![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
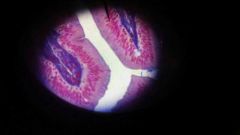
Nonciliated simple columnar epithelial |
1 layer of column - shaped cells;contains a surface modification called mircovilli that makes up the brush border in small intestine Function is abosportion Found in small intestine |
|
|

Simple squamous epithelium |
1 layer of flat cells Function in secretion,diffusion,filtration Can be found in alveoli of the lung,glomerular of kidneys,and endothelium of blood vessels |
|
|

Cilia Ted simple columnar epithelium |
1 layer of columnar - shaped cells; contains a surface medication called cilia (they are used to move substances across the surface of the cells) Function in moving substances Found in uterine tubes |
|
|

Stratified squamous epithelium |
Multiple layers of cells the apical layer contains flat cell Function is protection Can be found in the skin esophagus or vagina |
|
|

Areola connective tissue |
Looks almost like a tic-tac-toe grid Allows nutrients to diffuse into epithelial tissues Found in hypodermic of skin (actually under all epithelia) |
|
|

Adipose |
Contains large cells with open storage areas where fat once was in the tissue Provides insulation and stores energy Found in hypodermis |
|
|

Dense regular connective tissues |
Dense connective tissues (extracellular matrix is packed tightly) Fiber all run the same direction Resists tension in one direction/plane Found in tendon |
|
|

Reticular connective tissue |
Has very random pattern of fibers (looks like tree branches) Forms stroma (framework) of soft organs Found in liver,spleen,or lymph nodes |
|
|

Dense irregular connective tissue |
Fibers run in different direction;almost looks like raw steak Resists tension in varying directions Found in dermis of skin |
|
|

Elastic cartilage |
Extracellular matrix contains a great deal of elastic fibers causing it to have a very dark appearance Found in the ear Provides strength while also providing elasticity |
|
|

Compact Bone |
Has appearance similar to a cut tree duet rings formed within tissue Found in exterior of bones Provides protection and support |
|
|

Haylie cartilage |
Has a glassy appearance to extracellular matrix Found in the ends of long bones and trachea Function depends on location; to provide smooth surface at ends of bone;to provide support in shape of trachea |
|
|

Elastic connective tissue |
Fibers appear very dark due to stain and have a coiled appearance Allows tissue to expand and recoil back to original shape |
|
|

Blood |
Due to numerous red blood cells contains many cells that look like small red doughnuts Function to transport nutrients and waste throughout the body Found within blood vessels |
|
|

Simple squamous epithelium |
1 layer of flat cell Function in secretion diffusion and flirtation Can be found in alveoli of lungs glomerulus of kidneys and endothelium of blood vessels |
|
|
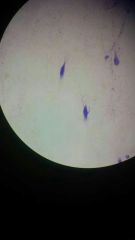
Nervous tissue |
Primary function of nervous tissue is to communication throughout the body Subdivided in two categories of cells; neurons - actually communicate neurogila- helps and support the neuron Nerons contain several distinct components : dendrites -receive signals coming from particular neurons cell body-largest portion of a neuron;contains the nucleus Axon-"output" component; sends information from neuron to another structure |
|
|

Cardiac muscle |
Fibers are branched in shape Also contains striation in the light microscope Is under involuntary control (meaning an individual does nor consciously control it's contractions ) Typically each cell has only one nucleus Is only found in the walls of the heart Contains special juniors called intercalated discs |
|
|

Thin skin |
Thin skin |
|
|
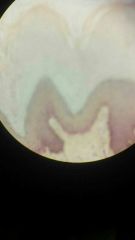
Thick skin |
Doesn't have hair Only found on the palms of hands and soles of feet No sebaceous gland (no sweat) |
|
|

Pacinian corpuscle (lamellated) |
Large oval structure composed of connective tissue capsules enclosed in the dendrites Adapts rapidly Located throughout the body; in the dermis, around joints,tendons,muscles,in mammary glands, external genitalia, pancreas and urinary bladder |
|
|

