![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of life |

make energy, metabolism, made of cells, homostasis, respond to stimuli |
|
|
Hiearchy of organization |

things are made up of other things, atoms ecosystem biosphere. ecosystems included everything below it. all part of the larger scale |
|
|
elements |

pure substances, other compounds, multiple _______. Anything in the universe is made up of some or more __________ we have alot of compounds |
|
|
macromolecules (in the body |

4 in the boyd protin carbs lipids nuclic acids Chon |
|
|
polymer (chain) |

made of many monomers. protein polysac nuclcacid |
|
|
protein |

polymer of amic acids. Important to function shape |
|
|
DNA |

polymer of nuclitides |
|
|
dehydration synthesis |

build a polymer takes away water. Breaks hydrolosys- (adds water) |
|
|
purpose of science |

to learn answer questions. to figure out what is going on to answer questions. Passive answer but needs testing hypothesis more data becomes a theory |
|
|
peer review journal |

published work, make sure the research is good |
|
|
lipids |

long term energy shortage, not a polymer |
|
|
emergent properties |

put things together that when looked at, the properties can not be seen. |
|
|
Prokayroke |

no nuclius cell membrane, cell wall, ribosomes. no membrane band organelles |
|
|
Eukariotic |

With Cell, bigger membrane bond organelles |
|
|
Concentration gradient |

alot of stuff put together, Go down |
|
|
diffusion |

no energy (passive). High to low concentraction |
|
|
osmosis |

diffussion of water across the membrane |
|
|
first law of thermondynamics |

energy cannot be created nor destroyed |
|
|
arobics |

refers to oxygen, a level that is not to sternuous so you use air cellular resperation to keep during that and supplying energy |
|
|
3 stages of resperation |

sugar oxygen gives off CO2 and water to energy break sugar glycolsis krebs cycle sugar + o2 > (atp gives off) co2 h2o photosynthesis< cytoplasm, where glycosis takes place |
|
|
photosynthesis |

energy from sun, use co2 and water, they give off oxygen
|
|
|
signal transduction |

ligands grabs reception creates chain of chemical reactions to get the desired outcome |
|
|
mitosis (2 identical) |

4 cells with y2 DNA (genetically variable) 2 halfs together |
|
|
Diploid |
2 sets of chromosomes or genetic information |
|
|
haploid |
1 set of chromosomes or genetic information |
|
|
miosis |
2 things to determine genetic diversity. Crossing over between chromosomes and random fertilzation. |
|
|
independent assortment |

division of chromosomes |
|
|
40 chromosomes |

how many are in gamets. |
|
|
cell cycle |

Mphase - mitosis cytokinisis > inter -cell's life > m phase - ready to divide> S Phase - DNA is synthesised |
|
|
zygote |

sperm+Egg |
|
|
genetics |

traits people have. |
|
|
phenotype |

things that can be measured and seen. |
|
|
genotype |
DNA that is producing these phinotypes |
|
|
complete dominance |
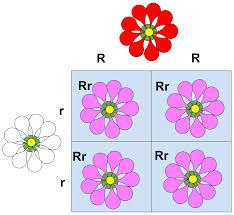
2 pieces of info but one phenotype |
|
|
Heterozygous |

both give dominance. AA Aa |
|
|
homozygous |
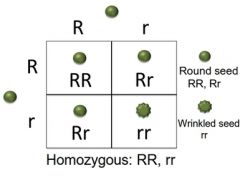
resseseve aa |
|
|
alle versions of a gene |
same genes different versions it doesn't get blended away over time. |
|
|
Genes |

the allets do not randomly assort when they are right next to each other on the chromosome.they are linked really close together |
|
|
monomer |

a acid monosac nucliatide |
|
|
AGCT |
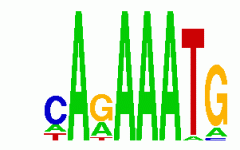
20% is A
30% is G A 20 = T 20 30 G= C 30 |
|
|
semi conservative |

half new half old |
|
|
codon |

3 nuclitities |
|
|
transcription |

DNA to RNA |
|
|
Translator |
RNA to protein
|
|
|
Messenger RNA |
bring the information |
|
|
Transfer RNA |

brings the amino acids |
|
|
Rrna |
stomps it together |
|
|
mutation |

change genetic information |
|
|
Homologus structures |
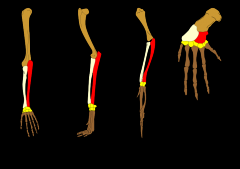
phylogeney show who all is related |
|
|
evolution |
micro small Macro big |

