![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is a stimulus? (2 PARTS IN 1 SENTENCE) Example? |
A change in the external or internal environment that can cause a response E.g. Temperature |
Change T |
|
|
What are Receptors? Example? |
A cell or a group of cells, able to detect stimulus (change) E.g. Pain receptors in skin |
Detect T Payne |
|
|
What are Effectors? Examples (2 PARTS) |
A cell, or group of cells, able to carry out some action E.g. Muscles or glands |
Action MASSSSSS, or digestion |
|
|
What systems provide a connection between Receptors and Effectors (2 PARTS) |
Nervous system (by ions, electrical) Endocrine System (by hormones, chemical) |
Nerve Hormones |
|
|
What are the parts of the Central Nervous System (2 PARTS) |
The brain and the spinal chord |
|
|
|
What are the parts of the Peripheral Nervous System? (2 PARTS) |
Nerves running into + out of CNS |
More nerves |
|
|
What is a Neuron? |
A nerve cell |
|
|
|
What do Motor Neurons do? |
Carry nerve impulses from CNS to a muscle or gland |
Carry |
|
|
Diagram of a Motor Neuron (9 PARTS) |

|
N Cell Den Ax Sch My Nod Ter Syn |
|
|
What is the function of the cell body? (2 PARTS) |
1. Receives nerve impulses from dendrites 2. Passes nerve impulses into axon |
Receive Pass |
|
|
Function of dendrites? |
Carry nerve impulses into cell body |
Into |
|
|
Function of axons? |
Carry nerve impulses away from cell body |
Away |
|
|
Function of Schwann Cells? |
Secrete myelin (fatty material) |
|
|
|
Function of myelin? (2 PARTS) |
Insulates (protects) axon/dendrites Speeds up nerve impulse |
Ins Speed |
|
|
Function of Nodes of Ranvier? |
Gaps between Schwann Cells |
|
|
|
What are Synaptic Endings? |
Where a synapse meets with a muscle |
|
|
|
What is a Sensory Neuron |
Carry nerve impulse from a receptor into the CNS |
Into |
|
|
Diagram of a Sensory Neuron (9 PARTS) |
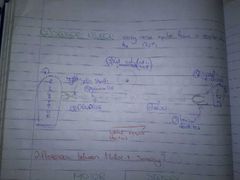
|
|
|
|
1. What does an Inter Neuron do? 2. Where is it located? |
Carry nerve impulse from sensory neuron to a motor neuron Located in the CNS |
Sense -> |
|
|
What is a Reflex Action? |
An automatic response to a stimulus that is not under conscious control |
response |
|
|
Examples of Reflex Actions (5 PARTS, LIST 3) |
1. Eye blink when something gets close 2. Iris reflex (light) 3. Knee jerk 4. Grasp reflex (baby) 5. Pull hand away from sharp/hot objects |
|
|
|
What is a Reflex Arc? |
Nerve pathway of a reflex action |
|
|
|
Diagram of the TS of a Vertebral Column |

|
|
|
|
Diagram of TS of Spinal Cord to show a Reflex Arc (14 PARTS) |
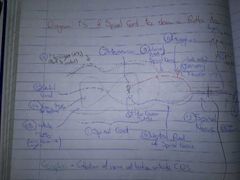
|
|
|
|
What is a ganglion? |
Collection of nerve cell bodies outside CNS |
Cell bodies |
|
|
What are the meninges? |
Membranes (x3) enclosing fluid -> protection |
Membranes |
|
|
What is White Matter? |
Nerve fibres with myelin |
Fibres |
|
|
What is Grey Matter? |
Cell bodies |
Bodies |
|
|
Diagram of TS of a nerve |

|
|
|
|
What is the Importance of Reflexes? (3 PARTS) |
1. Very fast + protect 2. Automatic so brain need not be involved 3. Conditioned reflexes -> form bases of learning (riding bike) |
Fast Brain Learning |
|
|
What is a Synapse? (2) |
A region between -2 neurons OR -a neuron and an effector |
Region Neurons...or eff |
|
|
DIAGRAM OF A SYNAPSE (8) |
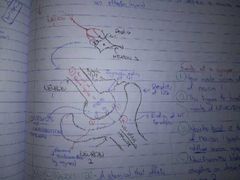
|
Arrival Vesicles Across cleft x2 Binding Removal Ending + dendrite |
|
|
What are the 5 Events at a Synapse? |
1. Nerve impulse arrives at end of Neuron 1 2. Trigger formation of vesicles of neurotransmitter 3. Vesicles burst at end of N1 + diffuses across synaptic cleft 4. NT binds to receptors on dendrite of N2 - generate nerve impulse 5. NT broken down by enzymes in S. cleft
|
Arrives Vesicles Burst Dendrites Broken down |
|
|
What is a Neurotransmitter? |
A chemical that affects the nervous system |
Chemical |
|
|
Examples of neurotransmitters? (3) |
Acetylcholine - released at synapses between motor neurons + muscles Dopamine + Seratonin - Brain NT
|
Acetyl Dope Sera |
|
|
A use for Seratonin? (1 + example) |
Used for anti-depressants -SSRI's , selective seratonin reuptake inhibitors |
SSRI |
|
|
Name and list the Symptoms, Cause and Treatment for a Nervous System Disorder (4) |
1. Parkinson's Disease 2. Shaky movement 3. Lack of Dopamine in brain/injury 4. Give L-Dopa (synthetic dopamine) or inject stem cells into brain |
Park Shake Dopamine L-Dopa |
|
|
Nature of Nerve Impulse: 1. Through what does it move by? 2. Describe the All or Nothing Law 3. Are all nerve impulses the same? 4. Do nerve impulses require energy? 5. Does a stronger stimulus produce a stronger impulse? |
1. Electrical ions 2. Stimulus must be stronger than Threshold Level to generate nerve impulse 3. All are the same 4. They require ATP 5. No, but it could produce more impulses |
1. Electric 2. Threshold 4. A.. 5. More |
|
|
Diagram of the Brain (5) |
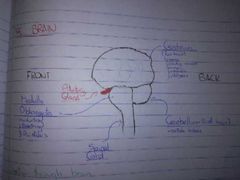
|
Cere x2 Pit Cord Longa |
|
|
Diagram of Section through Brain (2) |

|
Thalamus x2 |
|
|
Function of Cerebrum (5, state 3) |
Voluntary actions 1. Senses 2. Voluntary movement 3. Memory 4. Emotions 5. Intelligence |
Sen Voluntary Mem Emot Intel |
|
|
Function of Cerebellum |
For balance |
Bal |
|
|
Function of Medulla Oblongata (2) |
Involuntary actions 1. Breathing 2. Peristalsis |
|
|
|
Function of the Thalamus |
Relays nerve fibres to appropriate part of Cerebrum |
Relays |
|
|
Function of the Hypothalamus (+ 2 examples) |
Homeostasis -e.g. Body temp., blood pressure |
|

