![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Photolysis - Equation - How? - What purpose? |
2H20 --> 4H+ + 4e- + O2 - Via enzyme in presence of light - Donates electron to chlorophyll to replace those lost when light strikes |
|
|
What is photophosphorylation |
The generation of ATP from ADP and an inorganic phosphate in presence of light |
|
|
What are the products of non-cyclic phosphorylation |
ATP, Oxygen and reduced NADP |
|
|
What are the products of cyclic phosphorylation |
ATP in small quantities |
|
|
What are the steps of non-cyclic phosphorylation |
1. Photon of light strikes PS2 + energy is channeled to primary pigment reaction centre 2. Light energy excites a pair of electrons inside chlorophyll molecule 3. The energized electron escape the chlorophyll and is carried along the electron transport chain via an electron carrier to PS1 4. (The missing electrons are replaced by electrons from photolysis) 5. The excited electrons lose en energy as the move along the chain - this energy is used to transport protons into the thylakoid via proton pumps 6. This movement forms a proton gradient 7. Protons then move down the gradient into the stroma via ATP synthase 8. The protons cause a conformation change in the shape of ATP synthase, which then allows ADP to combine with an inorganic phosphate to make ATP. 9. Light energy is then absorbed by PS1 which excited the electrons to a higher energy level 10. Finally, electrons are transferred to NADP along with a proton from the stroma to form reduced NADP |
|
|
What are the steps of cyclic phosphorylation |
1. Photon of light strikes PS1 and energy is channeled to primary pigment reaction centre 2. This excites an electron which then travels to the electron carrier 3. Protons then diffuse across from released energy from the electrons and flow down gradient via ATP synthase 4. ATP can then be made from ADP and P1 5. Electrons are recycled by going back to PS1 |
|
|
Where does the calvin cycle take place? |
Stroma of chloroplasts |
|
|
What is the first step of the calvin cycle? What is the catalyst involved? |
Carbon dioxide is combined with ribulose bisphosphate to form two molecules of GP; RuBisCO |
|
|
What is the second step of the calvin cycle? What molecules are required for the reaction? |
ATP and reduced NADP are required for the reduction of GP to TP |
|
|
What is the final step of the calvin cycle? |
Ribulose bisphosphate is regenerated |
|
|
What is GP used for? |
Making amino acids and lipids |
|
|
What is TP used for? |
Remaking Ribulose Bisphosphate (5/6) and hexose sugars (1/6) |
|
|
How many times does the calvin cycle need to turn to make one hexose sugar? Why? |
6; Only 2TP are made on each turn - 3 turns = 6 TP - only one is saved for making sugar - need 6 carbons to make hexose sugar so need to molecules of TP = 6 turns |
|
|
Draw a labelled diagram of a chloroplast |
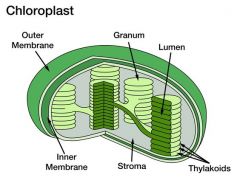
|
|
|
What are the two types of photosynthetic pigments is a photosystem? |
Primary pigments; accessory pigments |
|
|
What occurs in primary pigments? |
Electrons get excited |
|
|
What do accessory pigments do? |
Act as light harvesting systems by transferring the energy to the reaction centres |
|
|
What wavelength of light does PS1 absorb? |
700nm |
|
|
What wavelength of light does PS2 absorb best? |
680nm |
|
|
Where does the light dependent reaction take place? |
In the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts |

