNA?
|
RNA Polymerase |
|
|
What enzyme is responsible for 'unzipping' DNA? |
Helicase |
|
|
What keeps the DNA strands separated? |
Single stranded binding proteins |
|
|
What direction can DNA polymerase make DNA bases in? |
5' to 3' |
|
|
How can DNA polymerase work in the right direction on the lagging strand? |
Primase places primers down along the strand so that polymerase can work backwards (5'-3') |
|
|
What does primase make primer out of?
|
RNA |
|
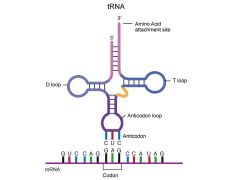
What is this? |
tRNA |
|
|
How many bases does tRNA read at a time? |
Three (codon) |
|
|
How are anti-codons joined together? |
Via peptide bonds |
|
|
How much of your DNA code is in each cell? |
ALL OF IT! |
|
|
How is DNA suited to specific roles? |
Different sections of DNA are 'turned on' depending on what type of cell they belong to. Eg: a skin cell does not produce digestive enzymes even though the code is there. But that code is turned on in a stomach cell |
|
|
What is gene regulation |
Only certain genes are 'turned on' in the entire DNA based on where a cell is in the body |
|
|
What part of a DNA nucleotide codes for traits? |
The nitrogenous bases |

