![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pyruvate hydrogenase |
Enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA |
|
|
Cycle of Gas exchange |
O2 is the input for Cellular respiration CO2 is the output. CO2 is the input for photosynthesis and O2 is the output. |
|
|
Where does photosynthesis occur |
In the chloroplasts of plant cells
|
|
|
Chlorophyll |
Pigment molecule that absorbs specific wavelengths of light energy (kinetic) |
|
|
Function of chloroplasts |
light energy bumps chlorophyll molecule to a higher, excited energy level |
|
|
Photosynthesis equation |
Carbon Dioxide+Water ---> Sugar + Oxygen |
|
|
Photosynthesis equation (formulas) |
6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
|
|
Energy conversion in photosynthesis |
Light (kinetic) energy to Chemical energy |
|
|
"Follow the Electrons" |
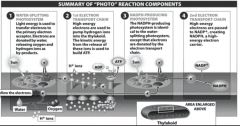
Systems 1&2 |
|
|
"Synthesis of Glucose" |
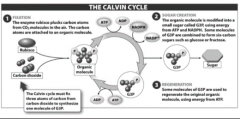
|
|
|
The mass of a plant comes from |
CO2 in the air |
|
|
Processes of Photoysynthesis |
Systems 1&2 -----> Calvin Cycle |
|
|
Two primary processes of life |
Metabolism and Reproduction |
|
|
Types of metabolism |
Respiration, photosynthesis |
|
|
Types of reproduction |
Mitosis, Meosis |
|
|
Haploid |
One copy of a chromosome |
|
|
Diploid |
Two copies of a chromosome (Maternal and Paternal) |
|
|
Homologues |
Contain genes at the same locus |
|
|
Sister Chromatides |
Identical replicated homologues. (pair) |
|
|
Human Genome |
23 Pairs of Homologous chromosomes |
|
|
Stages of nuclear division |
PMAT, Cytokenesis |
|
|
Apoptosis |
Cell death |
|
|
Weismann's Hypothesis |
Sex increases genetic variation |
|
|
Gametes |
Sex cells |
|
|
Meiosis cells and genome size |
Meiosis only passes on half of the chromosomes (23). Maintains stable genome size |
|
|
crossing over |
In meiosis when homologous chromosomes creates combinations of genetic material in "recombinant chromosomes" |
|
|
Basic science |
pursuit of science for knowledge's sake |
|
|
applied research |
Pursuit of science to fix a problem |
|
|
Hypothesis |
Tentative statement that could lead to a conclusion |
|
|
Null |
when a hypothesis is not true |
|
|
Prediction |
If, then statement based on a hypothesis |
|
|
Hypothesis vs theory |
One statement, verses a broad statement with many hypotheses under it. Theories usually accepted to be true |
|
|
Stages of scientific method |
1. Observation 2. Question 3. Hypothesis 4. Prediction 5. Experiment 6. analyze/conclude |
|
|
Cell theory |
1. All living things consist of one or more cells 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. all cells emerge from preexisting cells |
|
|
Valence shells |
Nucleus->2-8-8-2 |
|
|
Isotopes |
Same protons and electrons, different neutrons |
|
|
What distinguishes elements |
# Protons, atomic number |
|
|
#Electrons= |
#Protons |
|
|
Ionic Bond |
Electron is taken or gained. Ion or charged atom results |
|
|
Covalent Bond |
Electrons shared between interacting atoms |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Between molecules not atoms. Polar molecules attract. |
|
|
Atomic mass |
Mass of the protons and neutrons in the atom |
|
|
Atomic number |
number of protons in the molecule |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Main energy source. Connected sugars. Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides |
|
|
Carbohydrate energy reserves |
Starch in plants, glycogen in animals |
|
|
Lipids |
Fats, sterols, phospholipids |
|
|
Unsaturated fat |
Double bond, kinked |
|
|
Saturated Fat |
all single bonds, straight |
|
|
Transfat |
Hydrogen gas bubbled through. Crates another hydrogen bond. Has properties of sat fat but is unsaturated |
|
|
Sterols |
Regulate growth and development |
|
|
Phospholipids |
Used in cell structures. Both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions |
|
|
Proteins |
Growth, development, structure, regulatory |
|
|
Structure of proteins |
Amino acids linked by peptide bonds form proteins |
|
|
Eukaryotes |
DNA in nucleus, membrane bound organelles |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
No nucleus. DNA in cytoplasm |
|
|
Endosymbiosis |
Cells engulf others and less complex cells evolve into organelles |
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Phospholipid bilayer allows small molecules in. Large molecules can only pass through with the transport proteins |
|
|
Passive transport |
Diffusion, osmosis |
|
|
active transport |
Energy used to pass through cell |
|
|
Catabolic |
Large molecules broken down, energy released |
|
|
Metabolic pathway |
Enzymes modify substrate shapes in a chain to change the shape to an en product |
|
|
Cellular Respiration processes |
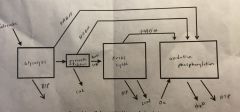
|
|
|
Gene |
Smallest unit of heredity. A certain combination of base pairs that code for a trait |

