![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What do DNA and RNA do? |
• DNA - Used to store genetic information (instructions to develop and grow from a fertilised egg to a fully grown adult). • RNA - transfer genetic information from DNA to ribosomes. |
|
|
|
What does the nucleotide consist of? |
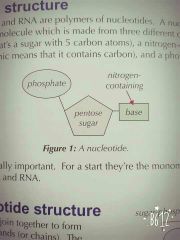
|
|
|
|
What happens when a nucleotide undergoes a condensation reaction? |
• Forms a phosphodiester bond (consists of a phosphate group and two ester bonds) • All of the nucleotides form to make a polynucleotide, this chain is also known as the sugar-phosphate backbone. |
|
|
|
What does the structure of DNA consist of? |
• Complementary base pairings. • Hydrogen bonds between bases. • Anti-parallel strands. • Polynucleotide strand with sugar-phosphate backbone. |
|
|
|
Which base pairing should there be more of? |
GC because it has three hydrogen bonds, which allows for more stability. |
|
|
|
Comparison of DNA and RNA? |

|
|
|
|
In the 1800s, scientists thought that proteins had to be the carrier of the genetic code as they were more genetically varied. But when the double helix structure was proven, then Watson and Crick were able to prove that DNA was the carrier of the genetic code. |
. |
|
|
|
How is DNA adapted to carry out function? |
• It has a very stable structure which maintains genetic information generation to generation and it rarely mutates. • The two strands joined be hydrogen bonds, allows them to separate for DNA replication. • Extremely large molecule so it can carry an immense amount of genetic information. • By having the sugar(deoxyribose)-phosphate backbone, it is protected from chemical and physical forces. • Base pairings lead to DNA to replicate and transfer information to mRNA. |
|
|
|
How is DNA anti-parallel? |
One strand runs in the 5' to 3' direction and the other runs in the 3' to 5' direction. (3' and 5' means prime carbons). |
|
|
|
How can nucleic acids be synthesised? |
'In vivo' (in life) in the 5' to 3' direction because DNA polymerase that assembles nucleotides to the hydroxyl (OH) group on the 3' carbon molecule. |
|
|
|
Why does DNA replicate? |
It allows for genetic continuity between generations of cells. |
|
|
|
How is DNA replicated? |
1) DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between bases on the two polynucleotide DNA strands which causes the helix to unwind and single strands to form. 2) Each strand acts as a template for a new strand. Complementary free-floating nucleotides line up against their complementary bases on the strand. 3) Condensation reactions join the nucleotides of the new strand together. This is catalysed by the enzyme DNA polymerase so hydrogen bonds are formed. Each DNA molecule has a new strand and an old strand. |
|
|
|
Explain Messon and Stahl's experiment. |
1) Two samples of bacteria grew in nutrient brother - one containing light nitrogen (14N) and one containing heavy nitrogen (15N). As the bacteria reproduced, they took up the nitrogen and it became a part of their DNA. 2) A sample of DNA was extracted from both of them and spun in a centrifuge. The heavy bacteria settledo at the bottom and the light settled at the top. 3) The bacteria grown in heavy nitrogen was taken out and placed in the light nitrogen broth. Then another sample was taken and placed in the centrifuge. 4) If it were conservative then the light and heavy would have settled in different places. 5) If it were semi-conservative then the light and heavy would have settled in the middle. 6) Semi-conservative was correct. |
|
|
|
How does cell division occur? |
• Nuclear division - Process by which the nucleus divides. • Cytokenises - Follows nuclear division and is the process where the cell divides. |
|
|
|
Why is energy important? |
Plants and animals need energy for biological processes to occur (active transport, DNA replication, protein synthesis) |
|
|
|
How do plants and animals get energy? |
Energy is released from glucose is used to make ATP. Once made, ATP diffuses to the part of the cell that needs energy. Then energy is stored between the high energy bonds of the phosphate group. |
|
|
|
How does ATP condense and how is hydrolysis used to remake ATP? |
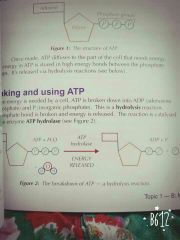
|

|
|
|
How do the phosphate ions have a low activation energy? |
Because they are unstable so it's easy to break them apart. |
|
|
|
Which processes can the synthesis of ATP occur from ADP? |
• Photosynthesis (plant cells) • Respiration (plant cells and animal cells) • Phosphate groups are donated from donor molecules to ATP (plant cells and animal cells) |
|
|
|
What is ATP used for? |
• Metabolic processes - provides energy to build macromolecules from basic units (e.g. starch from glucose). • Movement - Energy for muscle contraction so the muscles can slide over each other, this means that there'd be a shortening the length of muscle fibre. • Active transport - It provides energy to pass molecules/ions across cell membrane. • Secretion - Needed to form lysozyme necessary for the secretion of cell products. • Phosphorylation - where the released inorganic phosphate can be added to another compound making it more reactive. |
|
|
|
What can water dissolve as a solvent? |
• Gases (oxygen or carbon dioxide) • Waste (ammonia and urea) • Inorganic ions • Small hydrophilic molecules (amino acids, monosaccharides, ATP) |
|
|
|
Name some facts as to why water is important. |
• Metabolite - involved in metabolic reactions like condensation and hydrolysis reactions. • Solvent - substances dissolve in it due charges being attracted. Most metabolic reactions take place. • Temperature control - has a high specific latent heat and specific heat capacity. • Cohesive - helps water transport because they are polar. |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
An atom with an electric charge. |
|
|
|
What is an ion with a positive charge and a negative charge called? |
• Positive - Cation • Negative - Anion |
|
|
|
Talk about inorganic ions. |
• Iron ions - Fe2+ binds to oxygen becomes Fe3+ until the oxygen goes. • Hydrogen ions - More H+ present means the pH is lower and it's more acidic. • Sodium ions - Used in co-transport, helps other molecules/ions get across easily. • Phosphate ions - part of DNA, RNA, ATP so it's essential. |
|

