![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mendel discovered the principles of inheritance with experiments in which ----
|
Mendel discovered the principles of inheritance with experiments in which large numbers of pea plants were crossed
|
|
|
Gametes are ----so contain only --- allele of each gene
|
Gametes are haploid so contain only one allele of each gene
|
|
|
The two alleles of each gene separate --- haploid daughter nuclei during meiosis.
|
The two alleles of each gene separate into different haploid daughter nuclei during meiosis.
|
|
|
Fusion of gametes results in -- zygotes with two alleles of each gene that may be the same allele or different alleles
|
Fusion of gametes results in diploid zygotes with two alleles of each gene that may be the same allele or different alleles
|
|
|
--alleles mask the effects of recessive alleles but co-dominant alleles have joint effects.
|
Dominant alleles mask the effects of recessive alleles but co-dominant alleles have joint effects.
|
|
|
Many genetic diseases in humans are due to --- alleles of autosomal genes although some genetic diseases are due to - or --alleles.
|
Many genetic diseases in humans are due to recessive alleles of autosomal genes although some genetic diseases are due to dominant or co-dominant alleles.
|
|
|
Some genetic diseases are -- linked. The pattern of -- is different with sex-linked genes due to their -- on --- chromosomes
|
Some genetic diseases are sex linked. The pattern of inheritance is different with sex-linked genes due to their location on sex chromosomes
|
|
|
Many genetic diseases have been identified in humans but most are very ---.
|
Many genetic diseases have been identified in humans but most are very rare.
|
|
|
--and --- chemicals increase the mutation rate and can cause genetic diseases and cancer.
|
Radiation and mutagenic chemicals increase the mutation rate and can cause genetic diseases and cancer.
|
|
|
Who was Gregor Mendel?
|
- published about his experiments with garden pea plants - Gregor Mendel used artificial pollination in a series of experiments in which he carefully chose the pollen of various plants to fertilize other individuals of the same species. |
|
|
What is a Genotype?
|
The symbolic representation of the pair of alleles possessed by an organism, typically represented by two letters. Examples: Bb, GG, tt.
|
|
|
What is a Phenotype?
|
The characteristics or traits of an organism. Examples: fi ve fi ngers on each hand, colour blindness, type O blood. Dominant allele – An allele that has the same effect on the phenotype whether
|
|
|
What are dominant alleles?
|
An allele that has the same effect on the phenotype whether it is paired with the same allele or a different one. Dominant alleles are always expressed in the phenotype. Example: the genotype Aa gives the dominant A trait because the a allele is masked; the a allele is not transcribed or translated during protein synthesis.
|
|
|
What are recessive alleles?
|
An allele that has an effect on the phenotype only when present in the homozygous state. Example: aa gives rise to the recessive trait because no dominant allele is there to mask it.
|
|
|
What are co-dominant alleles?
|
Pairs of alleles that both affect the phenotype when present in a heterozygote. Example: a parent with curly hair and a parent with straight hair can have children with different degrees of hair curliness, because both alleles infl uence hair condition when both are present in the genotype.
|
|
|
What is a locus?
|
The particular position on homologous chromosomes of a gene (as seen in Figure 3.2 and labelled in Figure 3.21). Each gene is found at a specifi c place on a specifi c pair of chromosomes.
|
|
|
How is Homozygous?
|
Having two identical alleles of a gene (see Figure 3.21). Example: AA is a genotype that is homozygous dominant, whereas aa is the genotype of someone who is homozygous recessive for that trait.
|
|
|
What is heterozygous?
|
Having two different alleles of a gene (see Figure 3.22). This results from the fact that the paternal allele is different from the maternal one. Example: Aa is a heterozygous genotype
|
|
|
What is a carrier?
|
An individual who has a recessive allele of a gene that does not have an effect on the phenotype. Example: Aa carries the gene for albinism (like the penguin in the photo on the next page) but has pigmented skin, which means an ancestor must have been albino and some offspring might be albino; if both parents are unaffected by a recessive condition yet both are carriers, some of their progeny could be affected (because they would be aa).
|
|
|
What is a test cross?
|
Testing a suspected heterozygote plant or animal by crossing it with a known homozygous recessive (aa). Because a recessive allele can be masked, it is often impossible to tell whether an organism is AA or Aa unless they produce offspring that have the recessive trait. An example of a test cross is shown later in this section when we explore three generations of pea plants.
|
|
|
What is albinism?
|
Most animals are unaffected by albinism and have pigmented skin, hair, eyes, fur, or feathers. But some animals lack pigmentation. An individual with little or no pigmentation is called an albino.
|
|
|
When forming a punnett grid for humans, how should we interpret the data?
|
there is a 50% chance of producing offspring with genotype Aa and a 50% chance of producing offspring with genotype aa. Because humans tend to produce a small number of offspring, this is the interpretation that should be used. If the example was about plants that produce hundreds of seeds, the results could be interpreted in the following way: 50% of the offspring should be Aa and the 50% should be aa.
|
|
|
Each offspring is the result of ____coming together when the gametes fus.
|
each offspring is the result of two alleles coming together when the gametes fuse. In this process, the two haploid sex cells join to make a single diploid cell called a zygote. This is the fi rst cell of the new offspring.
|
|
|
What can the phenotypes be deduced from?
|
the phenotypes can be deduced by looking at the genotypes
|
|
|
Diseases such as cancer can sometimes be caused by ___chemmicals
|
mutagenic
|
|
|
What happens with radiation?
|
When radiation hits a DNA molecule, it can sometimes knock one or more base pairs out of place, modifying the genetic code. This causes a mutation that, as we have seen, can sometimes be benign (not harmful), but at other times it can be harmful to an organism. When the DNA mutation leads to cancer, as happened to Marie Curie, the organism’s health is in jeopardy.
|
|
|
What are sources of radiation?
|
Nuclear bombs and nuclear power plants
|
|
|
Explain why more men are affected by colour blindness than women?
|
Because the allele for colour blindness is recessive and sex linked, in order for a woman to be colour blind, she must have two recessive alleles, one on each of her X chromosomes: XbXb. In any other case, she would be carrying at least one dominant allele to cancel out the effects of the colour blindness allele. In most populations, it is rare to receive one of these recessive alleles and even more rare to get both alleles for colour blindness. On the other hand, it is much easier for a man to get the condition because there is no locus on the Y chromosome to carry a dominant allele to mask the recessive allele on his X chromosome. As a result, the presence of just one b allele is enough to give him colour blindness.
|
|
|
Using the CR and CW alleles for co-dominance in snapdragon flower colour, show how two plants could have some white-flowered offspring, some pink-flowered offspring and some red-flowered offspring within one generation.
|
The answer should show the Punnett grid for the cross CRCW × CRCW.
|
|
|
Draw a pedigree chart of the two generations described in question 12.
|
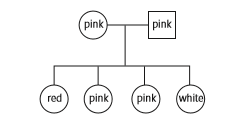
In the top row, one circle and one square should be joined by a horizontal line. They should both be labelled pink. In the next row, showing the F1 generation, the four offspring plants should show one red, two pink and one white. The offspring are shown here as all female, but any combination of shapes could be used. |
|
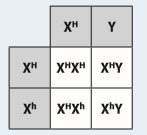
Look at the grid below showing the chances that a couple’s children might have haemophilia. (a) State the genotype of the mother and father. (b) State the possible genotypes of the girls and boys. (c) State the phenotypes of the girls and boys. (d) Who are the carriers in this family? (e) What are the chances that the parents’ next child will be a haemophiliac?
|
(a) XHXh for the mother and XHY for the father. (b) Girls can be either XHXH or XHXh and the boys can be either XHY or XhY. (c) Both possible genotypes for the girls give them normal blood clotting. The genotype XHY gives a boy with normal blood clotting but XhY is a boy with haemophilia. (d) The only carriers are the mother and any daughters with XHXh. (Males cannot be carriers.) (e) 1 in 4, or 25% |

