![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What elements can proteins contain? |
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur |
|
|
|
What are the functions of proteins? |
1. Structural proteins (e.g. collagen in ligaments, keratin in nails) 2. Enzymes 3. Some hormones (e.g. adrenaline, insulin) |
|
|
|
What are proteins? |
Polymers of similar monomers called amino acids |
|
|
|
What is the structure of an amino acid? |

|
|
|
|
What reaction creates a dipeptide? |
Condensation reaction forming peptide bond |
|
|
|
What is the definition of hydrophonic? |
Insoluble |
|
|
|
What is the definition of hydrophillic? |
Soluble |
|
|
|
What is the primary structure of a protein? |
The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide |
|
|
|
What is the secondary structure of protein? |
The alpha helix or beta pleated sheet formed by weak hydrogen bonds |
|
|
|
What is the tertiary structure of a protein? |
When the secondary structure folds on itself again as a result of bonding between the variable groups of amino acids |
|
|
|
What is a hydrogen bond? |
Bonding between slightly negative Oxygen and slightly positive Hydrogen in variable groups |
|
|
|
What are ionic bonds? |
Bonding between positively and negatively charged variable groups |
|
|
|
What are disulphide bonds? |
Strong covalent bonds between Sulfur containing variable groups |
|
|
|
What is a hydrophobic interaction? |
Hydrophobic elements clustering away from water |
|
|
|
What is the structure of globular proteins? |
1. Tertiary structure like a tangled knot 2. Soluble 3. Involved in reactions (e.g. hormones) |
1. Tertiary structure? 2. Soluble or insoluble? 3. What are they used for? |
|
|
What are fibrous proteins? |
1. 3D shapes fibres like a rope 2. Insoluble 3. Involved in structural roles (e.g. keratin, collagen) |
1. Shape? 2. Soluble or insoluble? 3. What is it involved in? |
|
|
What is the quaternary structure of protein? |
Bonding of proteins in the tertiary structure or non-protein groups to make functional proteins (e.g. haemoglobin is 4 polypeptides and 4 non-protein groups) |
|
|
|
What is the test for proteins? |
1. Add Biuret and heat 2. Purple is a positive result |
|
|
|
What are enzymes? |
Globular proteins which are biological catalysts which have a specific complementary active site to the substrate |
|
|
|
How are enzymes denatures? |
1. pH 2. Temperature Increases the kinetic energy breaking the hydrogen and ionic bonds in the tertiary structure |
2 factors and how they affect the structure |
|
|
What do enzymes do in a reaction? |
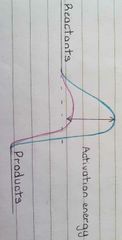
Lower the activation energy |
|
|
|
What is the lock and key method? |
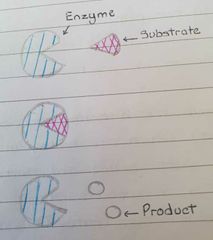
Active site is complementary to the substrate like a key bonding to form a enzyme-substrate complex |
|
|
|
What are limitations of the lock and key method? |
Assumes enzymes are rigid in shape but proteins can change in response to the enviroment (pH/temperature) or the binding of various substances |
|
|
|
What is the induced fit model? |
Active site is not precisely complementary but changes shape to bond to form a enzyme-substrate complex. The changed active site places a strain on the bonds in the enzyme lowering the activation energy |
|
|
|
What shape are competitive inhibitors and why? |
Shaped similar to the substrate to be complementary to the activesite and, therefore, bind blocking enzyme-substrate complexes from forming |
|
|
|
Will a reaction stop with competitive inhibitors? |
No as the proteins are not denatured |

|
|
|
How do non-competitive inhibitors work? |
Bind to the enzyme at the inhibitors bonding site (not the active site) changing the tertiary structure, therefore, changing the active site stopping enzyme-substrate complexes |
|
|
|
Will the reaction stop with non-competitive inhibitors? |
Yes as the tertiary structure is changed so the enzyme is denatured |

|
|
|
How will adding more substrate effect inhibitors? |
1. Competitive inhibitors will increase the reaction rate 2. Non-competitive inhibitors nothing will happen as enzymes are denatured |
|
|
|
How can temperature denature enzymes? |
As the temperature increases the kinetic energy increases so there are more enzyme-substrate complexes. As the temperature increases above optimum the kinetic energy begins breaking hydrogen and ionic bonds changing the tertiary structure and denaturing enzymes. |

How does kinetic energy effect enzymes? |
|
|
How can pH denature enzymes? |
Interfere with hydrogen and ionic bonds in the tertiary structure changing the shape of the active site |
|
|
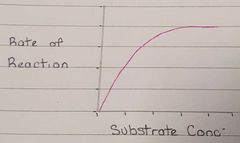
What limits the rate of reaction if the amount of substrate is increased? |
An increase in substrate will increase the amount of enzyme-substrate complexes until the active site of all enzymes are fully saturated (occupied) |
|
|
|
How does the concentration of enzymes effect the rate of reaction? |

As the concentration of enzymes increases the rate of reaction increases |
|