Messiner corpuscle |
Corpuscle of touch Touch receptors that are located in the dermal papillae of hairless skin Adapts rapidly Located in fingertips, hands,eyelids,tip of tongue,lips,nipples,sole,clit or is and tip of penis |
|
|
|
Supine |
Laying face up |
|
|
|
Prone |
Laying face down |
|
|
|
Superior |
Above/higher |
|
|
|
Inferior |
Below/lower |
|
|
|
Anterior |
Front |
|
|
|
Posterior |
Back |
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Back (same as posterior for humans) |
|
|
|
Ventral |
Belly (same as anterior in humans) |
|
|
|
Proximal |
Closer to a point of attachment |
|
|
|
Distal |
Further from point of attachment |
|
|
|
Lateral |
Movement away from the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Contralateral |
Opposing side |
|
|
|
Ipsilateral |
Same side |
Right hand right foot |
|
|
Intermediate |
Between two structures |
|
|
|
Medial |
Movement toward the midline of the body |
|
|
|
Superfical |
Closer to the surface of the body |
|
|
|
Deep |
Away from the surface of the body |
|
|
|
Planes |
Provide a point of reference to indicate the direction in which the specimen has been cut 4 types Sagiittal- results in 2 sides left and right (midsagittal vs. Parasagittal) |
90 degree angle |
|
|
Planes cont. |
Traverse -results in a top and bottom (superior and inferior portion) |
180 degree angle |
|
|
Frontal coronal plane |
Results in front and back (anterior and posterior portion) |
90 degree angle |
|
|
Oblique plane |
Do not follow a straight line |
45 degree angle |
|
|
Integumentary system |
Provide protection Includes hair nails skin and associated gland |
Outer protective layer |
|
|
Skeletal system |
Provides protection and support Includes bones skull |
Structural foundation (frame) |
|
|
Muscular system |
Used for movement of human body Located throughout body Bicep brachii |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system |
Removes foreign substance from. Look and lymph Includes lymph nodes spleen tonsils thymus |
|
|
|
Respiratory system |
Exchanges O2 and CO2 between blood and air Includes lungs nose trachea pharynx larynx |
|
|
|
Digestive system |
Performs digestion absorption of nutrients and elimination of waste Includes stomach esophagus small/large intestine pancreas liver and gallbladder |
|
|
|
Nervous system |
Regulatory system that control activities of the human body Includes brain spinal cord nerves |
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
Regulatory system that controls activities in the human body Includes pituitary gland ovaries testes pancreas thyroid gland adrenal glands |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
Transports nutrients and waste Includes heart arteries veins blood |
|
|
|
Urinary system |
Removes waste from blood and eliminates waste via urine Includes kidneys bladder urethra ureters |
|
|
|
Reproduction system |
Produces gametes (sperms or eggs) and promotes sexual characteristics of each gender Includes testes penis prostate gland in males; ovaries uterus vagina breast in females |
|
|
|
Dorsal body cavity |
Named because the two cavities that make it up are found closer to the dorsal surface of the body A. Cranial cavity -located within the skull. Houses the brain B. Vertebral canal located within the vertebral column. Houses the spinal cord |
|
|
|
Ventral body cavity |
named because the three cavities make it up are found to the ventral surface of the body Thoracic cavity (chest) houses lungs heart thymus esophagus and tracheai. Pleural cavities- houses the lungs onlyii. Mediastinum- located in between the two pleural cavities; houses all organs except lungsiii. Pericardial cavity -located within Mediastinum; houses heart only Abdominal cavity- separated from the thoracic cavity by the diaphragm; houses organs of the digestion system mainly (stomach small/large intestine ) Pelvic cavity - inferior to abdominal cavity; houses bladder and internal reproductive organs |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue 1 |
2 functions coverings/lining or they form glands Characteristics Closely packed together Avascular High rate of mitosis Have to be supported by connective tissue due to lack of blood supply Has a basement membrane -layer of connective tissue Found beneath epithelial tissues Apical surface= free surface of epithelia Basal surface = layer bound to basement membrane |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue 2 |
Shapes Squamous= flat cells Cuboidal = cube shaped Columnar = column shaped has goblet cell Transitional= variable shape Layers Simple =1 layer of cells Stratified = more than 1 layer of cells Pseudostratified = "falsely" appears to be stratified (only Pseudostratified cell is Pseudostratified columnar cell) |
|

